Cognitive Approaches to Learning
Cognition is a concept that includes many forms of awareness and knowing; this compromises of all the states and processes involved, like perception, conception, memory, reasoning and problem-solving abilities, judgement and imagination. It involves all conscious and unconscious processes by which knowledge is accumulated, which makes it a difficult field to study in a scientific matter. Cognitive psychology is a specified field of psychology that attempts to conceptualize all aspects of cognition and is the scientific study of the mind. They do so by studying interactions amid thinking, creativity, language, emotion and problem solving. The theories about cognition established can be interpreted and applied in the field of educational psychology and learning to explore how information is processed by learners and what can be done to aid these processes.
MAIN CONCEPTS
There has been an avid interest in mental processes within the psychology community that originates sometime after the decline of the behaviorist approach in the late 1950s. Initial pioneers of the cognitive approach like Piaget and Vygotsky published their works to shed light on the developmental aspects of the mind. While their research and theories are of importance, the majority of the field of cognitive psychology developed due to the arrival of computers. The mind is a complex structure that we have still not fully understood, but by comparing it to the much simpler and artificial system of a computer the necessary terminology and references can be given to comprehend it better. This is known as computer analogy and it alludes to the use of computers as a tool for creating an understanding as to how the mind handles all the massive amounts of information. In a sense, a computer codes (or translates) an input of information, stores it and then uses it to produce an output. It is this system that provided the basis for the information processing approach, which is a cognitive approach in which people manipulate information, monitor it and strategize about it. The most essential cognitive processes to this approach are memory and thinking.
This approach is also based on certain assumptions, like how information processing in humans resembles that in computers. Furthermore, the information made available from the environment as input must build on prior knowledge and be processed by a series of processing systems including attention, perception, encoding and storage. The process of storing itself includes the usage of other processes like rehearsal, prediction, checking, monitoring and metacognition. Additionally, the storage itself can be classified into several types of memory, such as sensory memory, short-term memory, working memory or long-term memory, which can be further separated into sub-types. All these processes must alter the information in systematic ways, much like how a computer codes or transforms information. The goal of research in these areas is to specify the processes and structures that underlie cognitive performance.
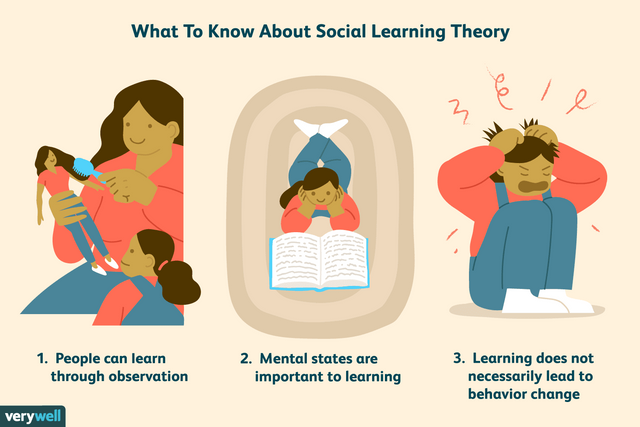
There is much debate though about how this metaphor may oversimplify the actual complexity of cognitive processes and ignore the influence of factors like motivation or human emotion. Other than the information processing approach, the social learning theory given by Bandura and meaningful learning introduced by Ausubel are also important cognitive theories.
APPLICATION IN EDUCATION PSYCHOLOGY
Research in cognitive psychology is of paramount importance in educational psychology as mental activity and processing of knowledge is the objective of learning. It is applied in many ways, like how instruction given to students should encourage them to become active constructors and the focus of teachers is more on the establishment of meaningful context. The basic characteristics of classroom instruction based on cognitive theories include concepts like:
• learner control, which is the active involvement of the learner in the learning process
• metacognitive training (ex. self-planning, monitoring and revising techniques)
• cognitive task analysis procedures, which uses hierarchal analysis to identify and describe prerequisite relationships
• emphasis on structuring, organizing and sequencing information to facilitate optimal processing; this uses cognitive strategies like outlining, summaries, synthesizers, advanced organizers, etc.
• establishing a learning environment that coaxes students to make connections with prior knowledge which can be done by recall of prerequisite skills, use of relevant examples and analogies
The cognitive approaches to learning have also led to the creation of various teaching methods:
COGNITIVE APPRENTICESHIP:
It uses Vygotsky’s basic principles of zone of proximal development. The method helps students grasp concepts and procedures under the direction of the teacher and consists of 5 steps – modelling, coaching, articulation, reflection and exploration. It promotes a student’s ability to view a problem from different perspectives and their ability to think independently.
RECIPROCAL TEACHING:
It consists of modelling, coaching, scaffolding and fading which are used to achieve instructional goals. Based on information processing, it occurs in the form of instructions as dialogue between teacher and student about a part of text that they are trying to bring meaning to. The teacher incorporates cognitive techniques like summarizing, question generating, clarifying and predicting to facilitate learning. This method promotes the amount of effort being applied to understand the information between the teacher and the student or among peers of students.
ANCHORED INSTRUCTION:
This method relies heavily on technology and problem-based learning in which instruction is created around some sort of case-study or problem scenario (in realistic context) that serve as anchors.
INQUIRY LEARNING:
With a basis in Piaget’s developmental theory, it works on the development of higher order thinking skills in children by having them investigate an issue or formulate and test a hypothesis. It involves the usage of combinational reasoning (looking at several things simultaneously from different angles), propositional reasoning (exploring assumptions and propositions) and hypothetical-deductive reasoning (going through different hypotheses) to solve problems. The conduction of this method requires 5 phases that end with testing a hypothesis for a possible answer.
DISCOVERY LEARNING:
Also based on Piaget’s developmental theory, it involves students asking questions, investigating a phenomenon, formulating hypothesis, doing experiments and research to discover principles and important relationships. Other than remembering of knowledge, this method encourages them to take responsibility for their learning and improves their high order thinking skills. Discovering for yourself is assumed to make the information be stored more firmly, and therefore easily retrievable later when needed.
PROBLEM BASED LEARNING:
It involves giving students an ill-structured, open-ended and real-life problem that could have many possible solutions and have them formulate ideas. They introduce this problem before instruction of facts and information in order so that there is focus on the child’s previous knowledge and a context is provided for further explanations.
The concept of cognition provides a clearer perspective on the mind and therefore a clear picture of the processes that facilitate learning. There may still be limitations to the effectiveness of the above-mentioned applications of the cognitive approach, such as the strict lab conditions research on such teaching methods is performed under, suggesting a low ecological validity. The various environmental factors that could possibly affect the learning process are looked over and the lack of external stimulus-response behavior for scientific measurement can be criticised.