Consensus algorithms. Part 1
Consensus comes from a latin word "consensus" which is roughly translated as "agreement". In the traditional sense, the consensus is a way of making a decision or a deal that involves finding a medium accepted by all the parties involved in the process. In cryptocurrencies, the consensus is used to find a commonly accepted truth among millions of people with regard to the ledger of transactions. This challenge is solved by using large computing powers - miners, and so-called consensus algorithms.
A consensus algorithm is one of the critical aspects in decentralized cryptocurrencies. No wonder that it is not needed on decentralized ones as the ledger is kept by a single trusted party. In decentralized ones, though, this algorithm is used to validate transactions and build blocks on top of one another in the ledger.
In this article, we're gonna compare the two most popular algorithms - Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Stake. The following articles will also highlight DPoS, LPoS, BFT, PoC, PoI, PoA, PoB.
Proof-of-Work
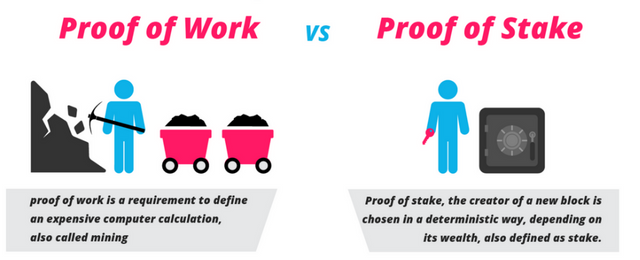
PoW is the first successfully implemented decentralized consensus algorithm in blockchain. It is used in Bitcoin, Ethereum (though it is planning to move to proof-of-stake), Litecoin and a lot of other platforms.
It works in the following way: Firstly, users send coins to each other, then, all the transactions form the blocks and are registered in the ledger - blockchain. All the transactions are verified by means of complex mathematical calculations, the legitimacy of which may be re-checked by any user of the system. Forming a new block is the job of miners. If miner successes at solving the mathematical problem, a new block is formed. The mathematical problem gets more complicated with time, as the number of users of the networks growths.
Proof-of-Stake
PoS requires from the system's users a share of the total coins supply to behold in their wallets. It was introduced for the first time in PPCoin (today, PeerCoin). PoS tackles the main drawback of PoW - enormous amount of electricity used to mine coins.
Transaction's validity is confirmed by "validators" so that each new block is created by a nod in the network - a single wallet's address that holds the largest amount of coins in the system. This nod may be chosen either as random one among the wallets with the largest stakes or among the oldest wallets. PoS helps at stopping the fraudulent actions that involve the plenipotentiary powers shifting by checking the algorithm with the oldest and the most loyal users.