STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS
Staphylococcus aureus, is a common bacterium that lives on the skin or in the nose. It is also called golden staph. In most cases, Staphylococcus aureus is harmless. However, if it enters the body through a cut in the skin, it can cause a range of mild to severe infections, which may cause death in very few cases.
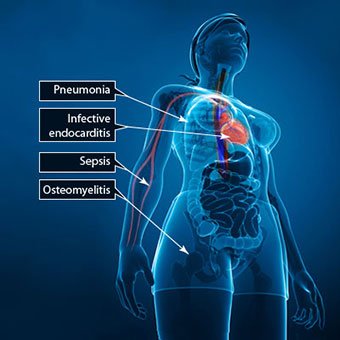
Image source:http://images.medicinenet.com/images/appictures/staph-infection-s6-types-of-diseases
Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram positive bacteria. It is a non-moving small round shaped cocci. It is found in grape-like (staphylo-) clusters. This is why it is called Staphylococcus.

Image source: http://www.news-medical.net/image.axd?picture=2010%2f1%2fstaph
Staphylococcus aureus belongs to the family Staphylococcaceae. It affects all known mammalian species, including humans.
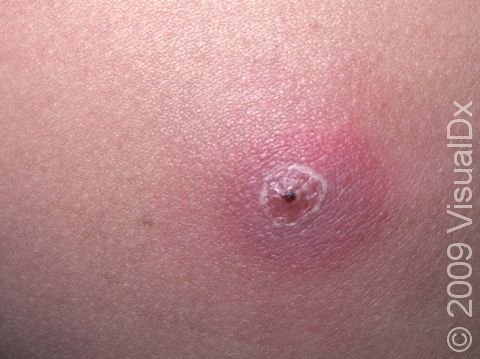
Image source:https://static.skinsight.com/dx/webAdult/furunculosisBoil_28461_lg
Signs and symptoms
Skin and soft tissue (impetigo): A small area of erythema that progresses into bullae (filled with cloudy fluid) that rupture and heal with the formation of a honey-colored crust
Scalded skin syndrome (Ritter disease): A relatively rare, toxin-mediated disorder with superficial fragile blisters that burst, leaving a tender base; accompanied often by fever and occasionally by mucopurulent eye discharge
Folliculitis: A tender pustule that involves the hair follicle
Furuncle (boil): Small abscesses characterized by exuding purulent material from a single opening; involves both the skin and the subcutaneous tissues in areas with hair follicles
Carbuncle: aggregate connected furuncles, with several pustular openings
Bone infections (osteomyelitis): In children, sudden onset of fever and bony tenderness or a limp; pain may be throbbing and severe; however, presentation in neonates can be subtle
Septic arthritis: Decreased range of motion, warmth, erythema, and tenderness of the joint with constitutional symptoms and fever; however, these signs may be absent in infants (in whom the hip is the most commonly involved joint)
Endocarditis: Initially presents as fever and malaise; peripheral emboli may be present; may involve healthy valves
Toxic shock syndrome: Fever, diffuse macular erythema, and hypotension, with involvement of three or more organ systems; can be rapidly progressive in previously healthy individuals
Pneumonia: Most common in infants, young children, and debilitated patients; a short prodrome of fever followed by rapid onset of respiratory distress; prominent GI symptoms may also occur
Thrombophlebitis: Fever, pain, and occasionally erythema at the insertion site of an intravenous catheter; usually a nosocomial disease
Deep tissue abscess and infection
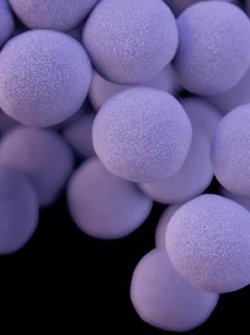
Image source: https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/images/16879_lores-staphy-250px
Transmission
S. aureus is most often spread to others by contaminated hands.
The skin and mucous membranes are usually an effective barrier against infection. However, if these barriers are breached, S. aureus may gain access to underlying tissues or the bloodstream and cause infection.
Persons who are immunocompromised or who have invasive medical devices are particularly vulnerable to infection.
Treatment
Oral / intravenous antistaphylococcal agents such as oxacillin or a first-generation cephalosporin such as cefazolin, combined with clindamycin
Drainage of pus collections is of paramount importance.
Empiric semisynthetic penicillin and clindamycin
In patients with allergy to penicillin, a first-generation cephalosporin and clindamycin
Vancomycin or linezolid when the other drugs mentioned are absolutely not tolerated or when resistance or the clinical course dictates
Minimum effective treatment time is 4-6 weeks; therapy can be completed orally.Surgery to drain purulent material from the subperiosteal space or remove infected foreign material
A combination of a beta-lactam and an aminoglycoside (eg, nafcillin and gentamicin)
In patients with MRSA, combinations of vancomycin with aminoglycosides
Rifampin can be added to combination therapy, especially for prosthetic valve endocarditis.
References
Awareness is 99% of the battle. Excellent article, very well written and referenced. Many thanks.
.
ColdMonkey mines Gridcoin through generating voluntary BOINC computations for science...
Thanks coldmonkey for the complement.....
Good post describing this common bacteria of which increasing numbers of antibiotic resistant variants are emerging.
Thank you very much @justtryme90 for taking time to go through it.... I really appreciate