BASIC THEORY OF MUSIC
WHAT IS MUSIC ART?
The art of music is art that is conveyed through the medium of human voice or the sound of musical instruments.
TONE
Tones are regular sounds, which have a single single frequency. In music theory, each tone has a certain pitch or tuning according to its frequency or according to the relative distance of the pitch to the benchmark pitch height. The basic tone of a musical work determines the frequency of each note in the work. Tones can be arranged in different scales. The term "tone" is often exchanged for use with "notes", even though both terms have different meanings.
The tone in notes is divided into 3 forms, namely:
Not numbers: notes denoted by numbers, for example 1 (do), 2 (re) etc., Not numbers are divided into 3, namely: high octave, moderate octave, and low octave,
Not letter: notes denoted by letters, for example C, D, E, F etc., Letter notations can be divided into 5, namely small octaves, 1-line octaves, large octaves, octaves cons and sub cons,
Not beam: a songwriting system or other musical work which is written in the form of an image. Beam notes are based on paranas with symbols for each tone indicating the duration and height of the tone. The pitch is described vertically while time (rhythm) is drawn horizontally. The duration of the tone is indicated in beats.
The term in musical notes
PARANADA is five straight lines that line horizontally and equidistant. Paranada is used to write sound symbols in accordance with the nature of the tone symbolized.

KEY SIGNS are signs to determine the location of one note in notes. To write guitar scores, the G key is used, meaning that in the musical note the note G is located on the second line.

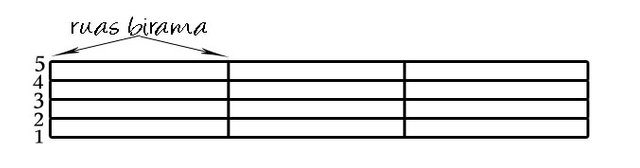
BIRAMA is a melody that is organized in a song or other musical work. The line of bars is a line that is written perpendicular to the paranada which functions to limit between one segment of the parallel to the other parallel segments.

BAR (section length) is the segment that is located between two bars. The bar functions to write notes according to the time used. the value of notes in a bar is always the same. maybe friends often find the value of the notes found in the first bar and the last bar is different from the other bars. but if the number of notes found in the two bars counts, it will be the same as the other bars.
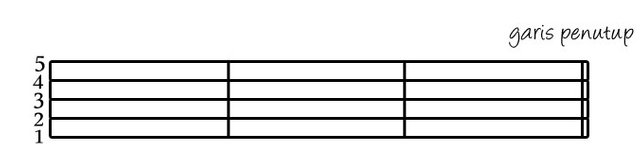
CLOSING OUTLINE is two thin thick lines written perpendicular to the paranada that serve as a clue to the end of a song or other musical work.
RITME
Rhythm is a sound arrangement in time. Bars is a group division of beats in time. The sign of timama indicates the number of beats in the bars and which notes are counted and is considered as one beat. Certain tones can be accentuated by giving pressure (and differentiating duration).

NOTATION
Music notation is a written depiction of music. In beam notation, pitch is described vertically while time (rhythm) is drawn horizontally. The two elements form a paranada, in addition to the instructions for the basic tone, tempo, dynamics, and so on.
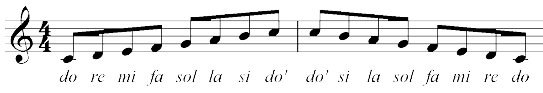
MELODY
A melody is a series of tones in time. The circuit can be sounded alone, that is, without accompaniment, or can be part of a series of chords in time (usually the highest set of tones in these chords).
Melodies are formed from a series of tones horizontally. The smallest unit of melody is Motif. Motives are three or more tones that have musical intentions or meanings. The combination of Motives is Semi Phrases, and the combination of Semi Phrases is Phrases. The most common melody usually consists of two semi phrases, namely the question sentence (antisiden) and the sentence answer (consequent).
HARMONY
Harmony in general can be said as the occurrence of two or more tones with different heights sounded together, although harmony can also occur if the tones are sounded sequentially (as in arpeggio). Harmony which consists of three or more tones that are sounded together is usually called a chord.
MUSICAL SCALE
Tone ladder is a tiered arrangement of the main notes of a tone system, starting from one of the basic tones to the octave, for example do, re, mi, fa, so, la, si, do
MAJOR SCALE
In music theory, a major scale or a major scale is one of the diatonic scales. This scale is composed of eight notes. The interval between consecutive notes on a major scale is:
1, 1, 1/2, 1, 1, 1, 1/2
For example, A major scales are C, D, E, F, G, A, B, C '
Characteristics of major scales:
His mood is cheerful
Excited
Usually begins and ends with a Do tone
Has interval patterns: 1, 1, ½, 1, 1, 1, ½
MINOR SCALE
In music theory, minor scales are one of the diatonic scales. These scales are composed of eight notes. The interval between consecutive notes in minor (original) scales is:
1, 1/2, 1, 1, 1/2, 1, 1.
For example, A minor scales are Am, Bm, Cm, Dm, Em, Fm, Gm, Am '
Minor scales can be seen as the sixth musical mode in the major scales. Minor scales are sometimes considered to have sounds that tend to be sadder than the major scales.
Characteristics of minor scales:
Her mood is sad
Less enthusiastic
It usually starts and ends with La = A
Has interval patterns: 1, ½, 1, 1, ½, 1, 1
PENTATONIK SCALE
Pentatonic Scale or Pentatonic Tone Ladder is a scale consisting of five tones for each octave, Penta (five) and Tonic (tone), so this pentatonic tone removes the 4th + 7th tone (type A) and 2nd tone + 6th tone (type B) of 8 notes per octave.
Diatonic (c - d - e - f - g - a - b - c ') = 1 octave
Pentatonic type A (c - d - e - g - a - c ') without' f 'and' b '
Pentatonic type B (c - e - f - g - b - c ') without' d 'and ‘a'
BASIC KEY
Base notes are the first tones found on a scale.
The way to find the tone used in a scales is to use a 1-1-1 / 2-1-1-1-1 / 1 interval scale Major
BASIC PATTERN PATTERN
Pattern in a basic tone:
The way to find chords in a basic tone is to use Patterns 1-4-5 for Chord Major and 2-3-6 for Chord Minor
The conclusion is like this:
The order of 1 chords is always major
Sequence of 2 chords is always minor
Sequence of 3 chords is always minor
The order of 4 chords is always major
The order of 5 chords is always major
Sequence of 6 chords is always minor
The order of 7 chords is always diminished
To start learning and producing a musical composition, the basic theory of music that has been explained above is a necessity because it becomes the foundation in building the structure of a composition.
Hope useful.