Impact of Value Added Tax (VAT) on Demand and Supply in UAE Market
Taxes are mandatory financial charges imposed by the government to increase the revenue, but also to keep the selling and buying of goods going, hence to maintain the economy of a country. A common form of tax is a sales tax, which is added on to the price of a product and paid by the consumer. Another common type of tax is a VAT (value added tax) which is paid by the producer along their production chain.
What is VAT? According to Wikipedia, it stands for value-added tax and is a type of general consumption tax that is collected incrementally, based on the increase in value of a product or service at each stage of production or distribution. Investopedia explains it in simpler terms as a type of consumption tax that is placed on a product whenever value is added at a stage of production and at the point of retail sale. It is basically a value-added tax on a product throughout its production process.
Read more: Value-Added Tax (VAT) https://www.investopedia.com/terms/v/valueaddedtax.asp#ixzz577RlrM2s
Follow us: Investopedia on Facebook
VAT is very common in the developing countries. Value-added taxation is being used in more than 160 countries, most commonly in the European Union, with rates ranging from 10-25%. It is a consumption tax that reduces the incidence of non-compliance. It is ideal for investors who prefer a safer and profitable overseas investment. But it is very important to know whether the prospective country used VAT or not.
The existence of VAT doesn’t really have a significant effect on the economy of a country, but a bit of a positive and negative, both, depended on the economy of a country.
The UAE Minister of State for Financial Affairs has decided to implement VAT from January 2018 with a rate of 5% excluding healthcare, food items and education. It is expected that other GCC countries will also introduce this system from January 2019. The minister claims that each country will have the flexibility to introduce VAT within this time frame for a profitable investment for both the countries.
Gulf News, in their article on “New Era in UAE as VAT Takes Effect” states that:
“The introduction of a Value Added Tax (VAT) regime in the UAE marks the beginning of a new era in the history of the UAE economy where the general public will start sharing the burden of budgetary expenditure, starting today (January 1, 2018).”
According to the Wikipedia, GDP is the total value of goods produced and services provided in a country during one year. The GDP is responsible for the rise and fall of the economy of a country. In 2015, there was a drastic fall (which can be seen from the graph below) which continued all the way to 2016. When the revenue of the oil dropped in 2017, the Minister took charge as it had become vital to do something about the long prosperous economy of the UAE.
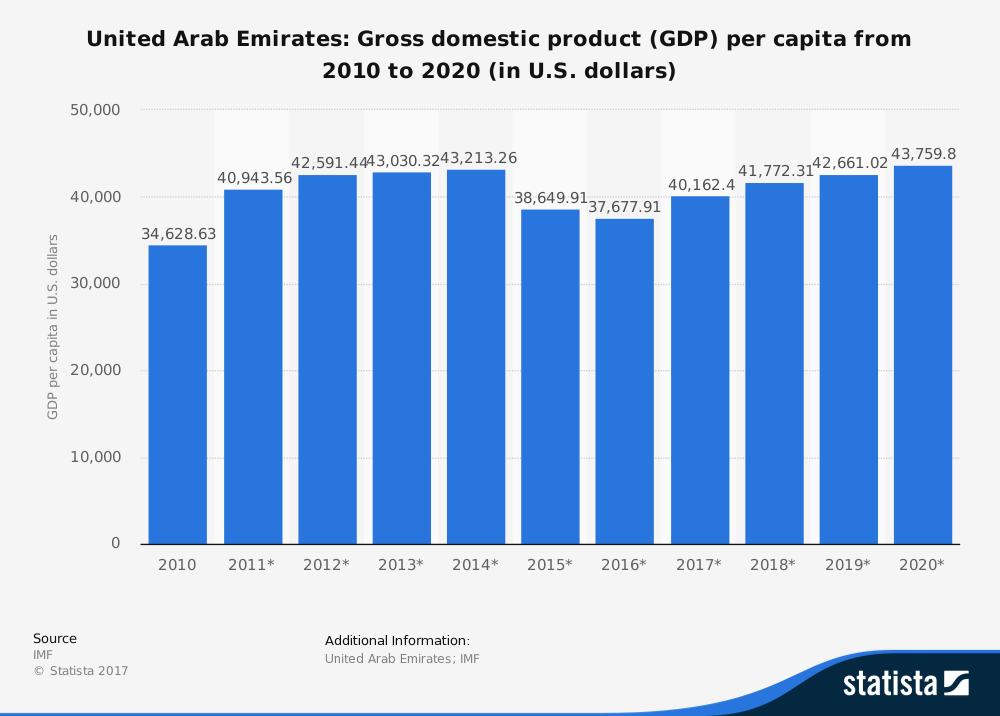
Picture source: Statista
It has become almost a necessity to introduce VAT in the UAE and to put an to the tax-free mode of living. One of the major reasons to introduce VAT is due to the drastic drop in the oil prices since last year, more commonly known as the Oil Revenue Slump, which badly affected the economy and the country had to come with an instant plan to find effective modes of revenue. 2017 was a slow growth and with the launching of VAT, the economic growth will pick up speed from 2018 onwards, although at a slower pace. UAE is expected to raise approximately $3.3 billion from the tax and bring up its economy again by the year 2020.
Investopedia explains that taxes reduce both demand and supply, and drive market equilibrium to a price that is higher than without the tax and a quantity that is lower than without the tax. A Supply Side is affected by taxes in numerous ways and can bring a sudden change in wages, taxes and oil prices. Subsidies, productivity of factors, especially labour, changes in the use of technology and production methods, direct taxes, such as income tax, via an incentive or disincentive effect, length of the working week and labour migration are just some the factors greatly affected by VAT.
FreeEconHelp.com explains the impact on demand and supply side by the following graph:
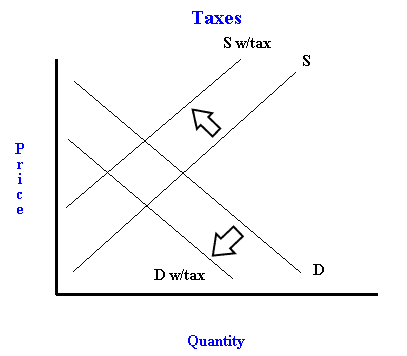
The sales tax on the consumer shifts the demand curve to the left, symbolizing a reduction in demand for the product because of the higher price. While demand for the product has not changed (all of the determinants of demand are the same), consumers are required to pay a higher price, which is why we see the new equilibrium point occurring at a higher price and lower quantity. The magnitude of the shift in the demand curve will be equal to the amount of the tax. This makes sense, because the change in demand is going to be equal to the change in price that is caused by the tax.
The VAT on the suppliers will shift the supply curve to the left, symbolizing a reduction in supply (similar to firms facing higher input costs). While supply for the product has not changed (all of the determinants of supply are the same), producers incur higher cost, which is why we will see a new equilibrium point further up the demand curve at a higher price and lower quantity. Once again, the magnitude of the shift in the supply curve will be equal to the amount of the tax introduced by the government. Essentially, the firms are passing on the tax to the consumers in the same way they would pass on higher input costs.
Although the economy won’t be as badly affected by the low prices of oil, but it will surely have an impact on the real estate prices. A couple of methods are taken to increase a country’s economy when it crashes or becomes weak such as purchasing financial securities and by cutting interest rates. Another method is imposing taxes such as VAT which increases household demand by increasing workers' take-home pay.
VAT will prove to be a crucial step in ensuring a stable economy which is less reliant on oil revenue. The retail sector will be protected as much as possible, with price increases not being too much of a shock to middle and low income earners. Imposing taxes can lead to better economic benefits. If all income earners will pay the right amount of tax, the government can collect more money to support its objectives such as building roads, schools, better government salaries and improve government services.
Understanding taxes can be a real head-scratcher, but it’s essential to grasp how they work, especially when it comes to VAT. VAT, or Value-Added Tax, is a type of consumption tax that’s applied at each stage of a product’s production and distribution. It's designed to ensure that tax is collected incrementally based on the value added at each step. If you're dealing with VAT and find yourself needing to manage or even cancel your VAT registration, I highly recommend checking out https://vatcompliance.co/canceling-your-vat-registration-without-stress/. They offer excellent support for handling VAT matters smoothly and stress-free. Their expertise can make navigating these complexities much easier!