Objects That (Apparently) Go Faster Than The Speed Of Light

First, no object (as far as we know) can go faster than the speed of light. Second, nothing with a non-zero rest mass can go at the speed of light.
Having said that there are ways to make it appear that something is going faster than the speed of light.
A few technical terms here for the non-technical among us:
Supraluminal - means faster than the speed of light.
Collimated - means a beam whose rays are parallel (i.e. it doesn't spread out)
Type #1: Illusory Objects
Imagine you have a very powerful laser that is highly collimated (doesn't spread out much). It is so powerful that you can see the dot when you point it at the Moon. You point it at one edge and then flick it across the face of the Moon. The Moon, with a diameter of 3474 km, has a disk face that looks like it is 3474 km across.
If you flick that laser dot across the Moon in 0.01 seconds then the dot will look like it is going 347,400 km/s which is faster than the speed of light (300,000 km/s).
The flaw here is that the dot itself is not an object. It is something that is composed of many different photons all going at the speed of light and then arriving on the surface of the Moon at different times.
So this one is a basically an illusion of going faster than the speed of light.
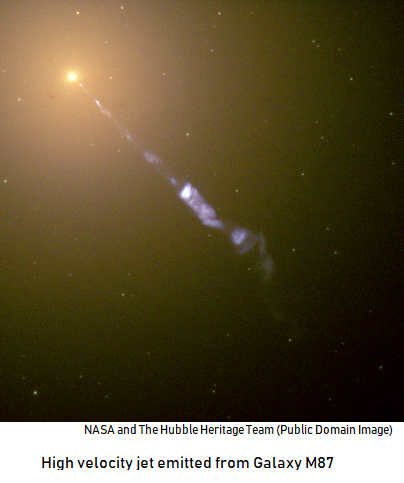
Type #2: High Velocity Galactic Jets
There is a class of astronomical objects in which a supermassive black hole with an accretion disk shoots out a relativistic jet that is pointed almost directly at the Earth (the term 'relativistic' just means 'near the speed of light').
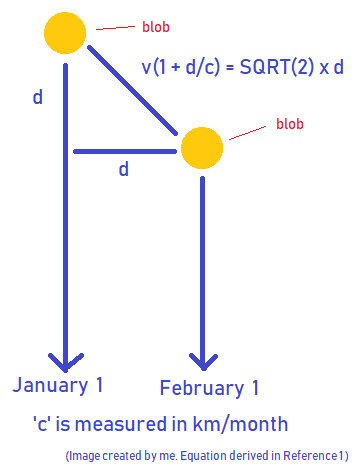
Let's say on January 1st that you make measurement of the position and distance of a blob in that jet. A month later on February 1st, you measure the position and distance of the jet blob again. You calculate its speed and figure out that it is moving faster than the speed of light.
What's wrong here?
On January 1st the object is 'D' km away from us and between January 1 and February 1 it has also moved 'd' km closer to us. In the first calculation we erroneously assumed that the light from the blob was emitted exactly one month apart but this is wrong.
Since the object is moving towards us near the speed of light the first light beam had much farther to travel. It was actually emitted 1 + d/c months earlier ('c' is the speed of light measured here in km per month). So the object has traveled that distance in more time than you first thought. That was the mistake.
The more acute the angle of sight is the more pronounced the effect can be.
Type 3: Expansion of The Universe
The Universe is expanding and apparently there is strong evidence that the rate of acceleration is increasing.
This means that eventually galaxies that are the furthest from us will cross some kind of 'cosmological event horizon' where the light they emit will never be able to reach us.
This is because, on that day, the expansion of the distance between us and that object will be faster than the speed of the light. Neither the Earth nor that distant galaxy are actually moving faster than the speed of light in their local space, it is the amount of space in between us that is getting larger at a rate faster than the speed of light.
That galaxy will appear to be going faster and faster and then as it reaches the speed of light it will simply disappear (well it will redshift into nothingness but that is a topic for another post).

Type 4: Quantum Entanglement Weirdness
Say a sub-atomic particle with spin 0 decays and emits two electrons and let's say that these electrons are both moving close to the speed of light.
Electrons have spin of 1/2, either 'up' (spin = +1/2) or 'down' (spin = -1/2). Spin is a conserved quantity, the spin of the system before the decay was zero so the spin of the system after the decay must also add up to zero.
This means one electron will shoot out in one direction with a spin and the other will shoot out in the other direction with the opposite spin. These two electrons are said to be entangled and due to quantum uncertainty neither electron will have a definite spin until you measure it.
Here's the weird part. Say in our experimental setup the electrons are a long distance apart when we measure them.
You set up your first measurement to occur at time 't' and it measures that electron to be spin 'up' in this case.
In advance you have set up your experiment to measure the second electron a small moment after the first measurement. As well, the time difference between the two measurements is smaller than the time for light to travel between the two detectors.
The second electron measurement will always be measured to be spin 'down'.
It thus appears that the second particle of the pair instantly "knows" what the result of the measurement that has been performed on its partner. It knows this even though there is no way for information to be transmitted between the particles.
The current understanding of this phenomenon is that although it seems that the second particle instantly "knows" what happened to its partner there is no way that this can be used to transmit information faster than the speed of light.
Investigation of entangled particles is an active area of physics and it can easily bake your noodle.
Closing Words
There are number of phenomena that make it look like information or objects are moving faster than the speed of light but as far as I can tell none of them have truly broken this speed limit.
Thank you for taking the time to read my post.
Post Sources
- http://math.ucr.edu/home/baez/physics/Relativity/SpeedOfLight/Superluminal/superluminal.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Faster-than-light
- http://www.stsci.edu/ftp/science/m87/m87.html
- http://www.stsci.edu/ftp/science/m87/press.txt

Immagine CC0 Creative Commons, si ringrazia @mrazura per il logo ITASTEM.
CLICK HERE AND VOTE FOR DAVINCI.WITNESS
Greetings from @davinci.witness and the itaSTEM team.
Even if you try anything, the speed of light is faster and in your post you showed it very well.
@ihsanbhr Follow :=)