|| Learn about the human reproductory system || (#burnsteem25)
Introduction
All living beings have to multiply a number generation after generation so that their own kind may live on.
Reproduction is the process by which living beings make their young. You must have studied about reproduction in plants and in this lesson we will be talking about reproduction in human beings.
Phases of the reproduction process in humans
Gamete formation: As in the case of plants, where the flowers produce the male ( inside the pollen) and the female gametes (the egg inside the ovary), in humans too, the male sex organs produce the male gametes called sperms and the female sex organs produce the female garment called the eggs.
Maturation of the sex organs: The teste (singular - testis) a part of the male sex organs and produced the sperms. The ovaries are part of the female sex organs and produce the eggs. Disco guns take their time to mature and grow. They develop around the age of 10 to 14 on an average. When they mature they produce their respective gametes. The time when they says organs mature is called puberty. Puberty indicate the onset of the sexually fertile period of an individual.
Fertilisation: The male and the female gametes come together and fuse to produce a single cell called the zygote.
Development of the embryo: The zygote grows and becomes a fully developed baby inside the mother's womb.
Giving birth: The baby is born when fully develop.
Nature and function of the male reproductive system
What made up the male reproductive system.
Let find out.
a) Testes: These are the sperm producing organs. They are two in number found lying just outside the body in a sac called the scrotum.
b) Epididymis: These are two tubes that come out from the respective testis.
c) Vas deferens: The epididmis continues into the body as tubes called the vas deferens. They are two in number.
d) Urethra: The urethra is a tube from the urinary bladder that carries urine outside the body. In males, the vas deferens joins up with urethra to transport sperms as well. The urethra passes through the penis which is a muscular organ.
e) Prostate gland and seminal glands: These are glands that are connected to the reproductive tract that secretes many juices. These juices are necessary for the survival of the sperms. The mixture of these juices and sperms is called semen.
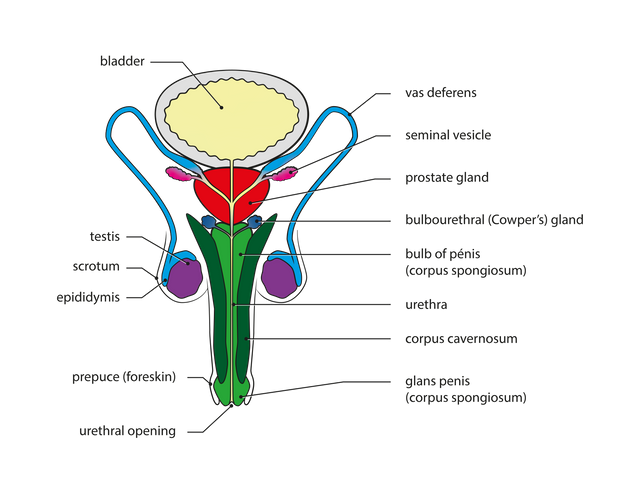
Source Male reproductive system
Nature and function of the female reproductive system
See what the female reproductive system is made of.
a) Ovaries: They are two ovaries found in the abdominal cavity of a female just below the kidneys. They produced the eggs.
b) Fallopians tubes: These are also called the oviducts. There are tips with a funnel-shaped mouth found close to the ovaries. Eggs released from the ovaries passed through the fallopian tibes (oviducts) to the uterus.
c) Uterus: This is a single pear-shaped organ. The fallopian tubes on a describe join up with the uterus. The uterus is also called the womb of the woman. It is a muscular organ which is lined on the inside with a thick layer of blood vessels. It is in the womb that the baby develops and grows. The muscular mouth of the uterus is narrow and is called the cervix.
d) Vigina: The vagina is a muscular tube. The cervix joins up with the vagina.
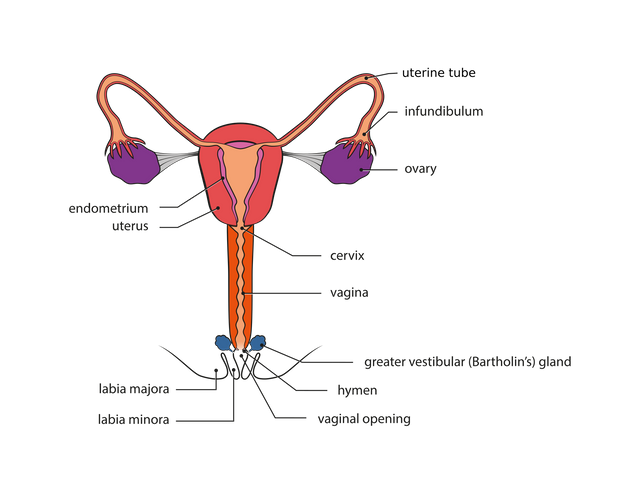
Source Female reproductive system
Process of fertilisation
- After puberty, the males produce many sperms.
- The females have a monthly cycle and produce only one egg per cycle.
- The sperms are released through the penis into the vagina of a female. This is called copulation or coutus.
- The sperm and the egg fuse to form the zygote.
- The zygote grows and attaches itself to the wall of the uterus. The embryo grows in the uterus for 40 to 42 weeks.
- When the baby is fully developed, the embryo separate from the uterus and comes out to the vagina. This is called giving birth to the baby or child delivery.
Functions of the Ovaries and Testes
Overies: The ovaries produce eggs in the females. The release hormones that help in preparing the uterus for pregnancy. The hormones also help in the development of secondary sexual characteristics like the development of the breast and widening of the hips. The brakes are also called a mammal glands. They produce milk in a new mother which helps in feeding the new-born child.
Testes: The testes produce sperms in males. They also produce the males hormones that help in the maturation of sperms.
The hormones also helps in the development of secondary sexual characteristics like the growth of hair, deepening of the voice and broadening of the shoulders.
All the functions of the ovaries and tetes mentioned above start only after puberty is reached.
Conclusion
I am glad you read to the end and I believe you must have learnt from this article.
Visit my blog again for more interesting articles.
25% to @null
Written by @udyliciouz
Thank you for contributing to #LearnWithSteem theme. This post has been upvoted by @fabio2614 using @steemcurator09 account. We encourage you to keep publishing quality and original content in the Steemit ecosystem to earn support for your content.
Regards,
Team #Sevengers
Very educative post, thanks for sharing with our kids, they will definitely learned from it.
Your post is very intresting related to human reproductory system.