RuffChain – Internet of Things 2.0 Part 3
by Future Blockchain
Part 3: Chain control. Lightning chain differential mechanism. Nodes
In Part 2 of the series, I performed a quick review of the main features of the Ruff blockchain. Let’s now look at the Chain Control mechanism and the blockchain node types.
Chain Control
The chain control is the way the devices or light nodes interact between themselves and the command center (control node) on the blockchain. Light nodes and the control node are on the same intranet. Once an Internet of Things device binds to the control node on the master chain, it can be controlled directly by it using specific commands sent directly to the blockchain.
The structure of the IoT networks requires it to be composed of multiple nodes mainly due to the fact nodes are often very small computing units with power consumption requirements and therefore low computing power and memory. This hardly makes a successful consensus processes execution, so in Ruff, applications will manage the local network in a centralized or decentralized way and go through the application interface to interact on the blockchain.
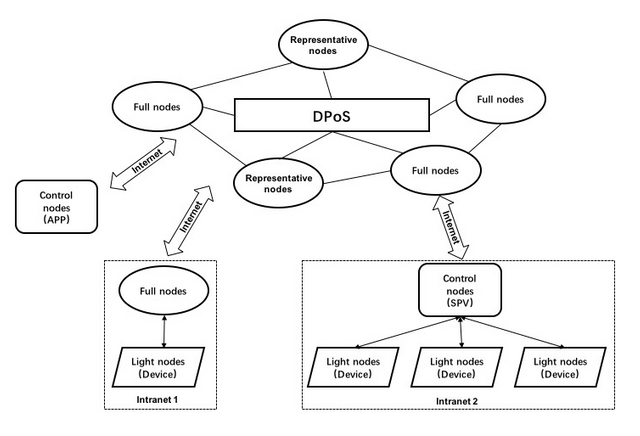
There are few types of nodes on the RuffChain:
• Light nodes (Executors) – Simple IoT device on the network, which after correct authentication on the control node can be operated by the user via smart contracts for activities such as the release of property access rights.
• Full nodes (Recorders) – As the name suggests, full nodes record all information on the blockchain, participate in event registration or modify broadcasts and vote for other nodes. Devices with high performance will act have a greater role as nodes on the network, becoming representative nodes.
• Representative nodes (Arbiters) – Are responsible for enforcing the rules on the blockchain and packaging blocks. These special rights come from the fact they were elected with most votes from every group of 105 nodes on the network. The representative node can also obtain revenue from mining by distributing blocks.
• Control nodes (SPV wallet) – They save all data on the blockchain and use it for transaction and contract verification. They also execute P2P commands to the other devices on the network. Control nodes don’t need to be online 24 hours per day and can run via smartphone app or through devices with relatively low storage.
The control node uses TX commands like CreateContract to operate other devices on the network. Common contract contents include: “If you give me certain tokens, I’ll allow you to use the following command on condition that”. The successful creation of the contract will return to save the contract block height and transaction hash (together referred to as the Contract Address).
Users can also initiate Call transaction contract to a contact address with a specific requirement and use it for multiple commands or activities. The control node validates if user has enough tokens for each operation and executes it, receiving the required amount.
In case a device is not performing normally or not executing any of the commands as it should be, the user can submit a Review transaction to the master chain, and the negative report will take effect. If a contract gathers numerous such reports, the control app will interactively prompt the user that the contract has many negative reviews.
Different command signatures are used to execute chain-based control:
Device initialization –Device-specific public-private key pair used to unlock it.
Device binding - The control node initiates a binding command, which contains the public key of the control node and its signature.
Control command verification – Specific command sent to the light node with command node signature.
Logging command history onto the master chain - The control node can log all control commands that have been issued
Next time I will review the Smart Contract of Things and applications of the RuffChain.
Social media
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Ruff_Chain
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/RuffChainProject/
English Telegram: https://t.me/ruffchain
Official Blog: https://ruffchain.com/blog/
Future Blockchain
Medium: https://medium.com/@futurebchain
Twitter: https://twitter.com/FutureBchain
Telegram: t.me/Future_blockchain
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/cryptofuturenews/
Steemit: https://steemit.com/@tst643