Is It Possible To Stretch A Battery?
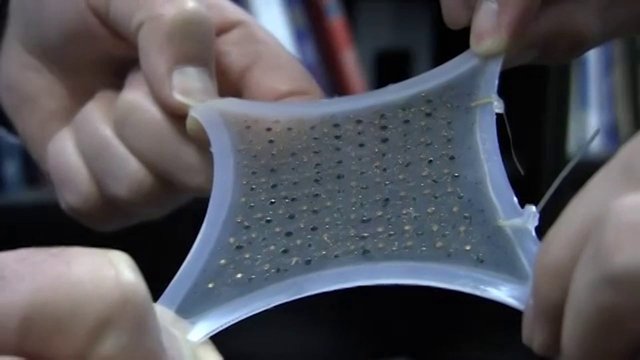
YES YOU CAN! After so many years of the Smartphone era, many always wonder what's next? For a long time, it has been impossible to have a flexible portable electronic device because of the materials such as a circuit board and microchips but have advanced far enough that we will, and have already started seeing the next generation of portable electronic devices.
But what about the power source? That usually ends up being the battery and to power these new devices is always challenging.
"Batteries are particularly challenging because, unlike electronics, it's difficult to scale down their dimensions without significantly reducing performance"
-John A Rogers, University of Illinois
Researchers at Northwestern and University of Illinois created the stretchable, flexible lithium-ion battery.
How Does It Work?
"We start with a lot of battery components side by side in a very small space, and we connect them with tightly packed, long wavy lines." These wires provide the flexibility. When we stretch the battery, the wavy interconnecting lines unfurl, much like yarn unspooling. And we can stretch the device a great deal and still have a working battery."
-Yonggang Huang, Northwestern University
Made up of hundreds of tiny cells connected by wires, on a stretchy silicone substrate. The wires are dubbed “a spring within a spring.” The wires stretch but never come taut. When the tension and flexion is relaxed, the battery returns to its original size and shape. Contains antenna and circuitry that also use the stretchy wires to be charged wirelessly through induction. Also consists of standard Lithium-ion cells, packed within a protective silicone sheath. Withstood 20 charge/discharge cycles and had very little loss in capacity. The battery life lasts about 8 to 9 hours.
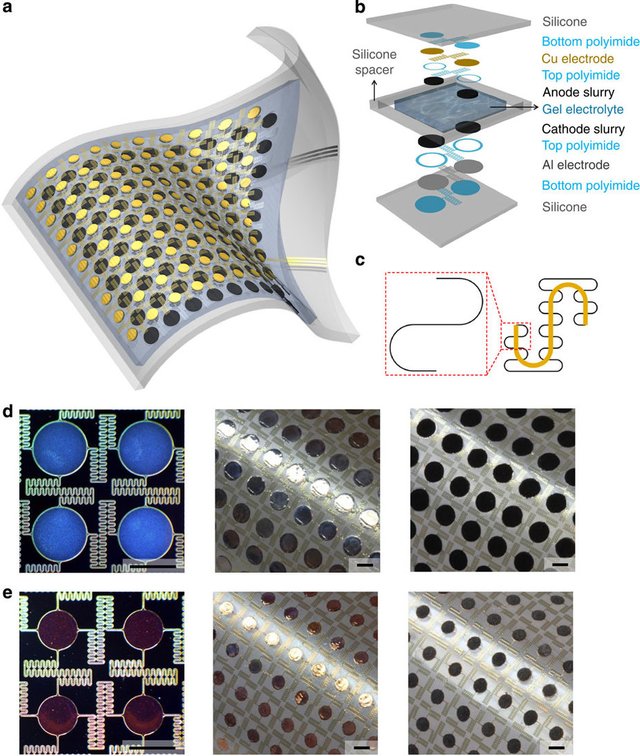
(a) Schematic illustration of a completed device, in a state of stretching and bending. (b) Exploded view layout of the various layers in the battery structure. (c) Illustration of ‘self-similar’ serpentine geometries used for the interconnects (black: 1st level serpentine; yellow: 2nd level serpentine). (d) Optical images of the Al electrode pads and self-similar interconnects on a Si wafer (left panel; top down view; ~4 unit cells), after transfer printing on a sheet of silicone (middle panel; top down view, in a bent geometry), and with moulded slurries of LiCoO2 (right panel; top down view, in a bent geometry). (e) Optical images of the Cu electrode pads and self-similar interconnects on a Si wafer (left panel; top down view; ~4 unit cells), after transfer printing on a sheet of silicone (middle panel; top down view, in a bent geometry), and with moulded slurries of Li4Ti5O12 (right panel; top down view, in a bent geometry). Scale bars in d and e are 2 mm.
Below is a circuit diagram of the wireless induction charging design.

(a) Circuit diagram. (b) Image of the integrated system with different components labelled. (c) Characterisation of the wireless coil with an alternating voltage input at a frequency of 44.5 MHz (black) and the resulting direct voltage output (red), as indicated in a. (d) Charging voltage (orange) and current (blue) curves as a stretchable battery is charged with 3 V output from the wireless circuit. The scale bar in b is 1 cm.
The video below is a live demonstration on how the battery stretches while continually powering the LED light bulb.
Edit: Checked the link and apparently they removed the video... Hmm..?
Here's a link to another video that explains the battery directly from one of the researchers that developed it.
http://newsarchive.medill.northwestern.edu/chicago/news-220941.html
Applications

It has been seen around for a while from Samsung and other mobile tech companies have already announced future devices with the "bendable" technology.
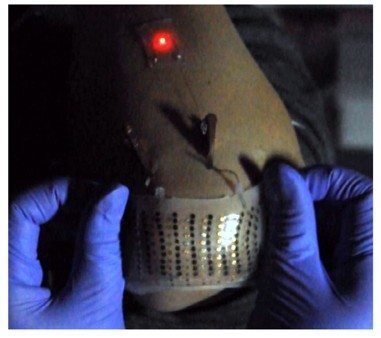
Medical applications such as heart monitors, bionic eyes, or other biological implants.
Wearable solar cells
Mobile phones
Computers
Flashlights
Flexible displays
Robotic skin
And more
Of course it is always a health and safety concern when using this type of technology for biomedical benefits but compared to our old technology, this is a heck of a lot better.
I wrote a post that discussed a newly developed saltwater antenna to help with communications. With saltwater being involved, there are always concerns about corrosion and especially for any electronic equipment, that is a nightmare. Considering the fact you need a power source, this technology of the stretchable battery can be water proof as well and could be something we can integrate with the saltwater antenna. Also find new uses for these type of technologies. A different design of this type of battery is demonstrated in the video below.
Thank you for taking the time to read and view my post.

Feel free to follow and find me in Smart Media Group on Discord.

 Facebook: @thesmartmediaproject
Facebook: @thesmartmediaproject Twitter: @the_smartmedia
Twitter: @the_smartmedia
 Instagram: @the_smartmedia
Instagram: @the_smartmedia
.gif)

That's cool. Have you checked this post by @the-future? Put together with yours, this gives amazing hopes for the future of the batteries :)
Interesting post of his. Yes, there is amazing hopes for the future. I tried to explain how exactly this technology is possible and it's multiple uses. I hope you were able to get an understanding of just how the technology works from the information I presented.
Steem on :)
I understand enough, but my background is probably helping :)
I'm sure you know more about me in things like these but as far as my grammar, some may not understand, but yea didn't really think twice about asking you that :P
Nice article!
I love batteries, especially high-density, high-output batteries. <3
hehe thanks. I wonder why you love those batteries? What would you need them for? :P
Flying cars, of course!
High-density means it'll be able to fly for a long time, and high-output means it'll supply plenty of power to the motors. Plus they'll probably be lighter-weight than a low-density battery.
ahh.
Nice job with this post @bitcoinparadise!
Thank you very much!