Features and Differences of Layer One Layer Two Coins
Layer 1 coins are cryptocurrencies that serve as the main layer of a blockchain network. The token is built as the base layer of the blockchain network and works on a block-side basis. They have their own core network. Some examples of first-tier coins are Bitcoin, Ethereum, Cardano, Polkadot, and Solana. Layer 1 coins are designed to provide decentralized security and form the basis of blockchain networks.
Layer 2 coins are cryptocurrencies that run on the second layer of an existing blockchain network. These tokens are designed to solve the scalability challenges of first-tier tokens and facilitate transactions. Reduce congestion by deploying various solutions to reduce congestion and increase network throughput. Layer 2 solutions include payment channel sidechains and government channels. Examples of layer 2 coins are Lightning Network and Polygon (formerly Matic Network).
Layer one and layer two coins are different types of cryptocurrencies. Which works on different layers of blockchain technology. Here are some key features and differences between layer one and layer two coins, the important ones I am providing below
Level One Coins:
Foundational Layer : Layer One Coin is the foundational layer of a blockchain network. Examples of layer one coins include Bitcoin, Ethereum and Cardano etc.
Mainnet Functionality: A layer of coins operate on their own mainnet, a fully functional blockchain network is the first to do everything.
Decentralization: One level of currency prioritizes decentralization and security. They use various consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to verify transactions.
Native Tokens : Layer One coins have their own native tokens, which are used for transactions, execution of smart contracts and other functionalities. Scalability: Layer One coins often face scalability challenges. This is because the transaction demand increases resulting in longer confirmation times and higher fees.
Smart contract capabilities: A layer coin like Ethereum has built-in smart contract functionality. Allows developers to create decentralized applications (dApps) and perform programmable transactions.
Level Two Currency: Built on Layer One : Layer two coins are built on top of the Layer One blockchain. While they provide solutions to scalability issues. Layer One takes advantage of existing security and decentralization of networks.
Scalability Solutions : Layer Two Coins provide scalability solutions that help reduce congestion and increase the throughput of the Layer One network. Examples include payment channels, sidechains, and state channels Faster and cheaper
transactions: Transactions are processed off-chain or in a more efficient manner. Tier two coins can achieve faster confirmation times and lower transaction fees than tier one coins.
Interoperability: Layer two coins can enable interoperability between different layer one networks. Allows users to seamlessly transfer assets and data across multiple blockchain platforms.
Enhanced Functionality: Some layer two coins introduce additional features and functionality that enhance the capabilities of the layer one network. Such as enhanced privacy, governance or special use cases.
It is important to note that specific features and differences may vary between tier one and tier two coins as each project has its own unique design and purpose.
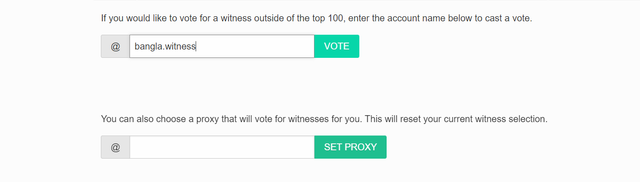
SET @rme as your proxy



X promotion link
https://x.com/mostofajaman55/status/1773062930696712543?s=20