Health Matters; Hyperhidrosis, Causes & Treatment
Hi friends, it is good to have you on my blog. Hyperhidrosis refers to the medical condition known for immoderate sweating, normally affecting the soles of the feet, palms of the hand, as well as underarms. Other parts of the body, like the chest, face, and back, can also be affected by hyperhidrosis. Let's talk about Hyperhidrosis.
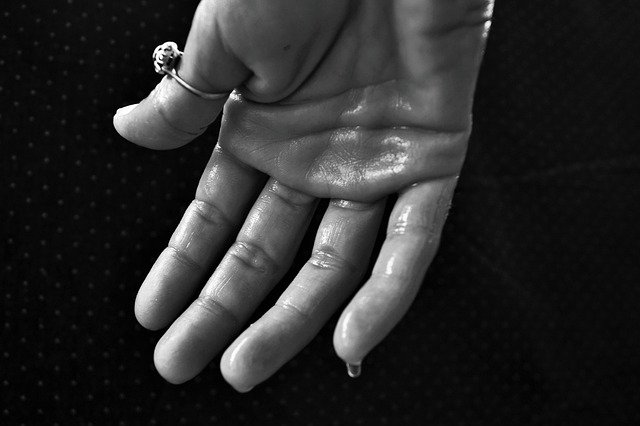 Source Source |
|---|
Primary Hyperhidrosis
This is the most common class of hyperhidrosis which accounts for roughly 90% of cases. The precise cause of primary hyperhidrosis may be unknown, but is believed to be related to the following:
• Genetics
Family background plays a meaningful role in primary hyperhidrosis.
• Overactive sweat glands
In people who have primary hyperhidrosis, the sweat glands are overactive, thereby producing immoderate sweat.
• Nervous system abnormalities
Most research suggests that primary hyperhidrosis may be connected to abnormalcy in the nervous system, specifically in the sympathetic nervous system.
Secondary Hyperhidrosis
Secondary hyperhidrosis is a result of inherent medication or medical conditions. Causes of secondary hyperhidrosis include:
• Hyperthyroidism
A condition of an overactive thyroid gland which can result in excessive sweating.
• Diabetes
Diabetic patients may experience excessive sweating as a result of low blood sugar or different complications.
• Menopause
Hormonal modifications in the course of menopause can result in hot flashes as well as excessive sweating.
• Medications
Some medications like blood pressure medications, antidepressants, and hormone replacement therapy, can result in excessive sweating as a by-product.
• Infections
Some infections, like tuberculosis or endocarditis, can result in excessive sweating.
• Cancer
Some classes of cancer, like lymphoma or carcinoid syndrome, may bring about excessive sweating.
• Neurological disorders
Conditions like peripheral neuropathy, Parkinson's disease, or multiple sclerosis may bring about excessive sweating.
• Hormonal imbalances
Excessive sweating can also be caused by hormonal imbalances like acromegaly or pheochromocytoma.
Key differences
| Primary Hyperhidrosis | Secondary Hyperhidrosis |
|---|---|
| Untraceable medical cause | Caused by an underlying medical condition |
| Usually begins during childhood or adolescence | Mostly begins in adulthood |
| Symmetrical sweating | Generalized sweating |
| Limited to particular areas like the palm | Connected with other symptoms |
 Source Source |
|---|
Hyperhidrosis can, in a significant way, impact the lives of those experiencing it, influencing different facets of their physical, emotional as well as their social well-being. These are a few ways hyperhidrosis can affect the daily lives of those who experience it:
Physical Effect
- Discomfort and skin irritation: Excessive sweating might result in skin redness, irritation, as well as discomfort.
- Skin infections: Bacterial or fungal infections can take place as a result of excessive moisture.
- Foot problems: Excessive sweating on the feet can result in athlete's foot, foot odor, as well as other foot problems.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
- Anxiety and stress: Hyperhidrosis can bring about significant anxiety and stress, particularly in social situations.
- Low self-esteem: Excessive sweating can result in feelings of shame and embarrassment, as well as low self-esteem.
- Avoidance behaviors: People that have hyperhidrosis can evitate public events, social functions, or activities that might aggravate their sweating.
Social Impact
- Social anxiety: Hyperhidrosis can bring about social anxiety, making interaction with others or forming relationships hard.
- Difficulty with intimacy: Making intimate relationships might be challenging due to excessive sweating.
- Career and education impact: Job performance, career choices, as well as educational pursuits can be affected by hyperhidrosis.
Daily Life Challenges
- Clothing and laundry: Regular change of clothing and frequent laundry are the resultant effects of excessive sweating
- Personal care: Person activities like showering and dressing might be more challenging due to hyperhidrosis.
- Leisure activities: Participation in leisure activities can be limited by excessive sweating.
| Treatments | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Oral treatments like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) | Generally are 50% to 80% effective for the reduction of sweat |
| Topical treatment such as Iontophoresis | 80% effective for temporarily blocking sweat glands making use of mild electrical current |
| Invasive treatments like Laser therapy | 90% effective as it makes use of laser energy to aim and mitigate sweat glands |
| Alternative therapies such as herbal supplements | Supplements like chamomile may help in the reduction of sweat production at an effective rate of 50% |
 Source Source |
|---|
- Diet and Nutrition
Staying hydrated will be necessary for the regulation of body temperature to reduce sweating in addition to avoiding acidic or spicy foods that might trigger sweating. Foods such as walnuts can be taken often as their Omega-3 fatty acid content is helpful for inflammation reduction and the promotion of healthy skin. - Choices of Clothing and Fabric
The wearing of them is advisable as they assist in modifying to fit changing temperatures and lower sweating. Breathable clothing made of natural fibers such as cotton should be worn as it allows for adequate airflow. - Stress Management
Get enough sleep per night to help regulate the response of the body to stress, and learn and engage in physical activities that can help reduce stress and anxiety, which can trigger sweating. - Personal Hygiene and Grooming
Regular bathing using antibacterial and antifungal soaps will not only help keep oneself clean but will also help in controlling bacteria growth. Excessive body hair helps in holding moisture as well as bacteria, worsening sweating; hence, it should be frequently trimmed. - Other Lifestyle Changes
Caffeine and nicotine should be avoided as they might arouse sweat glands and worsen sweating; in addition, tight clothing should equally be avoided as they trap moisture as well as bacteria, and this worsens sweating.
- Misconception — It is an indication of nervousness or anxiety:
This is a complete misconception. Although hyperhidrosis is triggered by anxiety, hyperhidrosis remains a medical disarray affecting the sweat glands. - Misconception — It is a hygienic issue.
People with hyperhidrosis are known to bathe or shower as frequently as they can. Therefore, hyperhidrosis does not result from poor hygiene as many think; it is a medical condition. - Misconception — Only affects the underarms.
Although immoderate sweating is common in the armpits, hyperhidrosis can actually affect other parts of the body like the face, palms, torso, and soles. - Misconception — It is a temporary condition.
Hyperhidrosis isn't a temporary condition but a chronic one that calls for continuous treatment and management. - Misconception — It is rare.
Many think that hyperhidrosis is a rare condition where approximately 5% of the populace is affected, and this makes it a somewhat common condition.
Knowing these misconceptions may help in the reduction of stigma and promotion of empathy and comprehension for individuals with hyperhidrosis as well as help us to bring it under control.
Thanks for being here
Am inviting @rossnenye, @sahmie and @chilaw