Understanding Smart Contracts - Part 2
What is Blockchain?
The beginning of the 21st century revealed multiple innovative technologies which produced substantial impact on the new data-driven economy, the most notable of which are: Cloud Computing, Big Data, Internet of Things, Augmented Reality and Blockchain. The latter technology, initially introduced as a technological backbone of cryptocurrency Bitcoin, started to have significance on its own. Governments and companies all over the world are puzzling over the possible implementation of Blockchain technologies in many areas of life, not associated with usage of cryptocurrency.
One of most promising areas of implementation of Blockchain technology is using it for creating fully automated contracts – agreements, which are performed without human involvement. Such agreements in IT-environment are frequently called “Smart” contracts.
So what's Blockchain?
This is, possibly, the first question, which the person making a deep dive in “Smart” contracts set of issues faces. In order to answer it, one has to understand the origin of this technology which is inseparably linked with Bitcoin cryptocurrency, forming the core of its technological infrastructure.
Bitcoin was developed by an unidentified programmer, or group of programmers, under the name of Satoshi Nakamoto, which is indicated as an author of White paper describing the basics of functioning of Bitcoin. In the most general terms, Bitcoin can be described as a decentralized, open-source software based peer-to-peer electronic currency. The key features of Bitcoin can be summarized as follows:
Decentralized nature
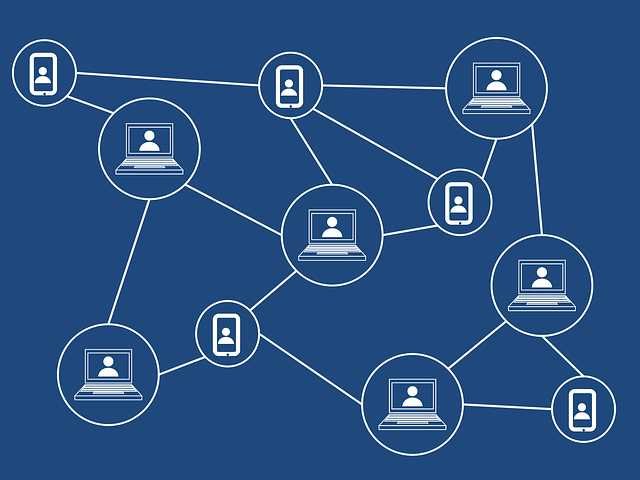
Bitcoin does not have a centralized emission center or any trusted central authority: maintenance of the Bitcoin transactions is performed by a network of communicating nodes running special software. From a technical perspective, Bitcoin as a currency unit is nothing more than a computer file, created based on special algorithm processed on computing power belonging to the Bitcoin community members.
Bitcoin protocol developers also don’t have control over Bitcoin-related transactions: since its code is distributed on the terms of MIT open source license, it is available for inspection for any interested person and modifications, which can become a standard only if accepted by the majority of the community.
Anonymous nature

One can use Bitcoin without any special registration or identification procedure. It is sufficient to install special wallet application to initiate transactions with Bitcoin. Each wallet consists of Bitcoin units, public key and private key. Private key is used for transfer of Bitcoin unit by its owner to another user’s wallet.
Without knowledge of the private key, the transaction cannot be signed and Bitcoin unit cannot be spent. Public key is used by other persons to send Bitcoin units to this wallet and is used by Bitcoin network for verification of transactions. Thus, Bitcoin is a pseudonymous currency, meaning that funds are not tied to real-world entities but rather to specialized addresses. Their owners are not explicitly identified, but all transactions on the Blockchain are public.
Mathematic algorithm as a basis of Bitcoin value

There is no specific intrinsic value in Bitcoin, similar to commodities with limited availability like gold, neither is there authority of the government like in fiat money behind it. However, it does not mean that Bitcoin does not have anything backing up its value. It is backed by mathematics, cryptography, and computer code. Bitcoin units are created during the process known as “mining”. Each person, who installed specialized software, may “mine” Bitcoin unit as a reward for solving a complex mathematical problem, associated with verification of transactions performed with Bitcoins.
The complexity of such problems is growing together with the amount of transactions performed in Bitcoin network. In other words, emission of new Bitcoin is a result of performance of computing activities to the benefit of all the Bitcoin community. Overall number of Bitcoins is defined by the protocol and amounts to 21 million bitcoins.
Since computational power is a valuable and limited resource, having intrinsic costs (e.g. for hardware involved and electricity), and Bitcoin has limited availability, which is ensured by mathematic algorithms, it is possible to claim that Bitcoin has some value behind it.
Absence of single administrator of transactions.
It is a well-known fact that electronic money is subject to the risk of double-spending. Unlike physical coins, electronic money like any computer data can be duplicated and thus be used more than once. Traditional electronic money systems prevent double-spending by having a centralized trusted administrator that follows established process for authorizing each transaction.
The problem with this solution is that the fate of the entire money system depends on the company running administrative function, with every transaction having to go through them, just like a bank. Bitcoin resolves double-spending problem by using a peer-to-peer network and this is where Blockchain technology plays the key role. All the transactions ever performed with all Bitcoin units are included in publicly available database.
Information about new transaction with Bitcoin is distributed through the network, is verified by miners and then is fixed with indication of the time it was made (timestamp) and unique number of Bitcoin unit. Thus, it is possible to trace all the history of transactions with each particular Bitcoin unit in the database of all the transactions with Bitcoin – Blockchain.
Resilience to data manipulations from outside
Cryptography used in the process of creating records on Bitcoin-related transactions in Blockchain database prevents tampering with the content of such records ensuring their perpetual nature. Whenever two people exchange Bitcoin units, an encrypted record of the transaction is sent out to all other nodes in the Bitcoin network.
The other nodes verify the transaction by performing complex cryptographic calculations on the data in the record («mining»), and notify one another each time a new “block” of transactions is confirmed as legitimate. When a majority of the nodes agree that a block passes review, they all add it to the Blockchain database and use the updated version as a cryptographic basis for encrypting and verifying future transactions. Each block is guaranteed to come after the previous block chronologically because the previous block's hash would otherwise not be known.
Each block is also computationally impractical to modify once it has been in the chain for a while because every block after it would also have to be regenerated. Thus, it is not possible to rewrite information about certain transaction once it is included in Blockchain: such information will be rejected by the network, unless the intruder possesses more than 50% of the overall computational power of the Bitcoin network. As a result all the members of Bitcoin community have a single version of “truth”, which is irreversible. Each participant to the transaction has a copy of the Blockchain database and it is synchronized with each other by using specialized algorithm. All this creates an unprecedented level of trust between the users of Bitcoin, where Blockchain is the core element facilitating such trust.


blockchain as a technology holds many applications, most of it's features are the missing blocks in many mainstream sectors, the fact that stuffs (Dapps) can be built on it makes it a hub for the applications of the future.
Yeah.
I believe there are many areas of blockchain technology that have not been explored yet.
But with time, I believe that as more people adopt this technology, we will eventually touch all of them