***A POWER PHYSICS WORLD***
A POWER PHYSICS WORLD



Surely you know what physics is, a science that studies how the world works. Starting from why the apple fell to earth, until the reason why the earth is round. While the people who study it, known by the name of physicist.
To this day, there are already hundreds and possibly thousands of scientists in the field of physics. But only a handful of them whose name is immortalized history. Only physicists find discovery, ideas, and theories capable of changing the world.
Of the many, here are twenty great physics scientists who have succeeded in changing the way people view them. Who are they?
*** Galileo Galilei (1564-1642)***
Credit: Justus Sustermans
Who has never heard of Galileo's name? It does not seem to exist. Everyone must know the football in the field of astronomy and physics. He was instrumental in encouraging the scientific revolution that began since the Enlightenment.
His greatest contribution is the refinement of modern telescopes, as well as the invention of the first and second law of motion. Thanks to that he earned various nicknames, such as the father of modern physics, the father of observational astronomy, and so forth.
Unfortunately his life ended tragically. He was punished by the church's excommunication because of his view of the earth that surrounds the sun. This view is considered heresy because it contradicts the belief of the church that the earth is the center of the universe.
It was not until hundreds of years later that Galileo's punishment was declared wrong by Pope John Paul II. Then on December 21, 2008, the name Galileo was restored as a scientist by Pope Benedict XVI.
Isaac Newton (1643-1727)
Credit: Oregon Department of Transportation
When you hear the name Newton, you must immediately remember anecdotes about apples that fall to earth. This story is identical with Newton. It is said that there is the idea of the law of gravity and the three laws of motion originating.
Although the above story is doubtful, the influence of Newton's ideas is real. His book Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica is touted as the most influential book in the history of science.
In this book, Newton describes the existence of a collection of natural laws that govern all the objects that exist on Earth and in space. This idea succeeded in breaking the scientists' doubt over heliocentricity, and pushing the scientific revolution wider. No wonder he was dubbed the father of classical physics.
Newton also had predicted the coming of Judgment in the manuscript in the year 1704. According to this physicist, the apocalypse is the fastest occurred in 2060. Background emergence of this prediction is that people do not recklessly predict the coming of the end.
Michael Faraday (1791-1867)
Image source: Wikimedia
The British physicist holds the title of the father of electricity thanks to his work in the field of electricity and magnetism. Three main discoveries are the basic principles of electromagnetic induction, diamagnetism, and electrolysis.
In addition, Faraday also found the burning Bunsen (Bunsen Burner) commonly used in laboratories, chemicals called Benzene, and popularized scientific teminology such as ions, cathodes, electrodes, and the like.
Not Something That Is Impossible For Someone Who Can Only Learn in Elementary School But Even That Only That Can Make Great.
Then he developed further by attending the lectures of Humphry Davy when he was twenty years old. From here the story of his life as a world scientist begins.
The greatness of this physicist is also recognized by Albert Einstein. Einstein even posted a photograph of Faraday on his laboratory wall, adjacent to Isaac Newton, and James Clerk Maxwell.
James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879)
Credit: David Dorren
Maxwell is a scientist in the field of mathematical physics from Scotland. He has a huge contribution to the development of science, even considered comparable to Einstein and Newton.
His greatest discovery was the theory of electromagnetic radiation. This theory is a major breakthrough in modern physics because it successfully combines three phenomena into one.
The phenomenon consists of electricity, magnetism, and light coming from the same phenomenon. This idea he published in 1865, and received a remarkable welcome from among scientists.
Maxwell's other great work is to develop Maxwell-Boltzman distribution, long-lasting color photos, and rigid frame analysis foundation in the bridge structure. Thanks to it all, Maxwell is considered a very influential 19th century scientist against the development of 20th century physics.
Wilhelm Röntgen (1845-1923)
From the name Röntgen of course you can already guess what he found. Engineer engineer and physicist is the first to discover X-rays, which is now used in medicine to radiate patients.
The name of the X-ray comes from a variable 'X' in math that refers to something unknown. The first person who tested X rays was his own wife, Anna Bertha. Anna was so shocked when she first saw the x-rays. He even exclaimed: "I like to see my own death."
Thanks to the discovery of X rays, Röntgen became the first German scientist to win a Nobel Prize in physics in 1901. He was also awarded a number of other prestigious awards, such as the Elliott Cresson Medal and Rumford Medal.
The most interesting thing about Röntgen is that he never patented his findings. The reason is that X-rays can be used for the benefit of mankind. What he does is similar to Pierre and Marie Curie who discovered radium.
In addition, Röntgen never completed his formal school. He was expelled from high school Ultrecht Technical School because of his unacceptable joke.
Regardless of his education, Wilhelm Röntgen's services are very useful to mankind. Therefore, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) perpetuates its name as chemical element to 111, roentgenium (Rg).
Marie Curie (1867-1934)
His full name is Maria Skłodowska-Curie. He is a radiology pioneer and one of the most influential female scientists. His radiological achievements were the discovery of the radium element (with her husband and Henri Becquerel), polonium, and the isotope isolating technique.
These findings led Curie to be the only female scientist to win two Nobel Prizes. The first Nobel Prize in Physics in 1903, and the next Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1911.
Unfortunately Curie's life ended tragically. He died in 1934 due to leukemia. Where the disease arises due to the frequent Curie exposed to radioactive substances that in fact is his own invention.
The memorable thing of this female scientist figure is his decision to never patent his findings. In his view, a discovery must be free from economic motives that can be used for the benefit of all mankind.
J. J. Thomson (1856-194)
Joseph John Thomson was the first to discover subatomic particles (particles smaller than an atom). At first the particles he named corpucles, but over time people call them by the name of electrons.
He also managed to uncover the ability of the gas to conduct electricity. This discovery led Thomson to the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1906.
But J.J Thomson's greatest contribution to the development of science is not the discoveries, but his success in guiding his disciples. Evident from a number of his former research assistant who won the Nobel Prize in Physics and Chemistry.
Ernest Rutherford (1871)
Former student of J.J. Thompson is dubbed the father of nuclear physics. The nickname was obtained after introducing he introduced the concept of half life radioactive. This concept describes the time it takes an atom to decay into half its original amount.
Half life also proves that radioactive involves changes in chemical elements, from one element to another. Not only that, it also divides the elements of radiation into two namely alpha and beta. For his remarkable achievements, Rutherford was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1908.
After the Nobel prize, Rutherford's name has soared thanks to a number of his works, such as the theory of atomic charges concentrated in the nucleus, and successfully dividing the atoms in the laboratory which is then named protons.
Rutherford died in 1937 because of a complication of a hernia. In honor of his services, he was buried not far from Sir Isaac Newton's tomb at Westminster Abbey, and his name was made a 104th chemical element, rutherfordium.
****Paul A.M Dirac (1902-1984)****
which became an extraordinary physicist's contribution to the major development of the basis of quantum mechanics as well as the greatest quantum electrodynamics of the work with Dirac's equations with images of fermian behavior and forecasting the existence of antimatter
Dirac also successfully won the 1933 Nobel Prize in Physics with Schrödinger for the discovery of a new atomic theory form. Therefore, he is considered one of the most important scientists of the 20th century.
Many scientists are recalling Dirac because of his unusual personality. Einstein himself called Dirac a balancing act between madness and genius. One interesting story about his personality was when he was a speaker at a conference.
After he finished his presentation, one of the scientists raised his hand and said; "I do not understand the equation in the top right corner."
The moderator also invited Dirac to answer the questions asked. Instead of answering, Dirac said instead; "That's not a question, it's a comment."
Werner Heisenberg (1901-1976)
Heisenberg lunge as a scientist is very interesting listened. He is a pioneer of quantum mechanics with contributions to the advancement of physics, especially the development of hydrodynamic theory of turbulent flow, ferromagnetism, atomic nuclei, and subatomic particles.
He was also caught as the main scientist in the atomic bomb project Uranveiren launched by the Nazis. Where in late 1941, Heisenberg met with Niels Bohr to discuss the development of the atomic bomb. But before their conversation was complete, Bohr had fled abroad.
The fate of the Uranveiren project also did not go smoothly, and was eventually canceled. According to news circulating, actually Heisenberg knew all about atomic theory, but deliberately pretended not to know that this bomb project failed.
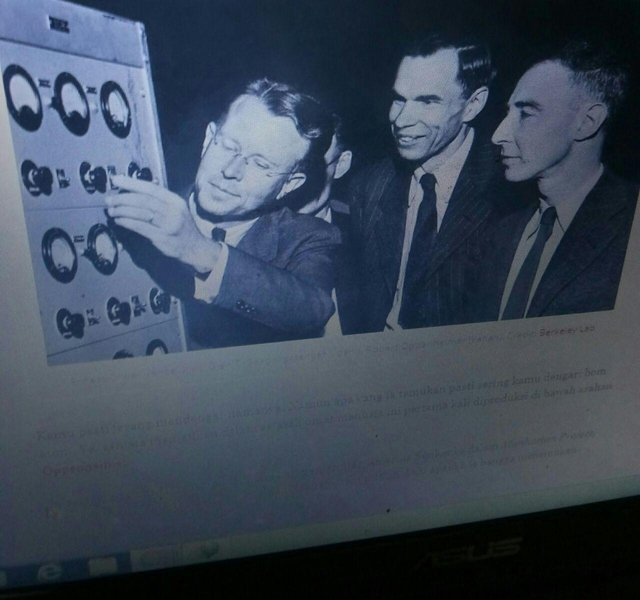
J. Robert Oppenheimer (1904-1967)
Ernest O. Lawrence (left), Glen T. Seaborg (center), and J. Robert Oppenheimer (right). Credit: Berkeley Lab
You must rarely hear his name. But what he finds you must have heard often: the atomic bomb. Yes, this deadly weapon in human history was first produced under the direction of Oppenheimer.
He and several other scientists recruited the United States government into the Manhattan Project, a secret US project that began in 1942. Then is he proud to find an atomic bomb?
Apparently not. He was very sorry. This feeling came after Oppenheimer witnessed how terrible the damage inflicted on Hisroshima and Nagasaki.
After the Second World War, he proposed international atomic energy control to prevent nuclear arms races, and refused the offer of developing thermonuclear weapons or hydrogen bombs.
***Enrico Fermi (1901-1954)****
Fermi is one of the scientists involved in the Manhattan Project. Fermi's best known works are beta decay, quantum theory development, and nuclear reactor development.
Yes, Fermi is the first to discover and build a nuclear reactor in the world. The nuclear reactor he builds is utilized to produce useful isotopes in the medical and research fields.
Because of this action, he was called by the nickname architects of the nuclear age and the architect of the bombing bomb. But after the Allies won the Second World War, Fermi decided to challenge the development of hydrogen bombs for moral and technical reasons.
In honor of his services, the Fermi name is immortalized to be the name of the fermium chemical element. This makes him one of sixteen scientists whose names are immortalized into chemical elements
Richard Feynman (1918-1988)
People dub Feynman as The Great Explainer. This name he got thanks to his ability in explaining complicated physics concepts to be simple. Where even a layman can understand what he describes.
His greatest discovery is the expansion of the theory of quantum electrodynamics, which combines relativity with quantum mechanics. Thanks to this, he earned the Nobel Prize in 1965.
Feynman is also one of the scientists involved in the Manhattan Project. He was recruited by Director Robert R. Wilson to develop an atomic bomb after Pearl Harbor was attacked by Japan. Previously, Feynman worked at Frankford Arsenal, Pennsylvania, as a ballistic missile researcher.
***Murray Gell-Mann (born 1929)****
Murray was awarded the Nobel Prize in physics in 1969 thanks to his discovery of the eight-element path to classify subatoms. According to him, protons, neutrons, and other hadrons are composed of smaller particles called quarks.
A number of international appreciation also managed to get it. For example the award of Ernest O. Lawrence Memorial Award from the Atomic Energy Commission, Franklin Medal from Franklin Institute, as well as honorary degrees from a number of top universities.
Beyond his interest in science, Murray also enjoys studying archeology, culture, farming, historical linguistics, and so on. Finally, Murray is the only surviving physicist on this list.
***Vera Rubin (1928-2016)****
Vera Rubin is the most influential female astronomer. It reveals the fact if the galaxy does not rotate as many scientists believe. This discovery brings itself to concrete evidence of the existence of dark matter or dark matter. Although at that time Rubin doubt his findings.
For his achievements, the New York Times called Vera Rubin as the bearer of change in the field of astronomy and physics through the observation of the galaxy. At the same time people who awaken the astronomers if what they observed so far is just 'the tip of the iceberg' called the universe.
He was also awarded a number of prestigious awards in the field of astronomy, the Bruce Medal, the Gold Medal of the Royal Astronomical Society, and the National Medal of Science. While his name is immortalized into one of the asteroid names, Asteroid 5726 Rubin.
5.72% @pushup from @lovelyworld