Global Warming
What is Climate Change?
Climate change refers to significant, long-term changes in the global climate.
The global climate is the connected system of sun, earth and oceans, wind, rain and snow, forests, deserts and savannas, and everything people do, too. The climate of a place, say New York, can be described as its rainfall, changing temperatures during the year and so on.
But the global climate is more than the “average” of the climates of specific places.
The Climate System
A description of the global climate includes how, for example, the rising temperature of the Pacific feeds typhoons which blow harder, drop more rain and cause more damage, but also shifts global ocean currents that melt Antarctica ice which slowly makes sea level rise until New York will be under water.
It is this systemic connectedness that makes global climate change so important and so complicated.
Picture
(Source: US Environmental Protection Agency)
What is Global Warming?
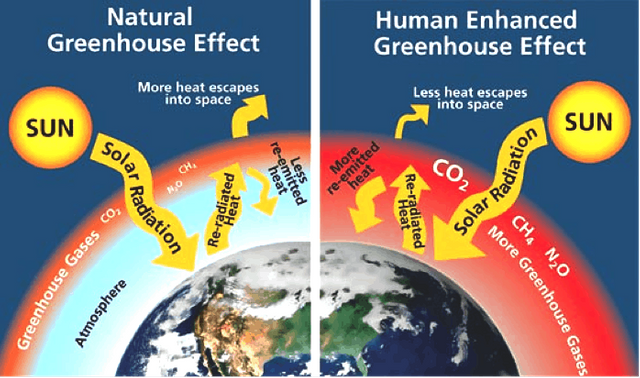
Global warming is the slow increase in the average tempera ture of the earth’s atmosphere because an increased amount of the energy (heat) striking the earth from the sun is being trapped in the atmosphere and not radiated out into space.
The earth’s atmosphere has always acted like a greenhouse to capture the sun’s heat, ensuring that the earth has enjoyed temperatures that permitted the emergence of life forms as we know them, including humans.
Without our atmospheric greenhouse the earth would be very cold. Global warming, however, is the equivalent of a greenhouse with high efficiency reflective glass installed the wrong way around.
Ionically, the best evidence of this may come from a terrible cooling event that took place some 1,500 years ago. Two massive volcanic eruptions, one year after another placed so much black dust into the upper atmosphere that little sunlight could penetrate. Temperatures plummeted. Crops failed. People died of starvation and the Black Death started its march. As the dust slowly fell to earth, the sun was again able to warn the world and life returned to normal.
Today, we have the opposite problem. Today, the problem is not that too little sun warmth is reaching the earth, but that too much is being trapped in our atmosphere.
So much heat is being kept inside greenhouse earth that the temperature of the earth is going up faster than at any previous time in history. NASA provides an excellent course module on the science of global warming.
How Does Global Warming Drive Climate Change?
Heat is energy and when you add energy to any system changes occur.
Because all systems in the global climate system are connected, adding heat energy causes the global climate as a whole to change.
Much of the world is covered with ocean which heats up. When the ocean heats up, more water evaporates into clouds.
Where storms like hurricanes and typhoons are forming, the result is more energy-intensive storms. A warmer atmosphere makes glaciers and mountain snow packs, the Polar ice cap, and the great ice shield jutting off of Antarctica melt raising sea levels.
Picture
(Source: US Environmental Protection Agency)
Changes in temperature change the great patterns of wind that bring the monsoons in Asia and rain and snow around the world, making drought and unpredictable weather more common.
This is why scientists have stopped focusing just on global warming and now focus on the larger topic of climate change.
What Causes Global Warming?
There are three positions on global warming: (1) that global warming is not occurring and so neither is climate change; (2) that global warming and climate change are occurring, but these are natural, cyclic events unrelated to human activity; and (3) that global warming is occurring as a result primarily of human activity and so climate change is also the result of human activity.
The claim that nothing is happening is very hard to defend in the face or masses of visual, land-based and satellite data that clearly shows rising average sea and land temperatures and shrinking ice masses.
The claim that the observed global warming is natural or at least not the result of human carbon emissions (see Climate Skeptics below) focuses on data that shows that world temperatures and atmospheric CO2 levels have been equally high or higher in the past. They also point to the well understood effects of solar activity on the amount of radiation striking the earth and the fact that in recent times the sun has been particularly active.
In general, climate scientists and environmentalists either (1) dispute the data based on, for example, new ice core data or (2) suggest that the timing issue – that is, the rapidity with which the globe has warmed and the climate changed simply do not fit the model of previous natural events.
They note also that compared to other stars the sun is actually very stable, varying in energy output by just 0.1% and over a relatively short cycle of 11 to 50 years quite unrelated to global warming as a whole.
The data strongly suggests that solar activity affects the global climate in many important ways, but is not a factor in the systemic change over time that we call global warming.
As for the final position that global warming and climate change result from human activity (are “anthropogenic”), scientists attribute current atmospheric warming to human activities that have increased the amount of carbon containing gases in the upper atmosphere and to increased amounts of tiny particles in the lower atmosphere. (NASA offers a good course module on “The Carbon Question.”)
Specifically, gases released primarily by the burning of fossil fuels and the tiny particles produced by incomplete burning trap the sun’s energy in the atmosphere. Scientists call these gases “greenhouse gases” (GHGs) because they act like the wrong way reflective glass in our global greenhouse.
Picture
(Source: EARSI)
Picture
(Source: State of the Planet )
Scientists call the tiny particles ‘black carbon’ (you call it soot or smoke) and attribute their warming effect to the fact that the resulting layer of black particles in the lower atmosphere absorbs heat like a black blanket.
Scientists date the beginning of the current warming trend to the end of the 18th or beginning of the 19th century when coal first came into common use.
This warming trend has accelerated as we have increased our use of fossil fuels to include gasoline, diesel, kerosene and natural gas, as well as the petrochemicals (plastics, pharmaceuticals, fertilizers) we now make from oil.
Scientists attribute the current warming trend to the use of fossil fuels because using them releases into the atmosphere stores of carbon that were sequestered (buried) millions of years ago.
The addition of this “old” carbon to the world’s current stock of carbon, scientists have concluded, is what is heating our earth which causes global warming.
What are the most important greenhouse gases(GHGs)?
The most common and most talked about greenhouse gases is CO2 or carbon dioxide. In fact, because it is so common, scientists use it as the benchmark or measure of things that warm the atmosphere.
Methane, another important GHG, for example, is 28-36 times as warming as CO2 when in the upper atmosphere (USEPA GWP – Global Warming Potential – estimate over 100 years), therefore, 1 ton of methane = 28-36 tons eCO2 or CO2 equivalents.