How does wireless charging work?
Since the invention of electricity, transmitting electricity without a cord or other physical conductor has been a fantasy. At the end of the nineteenth century, Nikola Tesla made high-profile attempts at wireless power transmission and hoped to create a worldwide power "network" with his technology. There is still no such global solution 100 years later, but technology has made its way into our homes. But how does it work in practice? Is it also dangerous?
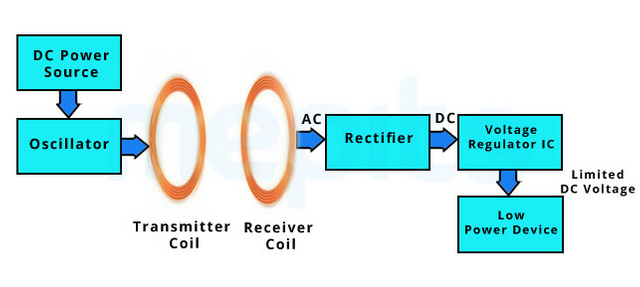
Wireless charging is a form of contactless power transfer that does not involve electricity passing through the air. Induction is the most popular technology for wireless charging of cell phones and electric toothbrushes, and it can handle a distance of about five millimetres between charger and user.
The main advantage is the decreased wear on contacts in chargers and rechargeable batteries, the ability to conveniently shield, for example, an electric toothbrush from water, and the ease of charging a little every now and then. This implies that devices can handle smaller (lighter, less resource-intensive) batteries. As a result, the technology is no more risky than rechargeable batteries in general.
Magnetic coils are used in both the battery and the unit that can be charged by using induction charging. As the charging station's coil receives electricity, it generates a magnetic field that can be used to transfer energy. When a device with a built-in similar coil is put in the magnetic field, an electric voltage is produced, which charges the device's built-in battery. This is how wireless charging for your smartphone and smartwatch works. As you can see, the system isn't completely new; induction charging has been used in electric toothbrushes since the 1990s.

Do you find the term "induction" from other household items? In reality, an induction cooker works in a similar manner: a magnetic field is formed in a coil beneath the stove's "plate." The magnetic field induces an electrical resistance in the pan's rim, which heats the food.
The plate does not actually heat up, but the bottom of the saucepan does, warming both the food and the soil underneath it. As a result, the argument that induction hobs do not get hot is false. However, since they do not heat up in the same way as a conventional stove, they cool down much quicker, reducing the chance of burning on the plate's after-heat.
Benefits of Wireless Charging
You won't have to scramble for a charger or free electrical outlets, and your home will be more pleasant without cables strewn around. As a result, the battery plate is also tucked away in a wall socket. The charging port and cord would be less abused. It's also nice to only be able to use the phone when it's lifted from the tablet.
Drawbacks
There is a waste of electricity. You can tell because you generate more heat than when you charge normally. It also means that charging is more time consuming. As a result, we're content to put off purchasing wireless chargers until the technology improves and they become more useful.