The James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope is the new-age replacement for the Hubble.
The Bigger the Better
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is going to be twice the size of the Hubble and filled to the brim with new technology. The JWST also has twice as many separate cameras bringing to total to four and increasing the range of photos dramatically.
The Mirrors
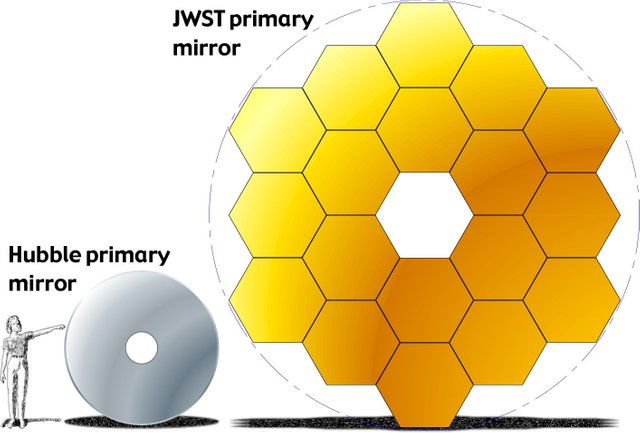
The largest and most noticeable difference compared to the Hubble is the primary mirror.
Scaling up the Hubble primary mirrors would be impossible. Above all the other complications it would simply be too heavy to launch. Scientists had to completely redesign the mirrors to be lighter and stronger. This led them to the use of beryllium, which is both light and strong, but they still had another issue. The mirror was still too big to fit in a rocket. The fix to this was simple, just fold it up. This introduces another problem, focusing the mirrors. Motors are used to keep the mirrors in sync. Each mirror has 6 on the back of it. The problem with this is that the mirrors must be aligned within a thickness of 1/10,000 of a human hair to focus correctly.
The Cameras
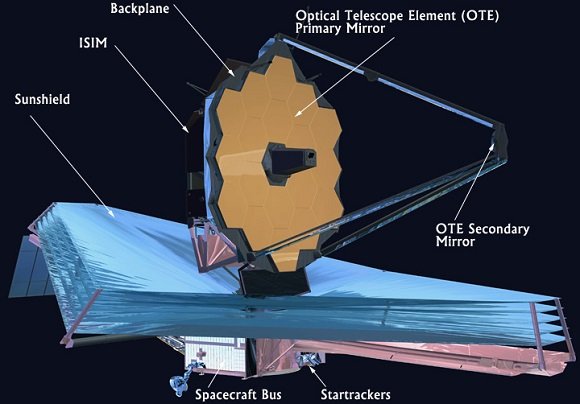
The NWST has four cameras for taking pictures. These cameras are all contained in the Integrated Science Instrument Module. The Cameras include: the Near-Infrared Camera, the Near-Infrared Spectrograph, the Mid-Infrared Instrument, and the Fine Guidance Sensor/ Near InfraRed Imager and Slitless Spectrograph.
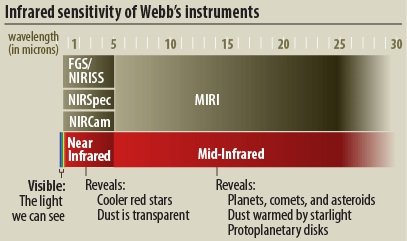
The Near-Infrared Camera is the primary camera for the NWST. This camera will be able to detect electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths 0.6 to 5 microns. The Camera has coronagraphs, which allow it to take pictures of dim objects around brighter objects. This allows us to see stuff like exoplanets a lot easier.
The Near-Infrared Spectrograph has the same range as the Near-infrared Camera. A spectrograph separates different wavelengths into a spectrum. Using this spectrum we can figure out what the object we are looking at is made of.
The Fine Guidance Sensor is used to line up directly with an object. Once the satellite uses this to determine where an object is exactly they use the other cameras to take more detailed photos. This instroment can drtect wavelengths from 0.8 to 5 microns long.
The Mid-Infrared Instrument is made to see wavelengths 5-28 microns long. The goal of this instrument is to measure redshifts of far away galaxies. This combined with the other instruments allows us to figure out how far away something is and how fast it is moving.
The NWST will be taking infrared pictures. Most telescopes are heated to keep the components working in space, but this drowns out the infrared. The electric components must be completely redesigned to sit at 40 kelvin (-233C). They also have to survive both launch and the vacuum of space. Testing of these is easy. They can put the NWST in a vacuum chamber with hydrogen cooling. This simulates the environment while it is in space. To simulate launch they put massive 150 decibel loudspeakers in front of it and turn them on. That simulates the shaking from the launch.
Facts
A few Nice facts about the JWST
- The mirrors are coating in a golf ball's worth of gold.
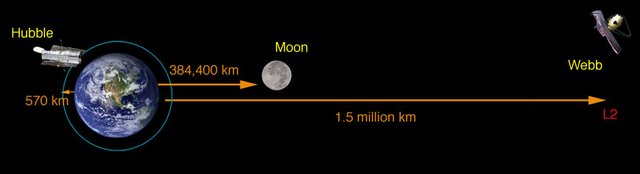
- It will be 4 times farther from the Earth than the Moon
- It is able to find water on Exoplanets
- The Mission Length is 10 years
JWST vs Hubble
The JWST will be launched in 2018, when the Hubble is 28 years old. The JWST will be packed with newer technology and will be better in every way.
The JWST will be 100 times as sensitive as the Hubble. These highly-detailed pictures will allow us to see things with an even greater clarity than the Hubble. The hubble can see two different ranges from 0.8 to 2.5 microns and 0.1 to 0.8 microns. In total the JWST will be able to cover wavelengths from 0.6 to 28 microns.
The JWST will be over 2500 times farther out than the Hubble. The JWST will be in a spot where gravity cancels out to basically zero, meaning it doesn’t need to constantly use fuel to stay up. This keeps it as far away from the atmosphere and any other sources of interference as possible.
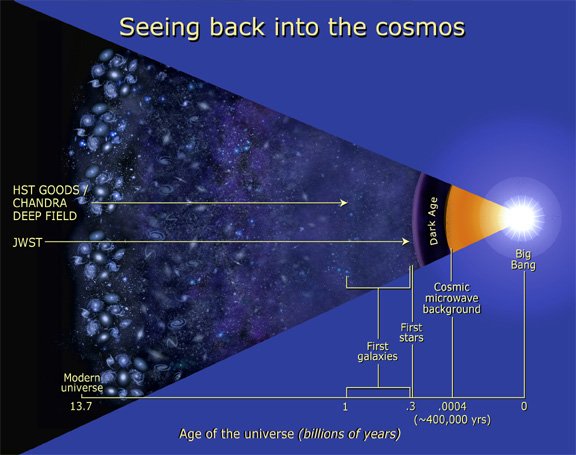
The NWST will be able to see the first galaxies just after they form. The youngest galaxy the Hubble has seen is about 300 million years old. The JWST will hopefully be able to find galaxies tens of millions of years old, or younger.
source
Here is a link to the James Webb Space Telescope website!
Thanks for a great article...
Sounds like a lot more than twice the Hubble?
I can't wait to see what we can see with this baby!
😄😇😄

Nice job with this post @anarchyhasnogods!
thanks bb
I ain't your bb, flags coming.
libtard cuck
bb like bb8? :D
Another great reading! :)