A Journey Through the Ages: A Brief Overview of Indian History
India, a land of diverse cultures, languages, and religions, has a rich and complex history that spans over thousands of years. From ancient civilizations to modern democracy, India’s historical journey is marked by remarkable achievements, profound philosophy, and intense struggles. This blog takes you on a journey through the major phases of Indian history, offering a glimpse into the events and personalities that shaped this vast subcontinent.
.jpeg)
- The Indus Valley Civilization (c. 3300–1300 BCE)
Suggested Image: A map highlighting the sites of Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro, with images of seals and terracotta figurines.
The roots of Indian civilization trace back to the Indus Valley, one of the world’s earliest urban cultures. Flourishing around 3300 BCE in present-day Pakistan and northwest India, the Indus Valley Civilization is renowned for its advanced urban planning, including well-laid streets, sophisticated drainage systems, and impressive architecture. The cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro stand as testimonies to the ingenuity of these ancient people. Despite its decline around 1300 BCE, the civilization left a lasting legacy on the subcontinent's culture and trade.

- The Vedic Age (c. 1500–500 BCE)
Suggested Image: A depiction of Vedic rituals or a page from the Rigveda manuscript.
Following the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization, the Vedic Age emerged, characterized by the composition of the Vedas, the oldest sacred texts of Hinduism. This period saw the rise of small kingdoms and tribes, as well as the development of a caste system. The Vedic Age laid the foundation for Indian culture, with profound philosophical and religious ideas that would shape the course of Indian history.
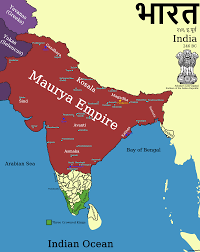
- The Maurya Empire (c. 322–185 BCE)
Suggested Image: A statue of Emperor Ashoka, along with the Ashoka Chakra, now part of India’s national flag.
The first major empire in Indian history was the Maurya Empire, established by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE. The Maurya dynasty, especially under Emperor Ashoka, saw the expansion of the empire across much of the Indian subcontinent. Ashoka, after a transformative experience following the brutal Kalinga War, embraced Buddhism and spread its principles of non-violence and tolerance. His reign is marked by the promotion of Dharma and the construction of stupas, many of which survive to this day.
.jpeg)
- The Gupta Empire (c. 320–550 CE)
Suggested Image: Artistic representations of Gupta-era temples or coins.
Often referred to as the Golden Age of India, the Gupta Empire was marked by significant achievements in art, literature, science, and mathematics. The period saw the creation of classical Sanskrit literature, advancements in astronomy and mathematics (including the concept of zero), and the construction of temples that defined the architectural styles of future generations. Under rulers like Chandragupta II, the Gupta Empire was a beacon of cultural and intellectual growth.
.jpeg)
- The Delhi Sultanate (1206–1526)
Suggested Image: Qutub Minar or an image of the Alai Darwaza.
The advent of Islam in India began in earnest with the establishment of the Delhi Sultanate in the 13th century. This period saw the rise of several dynasties, including the Mamluks, Khiljis, Tughlaqs, and Lodis, who ruled much of northern India. The Delhi Sultanate was a time of both conflict and cultural synthesis, as Islamic architecture, art, and education flourished alongside the existing Hindu traditions. The Qutub Minar, the tallest brick minaret in the world, stands as a symbol of this era.
.jpeg)
- The Mughal Empire (1526–1857)
Suggested Image: The Taj Mahal or a painting of Emperor Akbar.
The Mughal Empire, founded by Babur in 1526, is perhaps the most well-known period of Indian history. The Mughals brought unprecedented political stability, economic prosperity, and cultural flourishing. Emperors like Akbar, Jahangir, and Shah Jahan are remembered for their contributions to art, architecture, and administration. The Taj Mahal, built by Shah Jahan in memory of his wife Mumtaz Mahal, remains a symbol of India's rich history and the architectural genius of the Mughals.
.jpeg)
- Colonial India (1757–1947)
Suggested Image: An image of Mahatma Gandhi leading the Salt March or the Indian National Congress.
The arrival of European powers, particularly the British, marked a new chapter in Indian history. Following the Battle of Plassey in 1757, the British East India Company gradually expanded its control over India, culminating in the establishment of the British Raj in 1858. The colonial period was marked by exploitation and resistance, as India was subjected to economic drain and cultural upheaval. However, it also saw the rise of a national consciousness and the birth of the independence movement, led by figures like Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru, and Subhas Chandra Bose.
.jpeg)
- Independent India (1947–Present)
Suggested Image: The Indian tricolor being hoisted at the Red Fort on Independence Day.
India gained independence from British rule on August 15, 1947, marking the beginning of a new era. The partition of India and Pakistan led to widespread violence and migration, but India soon embarked on a path of democratic governance and economic development. Over the decades, India has emerged as a significant global player, with a strong economy, diverse culture, and robust democratic institutions. The journey of independent India is one of resilience and progress, as it continues to uphold the values of secularism, democracy, and social justice.
Conclusion
Indian history is a vast tapestry of events, ideas, and cultures. Each period has contributed to the country's rich heritage, making India a unique civilization with a deep-rooted historical legacy. From the ancient cities of the Indus Valley to the bustling metropolises of modern India, the story of this land is one of continuity and change, tradition and innovation.