Electricity-generating hydrogel while cooling of electronic devices
According to an international research group, a hydrogel film has been developed that may convert waste heat into electricity while simultaneously cooling electrical devices.
Whenever electrical equipment is turned on, it generates a significant amount of heat. That this heat raises the temperature of the device and reduces its efficiency is a big concern. Because of this, waste heat must be removed from the environment as soon as it is practicable. However, the fan and other cooling systems that are used to accomplish this function require energy. Moreover, uncontrollably discharging waste heat into the environment wastes energy that could otherwise be put to more beneficial use.
ImageA hydrogel can cool off electronics and generate electricity from their waste heat
Currently available equipment, such as thermoelectric generators, can recycle the waste heat generated by electronic devices. However, similar systems can also cause electronic devices to overheat because they restrict heat from moving freely through the device.
According to an international research group, a hydrogel film has been developed that may convert waste heat into electricity while simultaneously cooling electrical devices. Waste heat also provides all of the energy required for the cooling process, which is an added bonus.

ImageElectronic device
The thermogalvanic battery that the researchers have developed is a type of hydrogel material. In the same way as conventional batteries do, these batteries have two electrodes and an electrolyte solution through which electrical charges move. The fundamental difference between thermogalvanic and ordinary batteries is that the temperature differential between the electrodes is the factor that allows electric charges to pass between them. Regular batteries do not have this feature.
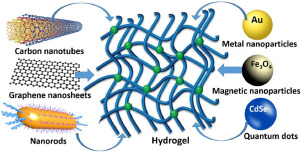
ImageDifferent nano-species loaded into polymer hydrogels result in novel features
While using electrical equipment with the hydrogel film that has been generated, some of the waste heat is converted into energy, and some is quickly removed from the environment by evaporation of the water that has been trapped in the hydrogel. A system that can cool electrical gadgets without the usage of external energy as a result of this development is created. Because the hydrogel takes moisture from the environment in which it is used and reclaims it, the system should be able to function without interruption for an extended period of time.
They put their hydrogel film to the test by covering a smartphone battery with it, and the results were encouraging. It was discovered that the hydrogel could lower the temperature of the battery by 20 degrees Celsius while simultaneously generating 5 watts of power.
References: