The Fundamental of Cell division and organelles
.jpg)
Definition of cell?
Cell can be defined as the smallest structural and functional unit of a living organism.
Cell is further divided into two;
- Meiosis
- Mitosis
- Meiosis: This can be defined as the reduction and division of cell.It has four daughter cells and it occurs mostly in the gonaltes. It is divided into two circles which are meiosis and meiosis.
meiosis 1 is divided into five stages which are;
.jpg)
a. Prophase 1
b. Methaphase 1
c. Anaphase 1
d. Telophase 1
e. cytokenesis 1
Meiosis 2 is also divided into five stages;
a. Prophase 2
b. Methaphase 2
c. Anaphase 2
d. telephase 2
e. cytokenesis 2
.jpg)
- Mitosis: This can be defined as the multiplication and division of cell. It has two daughter cell and it occurs in the somatic cell(all part of the body except the gonalte).
Mitosis is still divided into five stages;
a. Prophase 1
b. Methaphase 1
c. Anaphase 1
d. Telophase 1
e. cytokenesis 1
In prophase 1 of meiosis, it is divided into five stages;
- leptotene: In this stage the part of the cells are thicker and they are separated.
- zygotene: In this stage different type of cells begins to form.
- Pachytene: In this stage cells combine to form other cells.
- Diplotene: Cell formation is completed in this stage.
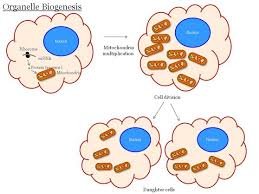
Cell Organelles
Cell organelles are the organs of the cell.
- Cell Membrane
- Nucleus
- Cytoplasm
- Golgi Bodies
- Ribosome
- Lysosome
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
- Centrosome
- Neucloplasm
- MIcrofilament
- Microtubules
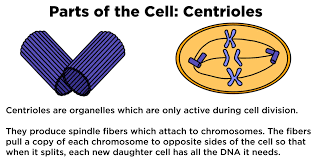
- Centrioles
- Mitochondrium
- Chromatide
- Cell Membrane: It is the power house of all the cell.
- Nucleus: It controls the activities of the cell.
- Ribosome: It is responsible for protein synthesis.
- Mitochondrium: It produces energy in form of adrenaline Triphosphate(ATP)
- Lysosome: It is a sensitive part that breaks down particles or some dead organelles within the contest of the cell.
- Chromatide: This the coming together of two chromosomes.
- Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum: It packages and transport substances or material inside the cell.