Learn With Steem; Learn How to Calculate the Conventional Cashflow Techniques - ARR (1st Edition)
Introduction
 Image Designed In PowerPoint
Image Designed In PowerPointThe conventional cash flow technique is used in capital budgeting to calculate several inflows and outflows of cash within a particular accounting period.
It's used to calculate the profitability of a project or investment to determine if it's viable to begin and if it will yield profit overt
What is capital budgeting
When a firm is posed with various challenges on where to invest its excess cash at hand or cash in the bank into a viable and long-term investment with the right and easy technique, the firm is said to be undergoing capital budgeting decisions.
For the firm or investor to consider this project, he or she will have it analyzed using the proper technique, and appraising such investment involves processes.
For a project to be considered viable, it must have lived more than a single accounting or fiscal year in which the investor can decide whether or not to continue.
Properties or Characteristics of Capital Budgeting
.jpeg) Link
LinkThe properties of capital budgeting are listed below:
Once the decision has been made by the investors on whether or not to commit its funds and the project kicks off, it's impossible to reverse funds committed into the project.
Huge lumps of money are involved with can be gotten from conventional sources some of which include taking a loan from the bank.
There are various risks associated with the project and it has to be carefully considered before one venture into it.
It gives room for reconstruction of initial projects in case the proposed project after the proper evaluation isn't fit to venture into.
For a project to be considered viable, it must have lived more than a single accounting or fiscal year in which the investor can decide whether or not to continue.
Strategies of Capital Budgeting
.jpeg) Link
LinkThe step by step processes involved in capital budgeting are;
1. Identification of the type of investment available for selection by the investors.
2. Consideration of different ways to achieve the objectives of the project in question using the available discounting techniques.
3. Select the suitable technique to be applied for project evaluation and review.
4. Evaluate the project using the selected technique.
5. Accept or Reject the project based on the results obtained and makes Recommendations where necessary.
There are two main traditional cashflow techniques which are;
- Payback Period (PBP)
- Accounting Rate of Return (ARc
Due to the ambiguity of the techniques, this edition will concentrate on one at a time and today's edition is Accounting Rate of Return (ARR).
Accounting Rate of Return (ARR)
 Image Designed In PowerPoint
Image Designed In PowerPointThis technique makes use of accounting information and profit to determine a percentage rate as a criterion for acceptance of redemption of a project for evaluation.
Another term for ARR is Return of Investment (ROI) or Return on Capital Employed (ROCE). It is used to evaluate the performance of a project by determining if the project is profitable, effective, and efficient.
It's important to note that, the higher the ARR rate, the more profitable the project geared towards is, and the lower the ARR rate, the less profitable the project geared towards is.
When using the ARR technique, there are two basic decision rules to follow. The rules are outlined below:
- For Independent Projects
For independent projects, the company will accept the project if the ARR rate is greater than or equal to (≥) the company's initial rate.
- For Mutually Exclusive Projects
The company will accept the project that has the highest ARR provided that the accepted ARR rate is greater than or equal to (≥) the company's initial cut-off rate.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ARR
 Image Designed In PowerPoint
Image Designed In PowerPointAdvantages
This technique is very simple to calculate and easy to understand by the user of this technique.
This technique uses accounting profits which is the net income obtained after deducting all other expenses made in the course of the accounting year from total revenue. In
ARR takes into account every profit element and gives them the chance to be evaluated.
ARR is used for the comparison of the performance of various companies in places of profitability, efficiency, and effectiveness.
The analytical figure obtained is rated in percentage terms (%), a term any user of the result obtained will be able to relate to and interpret.
Disadvantages
 Image Designed In PowerPoint
Image Designed In PowerPointARR doesn't recognize the time value of money. Time Value of Money means several money values more now than the same amount will be at a later date.
It's usually more difficult to get the accounting profits due to the series of calculations it entails.
ARR ignores all the risks involved in a project and management measures to mitigate these risks that are likely to occur.
The formulas used in calculating ARR may look complex and pose as difficult to compute.
Learn How to Calculate ARR
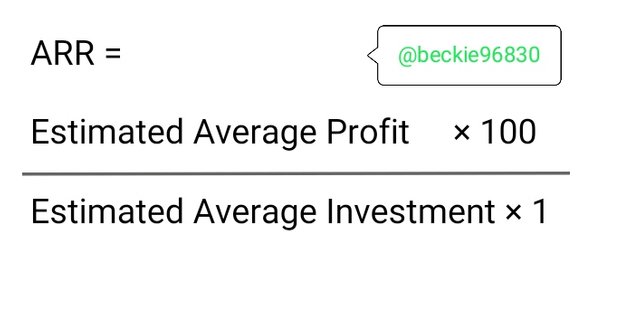
ARR is mathematically represented as;
Where:
Estimated Average Profit is derived from:
Estimated Average Investment is derived from:
Depreciation per year is derived from:
Total Profit is derived from:
Annual Cash Profits × Number of Years
Example;
Beckie96830 is considering investing in a project that has an initial plant cost of #150,000. The project's useful life is expected to be 5 years with a Scrap Value of #10,000. The project generates an annual cash flow of #50,000 during its life span.
Depreciation is set on a straight-line basis while the company's cost of capital is set at 20%. Required: Calculate the ARR of the project.
Solution:
- Total Profit = #50,000 × 5years = #250,000
- Depreciation Per Year= #150,000 - #10,000 = #140,000
#140,000 ÷ 5 years = #28,000 per year - Estimated Average Profit = #250,000 - #140,000(#28,000×5) = #110,000
#110,000÷ 5 years = #22,000 - Estimated Average Investment = #150,000 + #10,000 = #160,000
#160,000 ÷ 2 = #80,000
ARR = #22,000 ÷ #80,000 = 0.275
0.275 × 100 = 27.5%
Decision Rule: Beckie96830 firm should accept the project because the ARR calculated is greater than the company's cut ott rate.
Conclusion
ARR has always come through for investors and if properly calculated, it's enough for investors to decide whether or not to venture into the project.
Disclaimer: This post is not intended to give financial advice, but rather to teach how to calculate ARR to the best of my knowledge.



Thank you for contributing to the #LearnWithSteem theme. This post has been upvoted by @maazmoid123 using the @steemcurator09 account. We encourage you to keep publishing quality and original content in the Steemit ecosystem to earn support for your content.
Regards,
Team #Sevengers