The living matter
Author of the image @chetoblackmetal.
Biochemistry.
The constitution of the alive matter, in contrast to the inert or mineral matter, is much more complex than this, in the structural units that they characterize to the mineral world (atom and molecules), there join units provided with life, which constitute a biological level of top organization. The study of the life begins for the study of his composes simpler, be already chemical elements or be chemical compounds, constituted for his time for atom, molecules and macromolecules, approximately 98 alive % of the mass of an organism, they are formed by only six of 92 natural elements, which compose the matter that they constitute the universe.
 Frederik Wohler Frederik Wohler | The Biochemistry |
|---|---|
| For being a codiscoverer of the berilio, of the silicon and of the silicon nitride, as well as the synthesis of carbide of calcium, between others. In 1834, Wöhler and Justus Liebig published an investigation on the oil of bitter almonds. They demonstrated for his experiments that a group of carbon, hydrogen and atoms of oxygen can behave as an element, take the place of an element, and they can change for other elements into chemical compounds. This way there sat down the bases of the doctrine of radical compounds, a doctrine that had a deep influence in the development of the chemistry. | This science arose to half of the XIXth century, when the scientist Frederik Wohler discovered that a biological molecule as the urea, it was possible to synthesize from a component I do not live, by means of the warming of an inorganic compound, through the cianato amónico. |
The chemical elements of the alive matter.
Big similarity exists in all the alive organisms, both in his composition, and in the chemical reactions, which take place between his four principal elements: carbon (C), that is in the base of all the organic compounds, became oxygenated, (O), hydrogen (H), and nitrogen (N). the alive matter consists also of other elements that, despite being present in minor proportions in the textiles and fluids, it turns out to be also indispensable for the life: phosphorus (P), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), sodium (Na), Potassium (K), asufre (s) and chlorine (Cl).
The water and you them go out minerals.
The water is the principal component of the alive beings, and the most suitable vehicle, for the circulation of the nutrientes inside the organisms. You them go out minerals they are in the alive matter generally in the shape of dissolutions, which act as regulators of pH, of the osmotic phenomena and of the saltness of the internal organic way.
The carbohydrates.
The hydrates of carbons or glúcidos are immediate beginning formed by carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in an approximate proportion, which corresponds to the general formula: Cn (H2O) n.
From the chemical point of view they are constituted, for one or two units of polihidroxialdehido or cetona, according to the resultant one of the replacement of one of the functional groups of hidroxilio (-OH), for a group aldehídico (-COH) or cetónico (=CO).

It represents 1. The Grape they are a fruit in contained high place of hydrate of carbons, for his composition of azucares and carbon. (Taken photo edited for @chetoblackmetal).
Those of only one unit receive the name of monosacáraidos or sweeten, the ribosa, the glucose, the fructosa, are not hidrolizables, that is to say, they cannot decompose in others sweeten simpler and they are differentials, two units or disacáridos, they are joined by covalency by means of a linkage glucosídico, that has the peculiarity of hidrolizarse with facility as the acids. The most important are the saccharose, the maltosa and the lactose. On the other hand we have, which they are constituted by long chains, of hundreds or thousands of units of monosacáridos, the polisacáridos do not form truly watery solutions, but colloids, and for hidrólisis they decompose in disacáridos, of last we have the monosacáridos. The principal ones are the starch, which is a principal food reservation of the vegetables; the glucógeno, the reservation the animals.
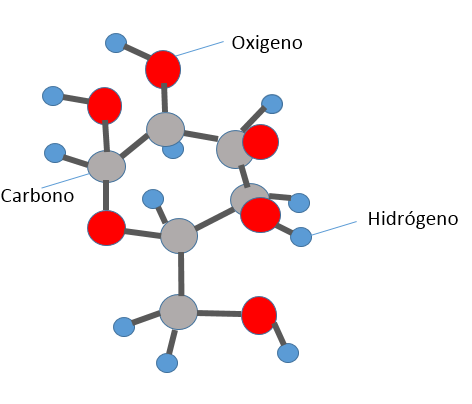
It represents 2. It shows us a molecule of glucose, atom of carbon is formed for síes, he is in the sugar, fruits, his organic function is the contribution of energy. (Prepared for @chetoblackmetal).
The lípidos.
They are organic compounds, which consist fundamentally of carbon, oxygen and hydrogen, the important of the case that very often phosphorus, sulfur and nitrogen, his consistency is greasy, oily, they do not dissolve in the water, but if not polar dissolvers, like the chloroform, the ether, the benzene, the sulfide of carbon or of alcohol. The greasy acids, they are organic acids of chains it chatters, since they possess from 4 to 24 atoms of carbon, only one group of carboxilo (-COOH), not polar tail hidrocarbonada, according to which his tail is completely saturated, thinking that it contains alone simple linkage, split into two groups:
Acids grease saturated and acids grease not saturated.
Acids grease saturated, example of this group, we have those fats occurred rarely to temperature ambience.
Acids grease not saturated, we have the oils, the majority liquids.
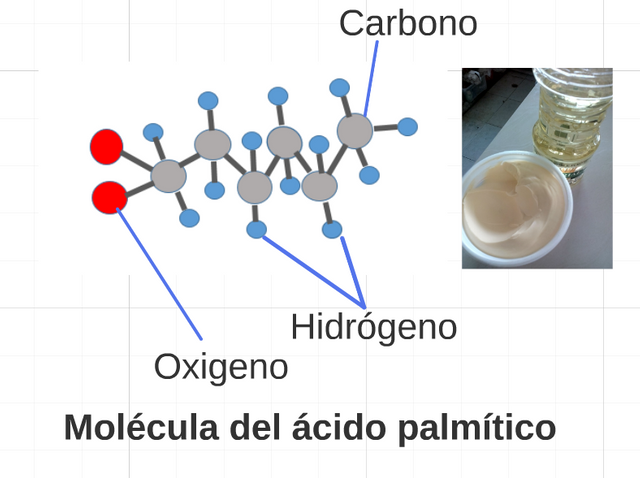
It represents 3. The lípidos are composed organic, constituted especially by carbon, I become oxygenated and hydrogen, the base of his structure there are the greasy acids, which split saturated and not saturated, necessary for the metabolism in the feeding. (Prepared for @chetoblackmetal).
Inside these groups also we have the greasy essential acids, which are needed for the metabolism and cannot be synthesized inside the proper organism from other substances, from what they must be present in the diet.
The proteins.
They are in the cells and in quite his constituent parts, across them the genetic information expresses itself, for it they can affirm that where there are no proteins, there is no life. It has protein nature in the enzymes, certain hormones and many of the structural components of the cells, the protein they contain, in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, on the structure of a protein his biological activity depends, the primary structure is represented by the succession of amino acids, which shapes a chain peptídica, defines the specificity of the protein and they are rigid for the genetic code.
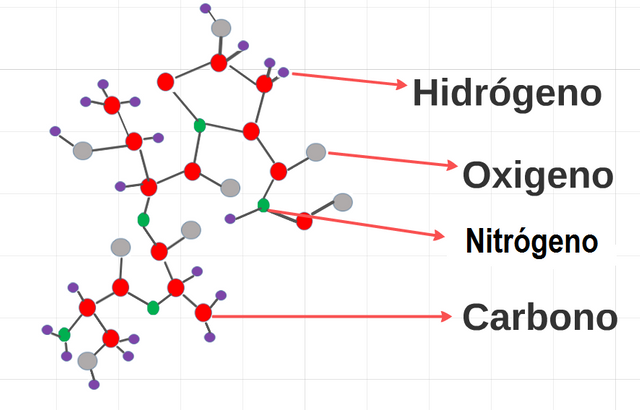
It represents 4. Structural model of a protein, contains carbon, hydrogen, I become oxygenated and nitrogen, (Prepared for @chetoblackmetal).
The secondary structure is related to the disposition that adopts the primary structure in the space, which he answers to two basic models: spiral and to laminate. The tertiary, exclusive structure of every protein, it is the result of his perplegamientos or enrollamientos of the secondary structure.
The linkage, which more help to support it are of type of disulfuro (--S-S-), only the proteins of high molecular weight, formed by the grouping of several chains polipeptídicas, that they have already acquired the tertiary structure, reach the quaternary structure.
The amino acids.
It is necessary to take in account that, the most primitive extinguished organisms, they are constructed by basic set of 20 amino acids, joined covalentemente and formed in sequence characteristics for possessing a group of carboxilo (-COOH), a group amino (-NH2), joined the same atom of carbon, so-called asymmetric carbon, which there joins the side chain, which characterizes to each one amino acid.
The amino acids are joined between yes by means of linkage peptídicos (-CO-HN), forming chains péptidos, the meeting of several chains of péptidos, form the molecule of protein. In the alive matter, also they exist péptidos free, with an intense biological activity, example for this case we have the hormone of the inulina.
The acids nucleicos.
They are very complex macromolecules, they are inside the cells, two principal types exist:
The acid deoxyribonucleic (ADN), which is located in the chromosomes of the cellular nucleus and is a principal reservorio of the genetic information.
The acid ribonucleic (ARN), he is in nucleus and in others he structures cellular, redeems an important role in process of synthesis of proteins.
ADN.
It is a polymer of several nucleótidos, these are formed by the union of a base of púrica or pirimidímica, a sugar and a phosphoric acid. The ADN, it is a biological present component in the cells, of all the organisms, he turns out to be located principally in the nucleus, in case of the eucariotas, in minor quantity also in the mitocondrias, presents a form of double helix, his principal role is to store and to transmit the genetic information from one generation to other one.
ARN.
It is a polymer of several nucleótidos, which differs in the sugar in the ribosa and I based them they are adenina, uracilo, guanina and citosina.
Types of ARN.
ARNr, is the principal component of the ribosomas, ARNt, he is the manager of deciphering the genetic information, and the ARNm, the manager of trasportar the genetic information, from the genes of the nucleus to the ribosomas of the citoplasma.
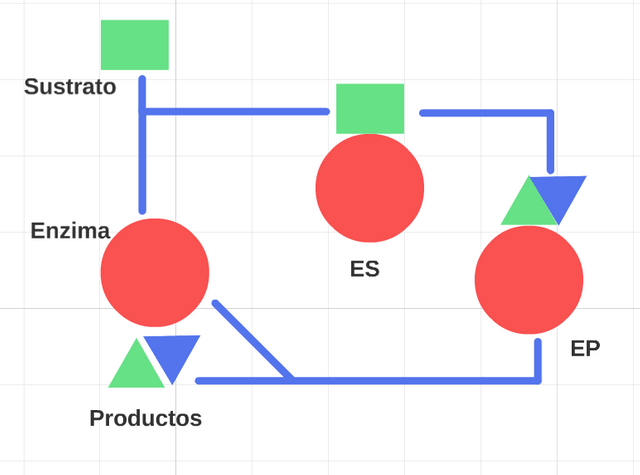
The enzymes.
They are functional units of the cellular metabolism, catalizan the hundreds of reactions staggered by means of that, there degrade themselves the molecules of the nourishing beginning, those in which there survives the chemical energy and trasforman, where they synthesize the macromolecules of the cells from simple precursors.
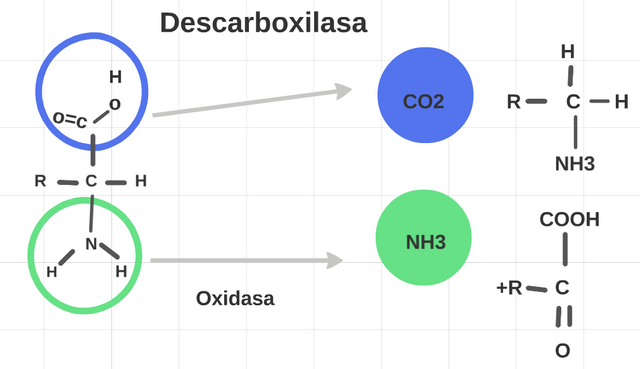
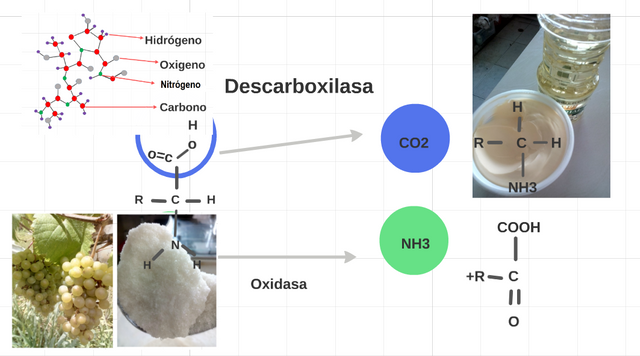
It represents 5. We have a metabolic reaction, in which an enzyme takes part, in where every enzyme cataliza alone a type of reaction, the oxidasa, oxidations; the descarboxilasa separates CO2. (Prepared for @chetoblackmetal).
Types.
Enzymes of pure proteins, as the holoezimas, formed by a component of protein nature (apoezimas), not protein other (Coenzymes), the unusual thing that both are inactive for yes same, join for the linkage covalentes to form the enzymes it activates catalíticamente.
The vitamins.
There are composed organic essential precursors of diverse coenzymes, the onlooker that they themselves can produce the plants, the coenzymes, but not possible in the animals.
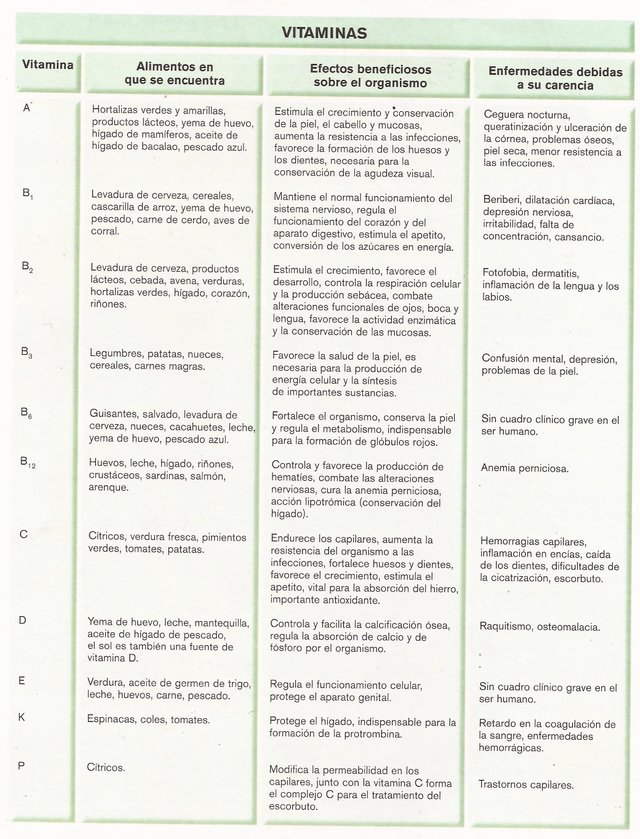
It represents 6. Table of the vitamins (Table edited for @chetoblackmetal).
The hormones.
They are substances produced by the proper organism, in specializing cells, and liberated in small quantities for glands endocrinas. Across the circulation they are trasportadas up to a textile, that it constitutes his target, in order to stimulate a specific biochemical or physiological activity.
.
I conclude that; His influence in the emergent technologies, since this science, it is demonstrating to have a wide and novel field of application in the creation of new technologies. Even the computer science has managed to make use of the biological computation, the manipulation of his genetic information, on the other hand we have, the food industry, for the food making, with the use of microrganismos, and the good use of the vitamins, for a good nutrition in our our health. The rest stays to our conscience.
Bibliographical references.
They go Der Vusse. Lipobiology. Vol.33 of Molecular Advances in and Cell Biology. (2004) Gulf Professional Publishing.
Varki A, Cummings R, Esko J, Freeze H, Stanley P, Bertozzi C, Hart G, Etzler M. Essentials of glycobiology (2008) Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2nd ed. isbn 0-87969-770-9
.W.R. PETERSON. “ Introduction to the nomenclature of the chemical substances ”. Ed. Reverté.
Beginning of Biochemistry 3ª/4ª edition. (2000/2005) David L. Nelson and M. M. Cox. Publishing Omega
PETRUCCI RH, HARWOOD WS and HERRING F G. 2002 “ GENERAL CHEMISTRY ”. Ed. Pearson Education. Madrid.
J.W. Baynes * M.H. Dominiczak, 2006. Biochemistry Medicates. 2 ed. Publishing house Elsevier.
A. Lehninger, 2001. Beginning of Biochemistry. 3 ed. Publishing Omega.
L. Stryer and cabbage., 2008, Biochemistry. 6 ed., Publishing house Reverté.
C.K. Mathews and K.E. go Holde, 2002, Biochemistry. 3 ed. Publishing house McGraw-Hill / Inter-American.
Skills of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology for David Freifelder.
5th biochemical Edition (2003) L. Stryer, J. M. Berg and J.L. Tymoczko. Ed. Reverté.
3rd biochemical Edition. (2002) C.K. Mathews, K.E. goes Holde, K.G. Ahern. Pearson Education S.A.
3rd biochemical edition (2002). H.Robert Horton, Laurance A. They reside, Raymond S. Ochs, David Rawn, K. Gray Scrimgeour Ed. Prentice Hall.
Beginning of 3rd Biochemistry edition. (2000) David L. Nelson and M. M. Publishing Cox Omega.
Biochemistry 2nd edition. (1995) Donald Voet, J.G. Voet Wiley * Sons.
Structure of proteins (2003) (coordinating) Carlos Gómez o Calder and Javier Sancho Sanz. Ed. Ariel Ciencia.
Biochemistry. The molecular base of the 3rd life edition (2003) T. Mckee and J.R. Mckee. Ed. McGraw-Hill.

Congratulations @chetoblackmetal! You have completed the following achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!