Fundamentals of Chemistry || Lecture 06 || Atomic Number and Mass Number
In this lecture, we will look at the properties that may be used to define atoms. If you are asked to describe a person, you are likely to cite qualities such as the color of their hair, the color of their eyes, their height, and so on. Similarly, there are characteristics we may use to characterize atoms. The atomic number is the first and maybe most essential of these characteristics.
The number of protons in an atom's nucleus is called atomic number. Atomic Number is extremely essential since the number of protons in an atom tells us what type of atom it is, i.e., is it a carbon atom? Is it a sulfur atom? Is that an oxygen atom, or something else? The atomic number is commonly abbreviated as upper case "Z." Elements in the modern periodic table are arranged on the basis of their increasing atomic numbers.
The mass number, which is typically abbreviated as upper case "A," is the next significant feature that we may utilize to describe atoms. The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus are called its mass number. People are frequently puzzled by the term "mass number." Because atomic number is the number of protons, everyone expects mass number to equal the number of neutrons, but it is not. In truth, there is no name for the number of neutrons in an atom; it is just the number of neutrons.
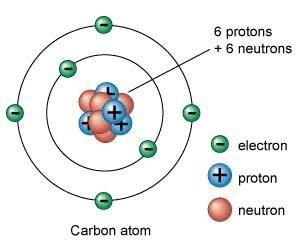
Let’s talk about an atom having atomic number 6. It is called carbon atom. It has 6 protons in its nucleus therefore, its atomic number is 6. It also has 6 neutrons in its nucleus so, its mass number will be 12. So,we can say that
Regards:
@waqarahmadshah
Sort: Trending


