At the cutting edge of IoT and blockchain
The maturity of internet of things is seen across sectors and industries, however, many challenges still need to be addressed. Where do IoT and blockchain meet?
Heading towards mass adoption
Internet of things (IoT), often described as the Internet of Everything, actually means interconnected products. Since its beginnings, IoT was perceived as a hyper-secure network, suitable for storing and transferring data. Or, as described on IoT Agenda:
“The Internet of Things (IoT) is a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.”
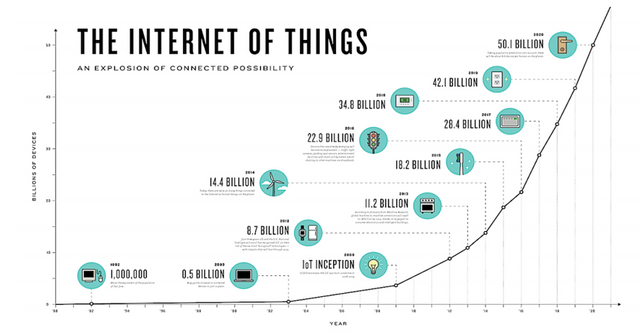
Gartner assumed there would be 25 billion individual units connected by 2020, whereas Cisco believes the number of “things” will be closer to 50 billion. Therefore, the IoT is here to stay, and across the globe, already brings the average return on investment of 34%.
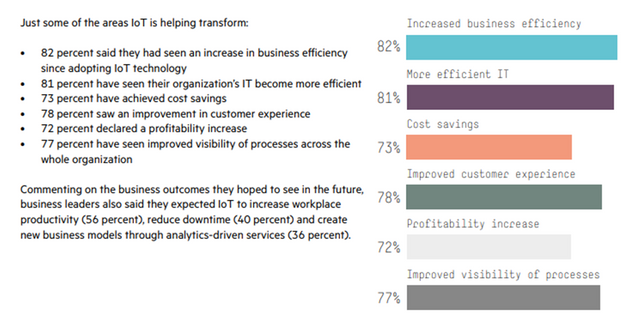
Source: Internet of Things, Today and Tomorrow
Heading towards mass adoption, there are some road blocks ahead — and, solving security issue is critical. An alarming number of 84% of organizations have so far experienced an IoT-related security breach, leading us all to answer the question: What will happen when all connected devices start using the network simultaneously?
Source: https://blockchain.ieee.org/images/files/pdf/201710-iot-blockchain_-_a-stavrou.pdf
How is IoT managed from technical point of view?
We could say that to IoT communication is central. But, how does the network actually work? In its current form, IoT consists of all the web-enabled devices that collect, send and act on data they require and uses server-client model to provide connectivity, meaning that devices communicate to the cloud which then processes the information received to decide upon its next actions. The reason we refer to this kind of communication machine-to-machine (M2M) is that the devices do the majority of work without human intervention.
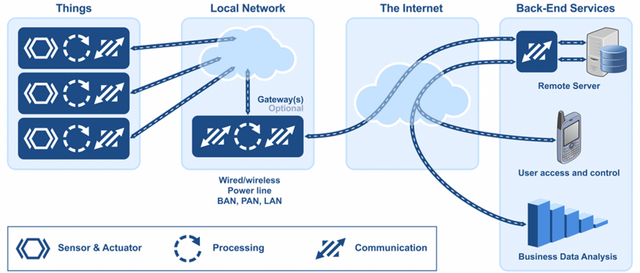
Source: https://www.micrium.com/iot/devices/
In her article, Anna Gerber focuses on technologies and standards adopted for IoT networking. From the top down, these layers are: application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link and physical whereas the Internet protocol suite provides a concrete implementation of these layers, as described below. If you wish to investigate this topic even further, we also recommend this read.
Network Access & Physical Layer
This TCP/IP Layer subsumes both OSI layers 1 and 2. The physical (PHY) layer (Layer 1 of OSI) is concerned with how each device is physically connected to the network with hardware, for example with an optic cable, wires, or radio in the case of wireless network like wifi (IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n). At the link layer (Layer 2 of OSI), devices are identified by a MAC address, and protocols at this level are concerned with physical addressing, such as how switches deliver frames to devices on the networkInternet Layer
This layer maps to the OSI Layer 3 (network layer), which relates to logical addressing. Protocols at this layer define how routers deliver packets of data between source and destination hosts identified by IP addresses. IPv6 is commonly adopted for IoT device addressing.Transport Layer
The transport layer (Layer 4 in OSI) is focused on end-to-end communication and provides features including reliability, congestion avoidance, and guaranteeing that packets will be delivered in the same order that they were sent. UDP (User Datagram protocol) is often adopted for IoT transport for performance reasons.Application Layer
The application layer (Layers 5, 6, and 7 in OSI) covers application-level messaging. HTTP/S is an example of an application layer protocol that is widely adopted across the internet.
As described above, the many networking technologies that enable IoT devices to communicate each other, applications or services, are all running in the cloud and several protocols exist to help establishing and managing such networks.
This brings us to the biggest issue: the IoT devices are deployed in different ways and no single networking technology fits them all. In other words, many companies wish as many users possible in their ecosystem and they lack the motivation for the unified standards. But, the bigger the IoT gets, the more internet traffic it generates, bringing bottleneck in IoT efficiency and overall performance.
Journeying Towards More Secure Communication
Blockchain = Blockchain or distributed ledger, is a technology comprised of unchangeable consecutive blocks of data that are exchanged directly between users within a network without the need for intermediaries. It is distinguished by its high security and transparency while secured by strong cryptography.
Blockchain = Blockchain or distributed ledger, is a technology comprised of unchangeable consecutive blocks of data that are exchanged directly between users within a network without the need for intermediaries. It is distinguished by its high security and transparency while secured by strong cryptography.
The reason blockchain is so attractive to IoT lies in the fact that the current IoT landscape lacks of unified standards. As a decentralized peer-to-peer network, blockchain can add an additional layer of security that can greatly benefit the IoT sector, helping with devices authentication, networking and transacting value. In this aspect, blockchain opens up a completely new way of how devices can communicate among each other, covering several scenarios, including a ledger/trail and their interaction, in which state they are and how they are handled.
By 2019, 20% of all IoT deployments will have basic levels of blockchain services enabled. (IDC)
Blockchain, especially the networks using permissioned chain such as Nxxtech, can resolve the IoT issues on a network protocol level. To establish mutual communication, among “things”, identification of devices within the network is crucial, helping build trust, reduce costs and accelerate transactions. This way blockchain technology can improve not just compliance, but also IoT features and cost-efficiency.
Follow our blog post series on IoT & blockchain as we will cover several issues Nxxtech has managed to solve to achieve transaction speed and seamless devices identification, paving our way towards standard adoption in IoT.

