Steemit Crypto Academy, Season 3: Week 2 || Homework lessons by @pelon53: Hash and Cryptography // Homework done by @xkool24
Hello everyone and welcome again to my blog as I participate in the crypto lessons presented by respected Professor @pelon53 which dealt comprehensively on Hash and Cryptography. I will be handling all questions from the homework task accordingly.
Explain what does the resistance to collision mean? And what does resistance to preimage mean?

Just as discussed about the major characteristics of the Hash function which include its safety while in use, efficiency ,irreversible, but not limited to its ability of been resistance to collision. The Hash function is a process where data are collectively and uniformly processed, stored in a file/blocked in an alphanumeric manner void of any repetition. As of today we have the most used and adopted hash functions of the series SHA with various versions but the most resistant of all is the version with the 256 which is SHA256 that is seen to be highly resistant to collision.
Though there other Hash functions that were assumed to be collision resistance that were later broken, the SHA-256 has be strengthened due to its rigidity and protocol used. But notwithstanding the collision resistance is a property of the cryptography hash function that is specifically built to be collision resistant. It has a minimum requirement length of 160bits unlike what is obtainable from the Preimage resistance and Second Preimage resistance with 80 & 90bits respectively. It is sometimes likened to be second Preimage Resistance due to its similarities and hence referred to as Weak Collision resistance.
Collision is something that ordinarily we should not expect to occur given to the different inputted data which should give different output but in some cases it gives same output due to some third party interference. Hence the use of the Hash function series of SHA256 is a more resistant to this kind of collision. This is likened to the function of the Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) during cryptocurrency mining that quickens the process of transaction when a consensus agreement is to be reached even when some of the nodes are attacked by malware.

This is when one is able to predict the input that gave a particular hash or output which should be fundamentally wrong. This was also evident in occurrence when there is a reversal in the computational process that produces the hash which makes it alot difficult to protect the hash tracks. Hence there was an introduction of the one-way function with a straight line computational process void of any reversal or divergence. It is seen that the one-way function is in agreement with the Preimage resistance with high potency of securing blocks/files.
For a hash function is said to be resistance to Preimage, it must be seen to have a minimum of 80bits with also a One-way function feature. One-way function can only be achieved when a Hash function is resistant to both Preimage resistances. This primarily makes it hard for the attacker to identify the Preimage that makeup the output.
For the Second Preimage Resistance, the property is seen to be computed in an infeasible manner that makes quite lard to obtain distinct inputs of the given output and inputs.
It also has same traits of the Preimage Resistance to work efficiently well with the One-way Function but at this time it is channeled to function with the same Output and Input domain or those that are similar. Also just as mentioned for Preimage Resistance with a minimum requirement of 80bits of length, the Second Preimage Resistance is seen to have a minimum required length of 90bits. This is on distinctive difference between the duo so we don't mistake them.
Use tronscan and etherscan to verify the hash of the last block and the hash of that transaction. Screenshot is required for checking.

Using the TRONSCAN: BLOCK-HASH

- Goto the site Tronscan.org or Navigate through your Tronlink App.
- For those that used the Trolink app, Click on the Discover icon
- Click on the Tronscan icon
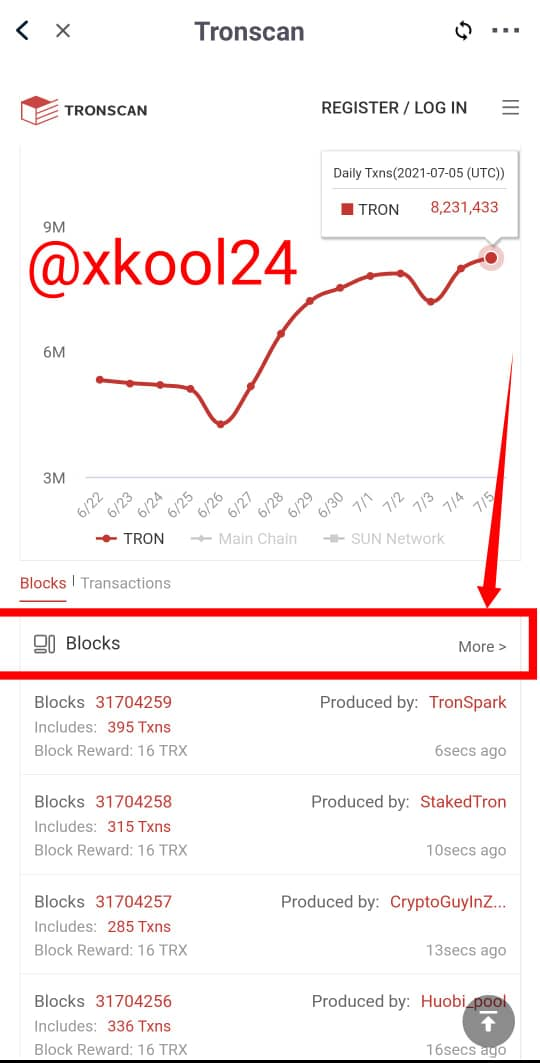
- From the Landing page, check on the down screen of your device and click on "Blocks - More"
- Details of the Block would pop up. Lets remember that it gets updated after every 3seconds.
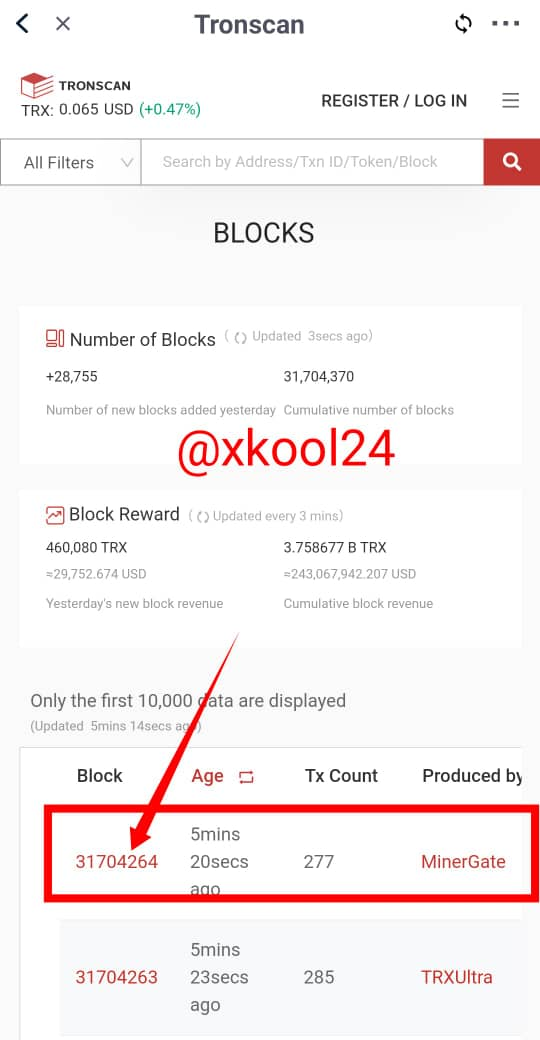
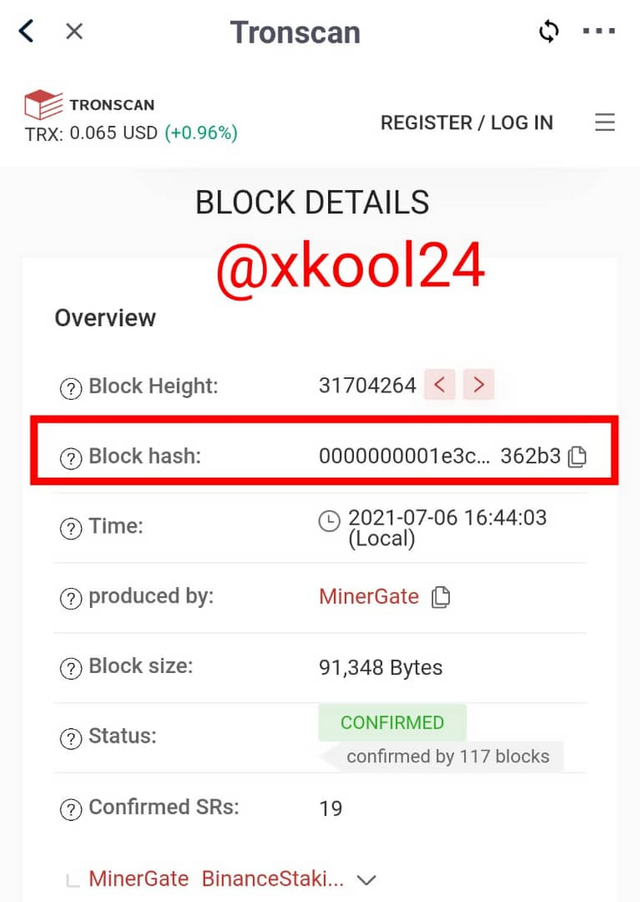
Total number of blocks captured as at the time of this post is 31,704,370 - Click on the last block in view to see details of the blocks and Hash.

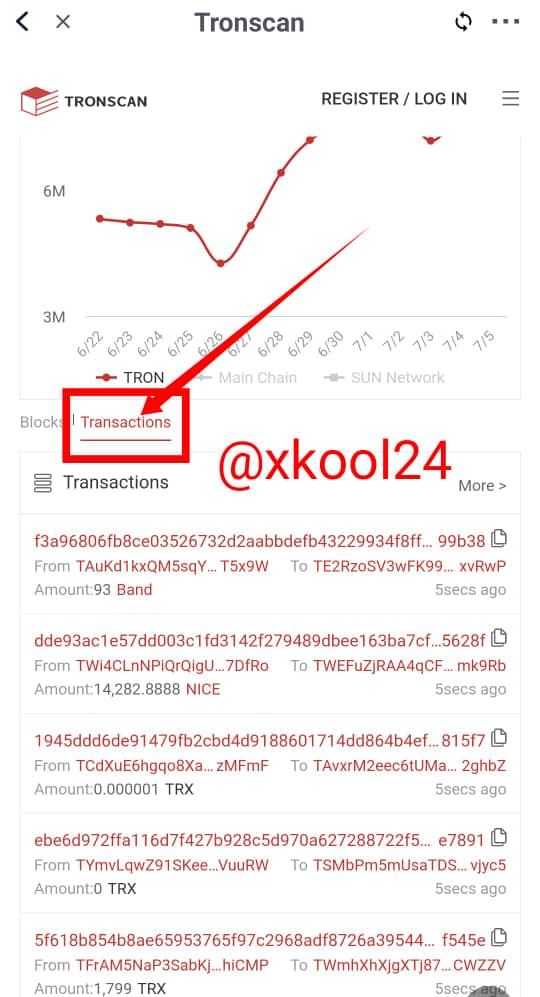
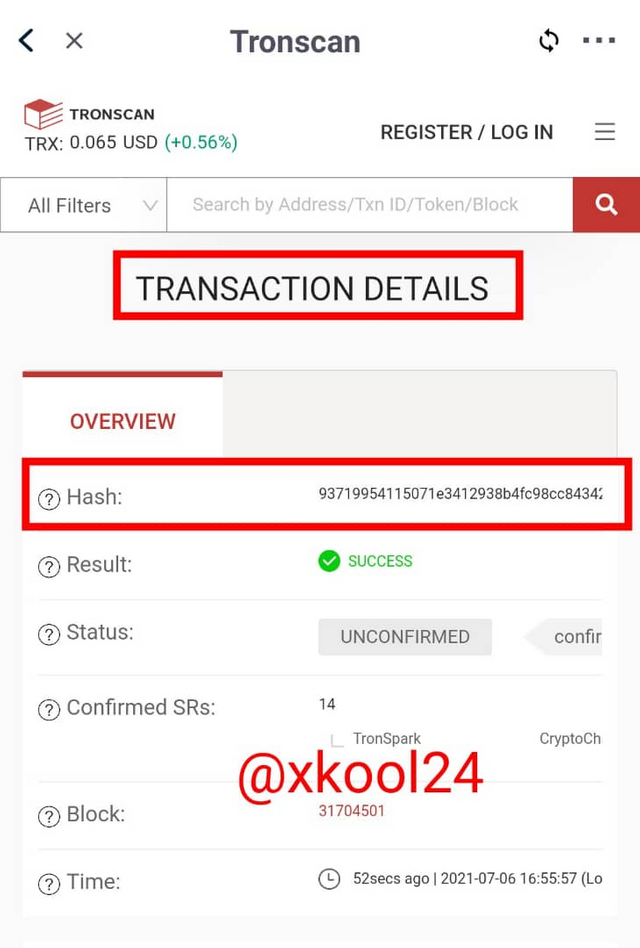
Using the TRONSCAN: BLOCK-TRANSACTION

- Go back to the landing page
- Click on the last block transaction in view
- Details of all the last block transaction would be displayed.

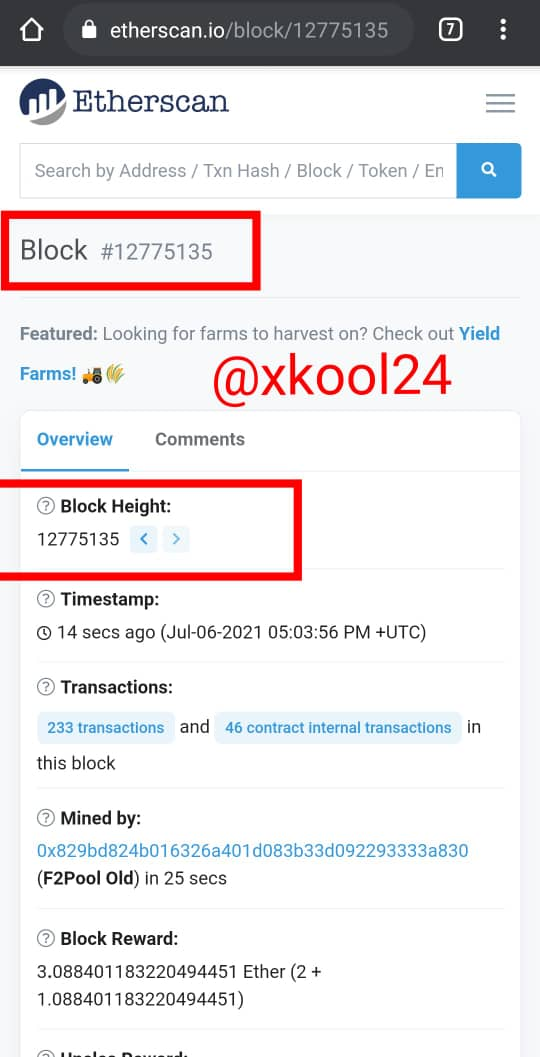
Using the ETHERSCAN: BLOCK-HASH

- Login to the Etherscan.io
- from the landing page you can see both features in display (Blocks and Transactions)
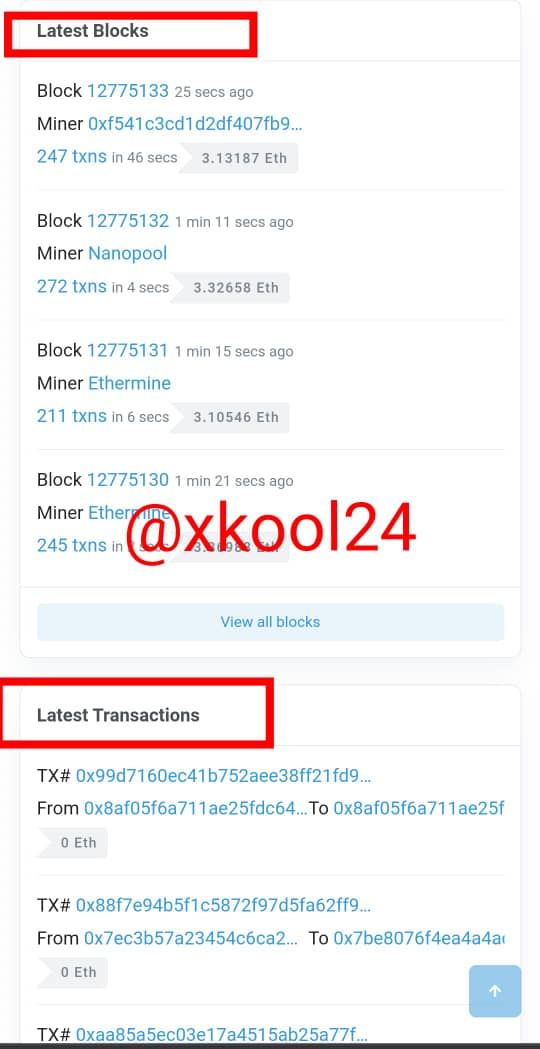
- From the screenshot last block captured is 12775135
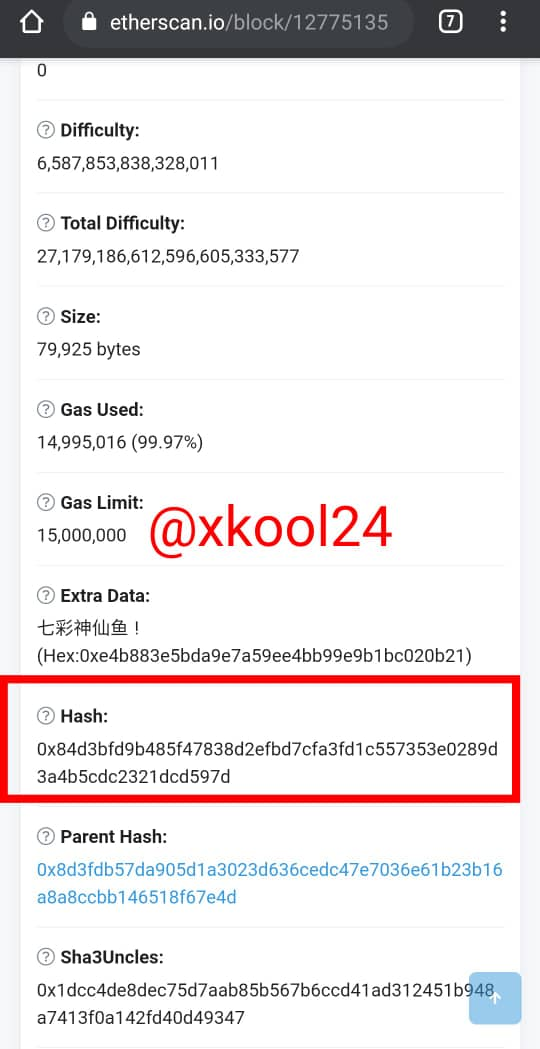
- Scroll down to enable you capture the Hash block ID

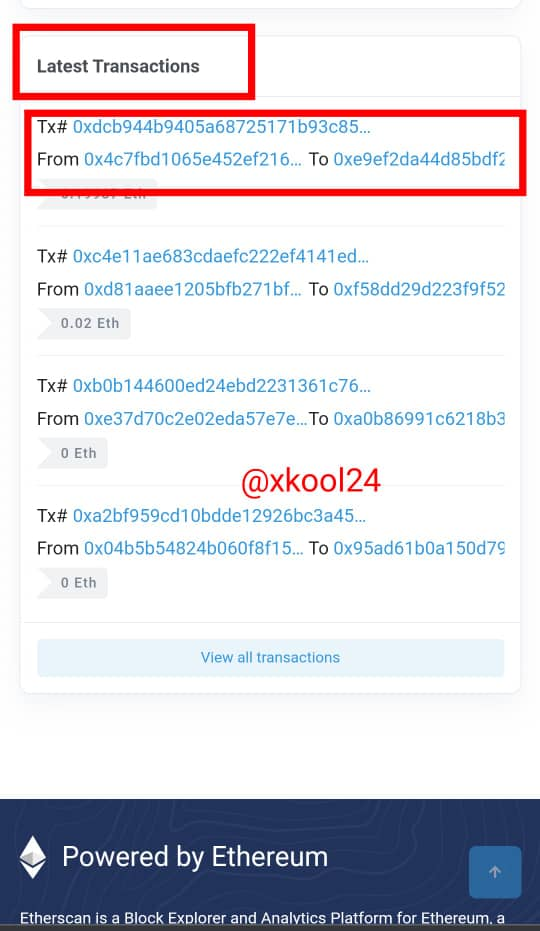
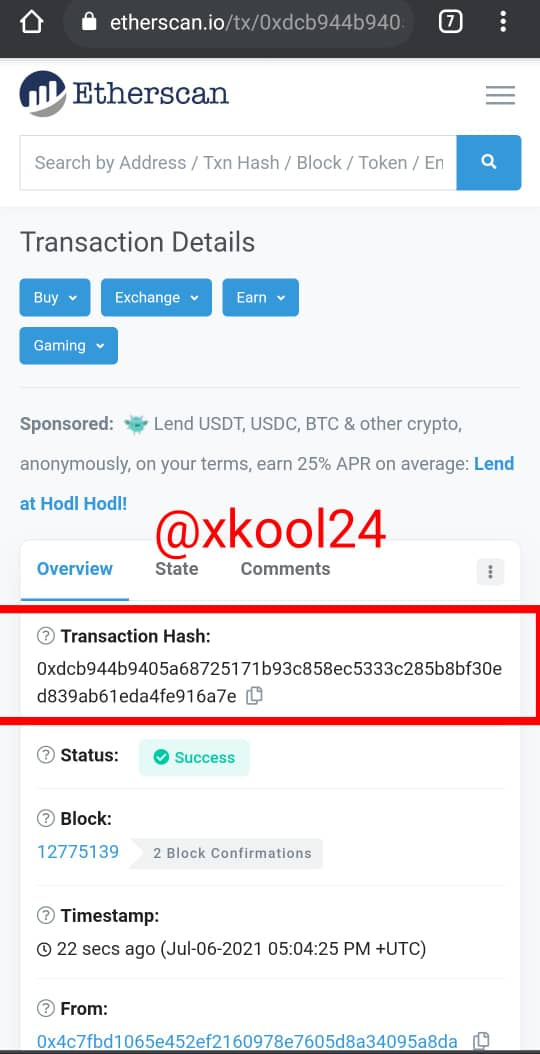
Using the ETHERSCAN: BLOCK-TRANSACTION

- Go back to the landing page
- Scroll alittle down to where you have "Latest Transaction", Click on it
- This displays the Hash Transaction details
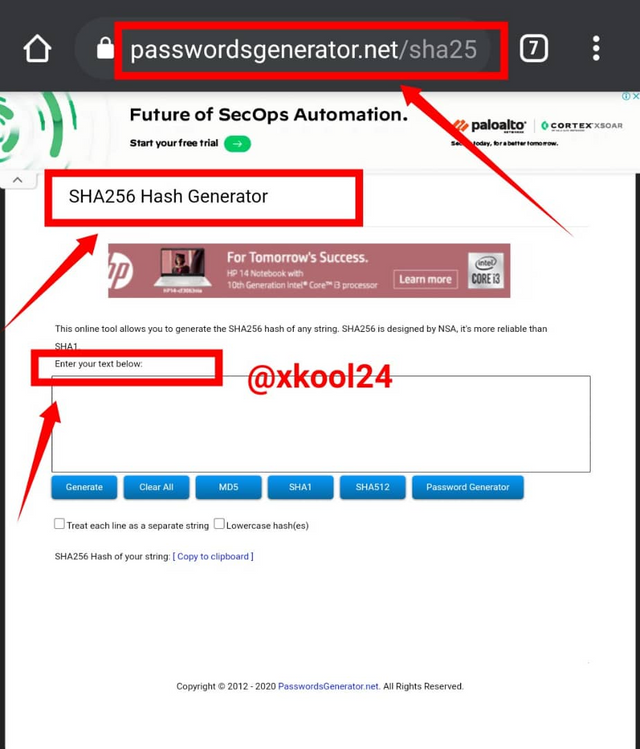
Generate the hash using SHA-256 , from the word CryptoAcademy and from cryptoacademy. Screenshot required. Do you see any difference between the two words? Explain.
To generate those words we will have to use the SHA256 hash generator
- Goto the Hash SHA256 generator Link
- Input the word which hash is to be generated.
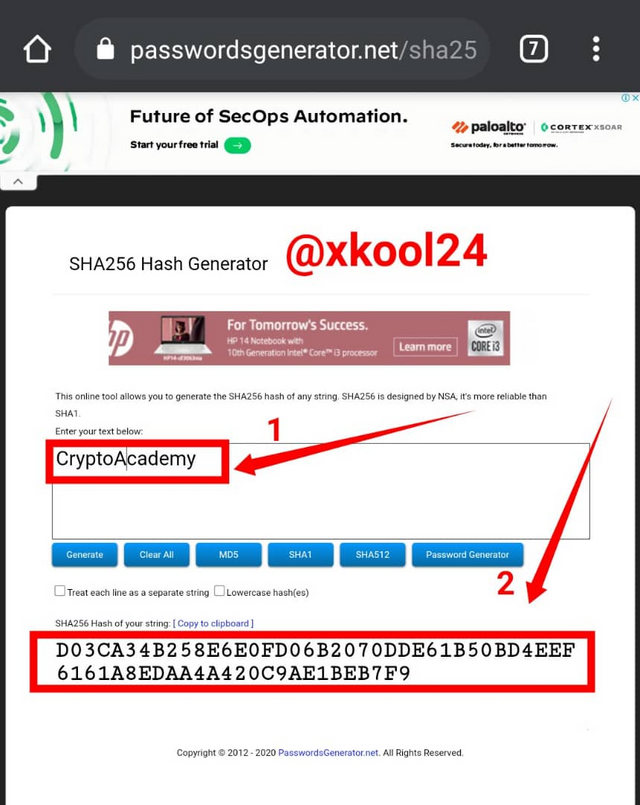
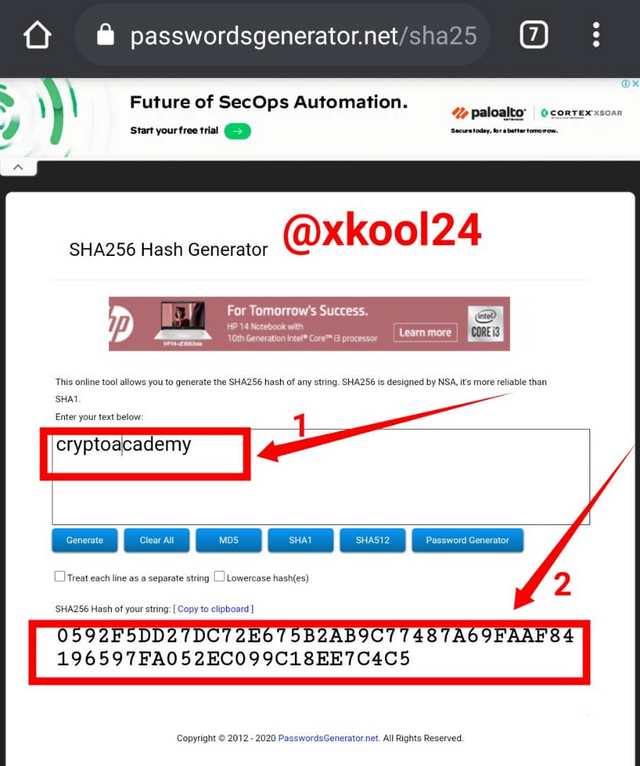
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN THE TWO(2) WORDS
CryptoAcademy: D03CA34B258E6E0FD06B2070DDE61B50BD4EEF6161A8EDAA4A420C9AE1BEB7F9
cryptoacademy: 0592F5DD27DC72E675B2AB9C77487A69FAAF84196597FA052EC099C18EE7C4C5
From the two words, they both meant the same thing but I observe the difference in the Capital Letters (Upper Cases) used for the C in Crypto and A for Academy. Whereas the second word has lower cases all through. These are clear different inputs so far the Hash function is concerned and definitely this would give us different outputs or Hash outcomes. This simply affirms the non-repeatability and uniqueness of the hash functions which sees that all inputs are encoded with a different hash so far they vary in their inputs.
In your own words explain the difference between hash and cryptography.
Cryptography is the science that Hash functions uses to generate its unique and non repeatable codes which is the main stay of the Hash function. Therefore the technology and mechanism behind the effectiveness and efficiency of Hash function is the Cryptography science.
Cryptography is simply that mechanism that basis its primary responsibility is on decrypting and encrypting of data which is geared towards the security of data and information as well as void of malware attacks. This data can only be accessed by the sender or receiver who has the required key, whereas the Hashing functions borrows a leave from the Cryptography with a one-way function that required only the sender to know what inputs generated the hash codes or outputs.
Thank you Prof @pelon53 for your lessons on Hash and Cryptography. This has exposed my in-depth knowledge on why it was the bedrock of cryptocurrency blockchain protocol, given to its highly secured efficient, non reversible and repeatable potentials.
Thank you all.


Pregunta 1: Bien explicada, aunque debe ser más clara la explicación.
Pregunta 2: Veo que no coincide el número de bloques colocado con el que seleccionas, en tronscan. Tú colocas: 31,704,370 y seleccionas: 3170426.
Debes copiar todo el Hash del bloque, ya que, no se puede observar completo.
Pregunta 3: Muy bien explicada.
Pregunta 4: Faltó un poco más de las diferencias.
Recomendaciones:
Explicar con mayor claridad y sencillez los conceptos solicitados. Hacer una conclusión.Calificación: 8.3