3D Printed Proteins: The future of medicine?
"3D printing or additive manufacturing is a process of making three dimensional solid objects from a digital file."
https://3dprinting.com/what-is-3d-printing/
"Amino acids are organic molecules that, when linked together with other amino acids, form a protein."
https://www.thoughtco.com/amino-acid-373556
"Step 3: Pick a Protein
Background: Protein Data Banking
When biologists and biochemists discover the structure of a new protein (most often by either by X-Ray Crystallography or NMR Spectroscopy) they are usually required to submit their new structures to one of several massive repositories online. These structures can then be accessed by scientists that want to verify, use, and improve upon their findings. These repositories are made available to the public as well, in an effort to educate the public about the discoveries being made, and share the results that their taxpayer dollars helped fund. Aptly named the Protein Data Bank, anyone with a computer has nearly all of the discoveries of modern science at their fingertips when choosing a protein model to print in 3D."
https://www.instructables.com/3D-Print-a-Protein-Modeling-a-Molecular-Machine/
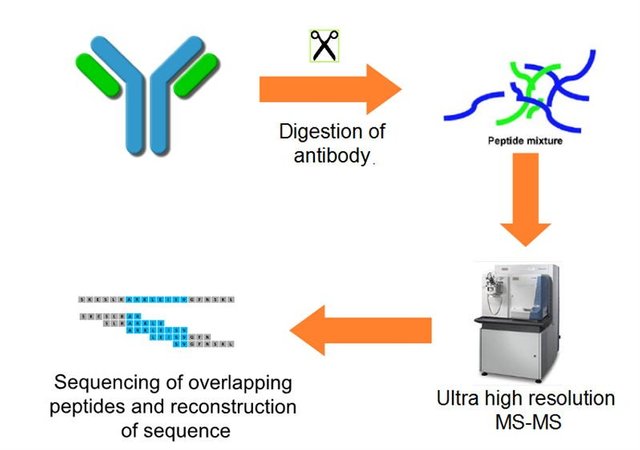
"the antigen to which the immune system responds is a relatively small number of amino acids or peptide."
https://www.who.int/teams/health-product-policy-and-standards/standards-and-specifications/vaccine-standardization/synthetic-peptide-vaccines
"synthetic antibody libraries can create particular antibodies against various protein antigens.
Moreover, a more complex synthetic antibody library can be developed to produce antibodies with high affinities and specificities beyond natural antibodies capacity"
https://www.ieyenews.com/natural-and-synthetic-antibodies-know-the-difference/
"The zinc finger antiviral protein (ZAP) is a recently isolated host antiviral factor."
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15542630/