Bitcoin's Trajectory - Crypto Academy S4W5 - Homework Post for @imagen
Hello @imagen. Thank you for giving us the opportunity to refresh our knowledge about Bitcoin history and development, consensus mechanisms, PoW and PoS, altcoins.

Question1 : How many times has Bitcoin been "halved"? When is the next expected? What is the current amount that Bitcoin miners receive? Mention at least 2 cryptocurrencies that are or have halved.
| Halving | Release Date |
|---|---|
| First Halving | 28th November, 2012 |
| Second Halving | 9th July, 2016 |
| Third Halving | 11th May, 2020 |
| Fourth Halving | 9th May, 2024 (expected) |
So far, Bitcoin has halved 3 times in total. The next halving is expected on 9th May, 2024.
Before the first halving, miners received 50 BTC as a block reward. This was before 28th November, 2012.
After the first halving on 28th November, 2012, miners received 25 BTC block rewards. That was until the second halving on 9th July 2016.
After the second halving on 9th July 2016, miners received 12.5 BTC block reward. That was until the third halving on May 11th, 2020.
After the third halving on May 11th, 2020, miners receive 6.25 BTC block reward. This will continue until the fourth halving, which is expected to be on 9th May 2024.
After the fourth halving, which is expected to be on 9th May 2024, miners will receive a block reward of 3,125 BTC.
The Verge-XVG has been halved this year. Before the XVG halving on 25th January 2021, the miners were rewarded with 200 XVG, while after the halving, this reward was reduced to 100 XVG.
Ravencoin (RVN), on the other hand, is expected to halve in February next year. After the halving, the block reward will decrease from 5000 RVN to 2500 RVN.
Question2 : What are consensus mechanisms? How do Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Staking differences?
In the blockchain system, information, data and all records are kept and stored on distributed ledgers. However, anyone connecting to the network must agree on the content held on these ledgers. This consensus is provided by the center in central systems. In these systems, all users trust the center.
However, in decentralized systems, such as blockchain, there are different consensus mechanisms for consensus. And still, studies and developments on these systems continue.
In short, consensus mechanisms are the method of doing the consensus work I mentioned above.
PoW - Proof of Work
It is the first decentralized consensus mechanism. Many cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin use Proof of Work.
In this system, there are miners, which we call miners. Using expensive equipment and lots of electricity, miners solve tricky math problems called hashes. In this way, miners contribute to the functioning of the network. They are rewarded for this too.
In a Proof of Work system, adding transactions to the network is very difficult. But it's pretty easy to verify transactions on the network. Anyone who connects to the network can see all transactions previously added to the network.
There is a 51% risk of attack on the Proof of Work system. Someone or a team that has captured 51% of the mining power can make a dubious-fraudulent transaction.
But in major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, it's nearly impossible to capture 51% of the mining power.
Proof of Work is an expensive and very energy consuming method. It also has problems such as long processing time. There are other security problems as well. For these reasons, alternative consensus mechanisms have been developed.
PoS - Proof of Stake
Proof of Stake is a consensus mechanism in which different versions are used in some cryptocurrencies.
When running Proof of Stake, expensive equipment and a lot of electricity are not needed as in Proof of Work.
There are no miners in the Proof of Stake algorithm as in Proof of Work. 'Validators' does the job of adding blocks.
Validators do not receive block rewards and only a 'network fee'.
Validators have to lock an amount of coins called 'Stake' into the network in order to add blocks to the network.
For example, when Ethereum starts using the PoS mechanism, we will have to lock some Ethereum to the network.
The amount of cryptocurrency that needs to be locked is not the same for all cryptocurrencies.
However, if more cryptocurrencies are locked into the network, the network fee to be received from the network will increase as well.
The biggest disadvantage of the Proof of Stake mechanism is that someone who locks few cryptocurrencies into the network will receive very little network fee from the network. This prevents small investors from locking cryptocurrencies into the system.
The higher the amount of cryptocurrencies locked on the network, the more reliable the network. Therefore, it is necessary to make it attractive for small investors to lock cryptocurrencies into the network. This has led to the emergence of different variations of the PoS system. Like DPOS, LPOS.
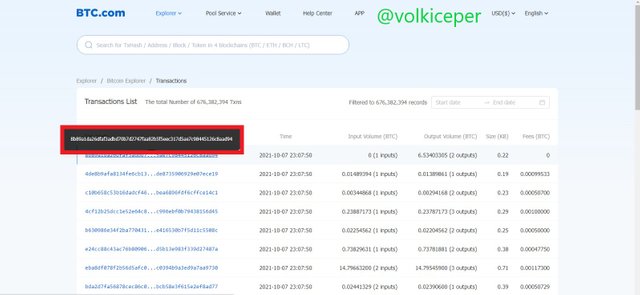
Question3 : Enter the Bitcoin explorer and indicate the hash corresponding to the last transaction. Show Screenshot.
For the answer to this question; I entered the website www.btc.com, which I made a habit of using.
The latest hash at the time (2021-10-07 23:13:30) of writing this article:
59057179907ada2344cc28eeb2a97d0f2d94ba8d0a55f8a0e22997b0bf9051e1
Question4 : What is meant by Altcoin Season? Are we currently in Altcoin Season? When was the last Altcoin Season? Mention and show 2 charts of Altcoins followed by their growth in the most recent Season. Give reasons for your answer.
All coins released after Bitcoin are called altcoins. This includes Etherium.
While it is difficult to answer the question of whether we are in altcoin season, there are some indications for this.
Let's consider the last season of the market. In the last season, 75% of the top 50 coins in the Market should outperform bitcoin.
We experienced the most recent altcoin season from January to April this year. At that time, altcoins gained great volume and value.
By that definition, we are not currently in altcoin season as very few coins have performed well against bitcoin.
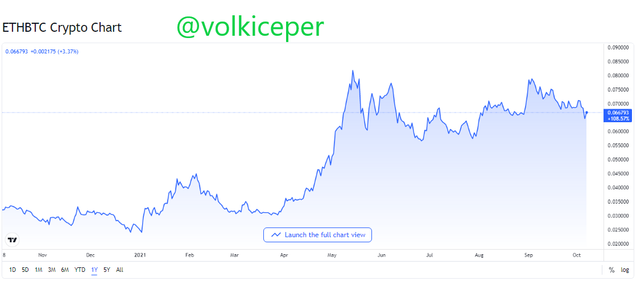
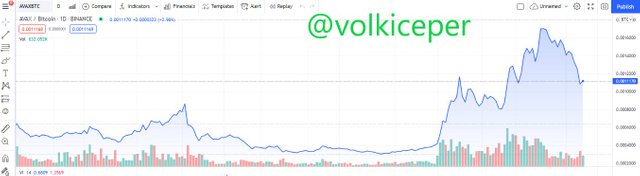
Looking at the charts of Ethereum and Avax cryptocurrencies, I can say that they perform very well against bitcoin.
Question 5 : Make a purchase from your verified account of the exchange of your choice of at least 15 USD in a currency that is not in the top 25 of Coinmarket (SBD, tron or steem are not allowed). Why did you choose this coin? What is the goal or purpose behind this project? Who are its founders / developers? Indicate the currency's ATH and its current price. Reason for your answers. Show Screenshots.
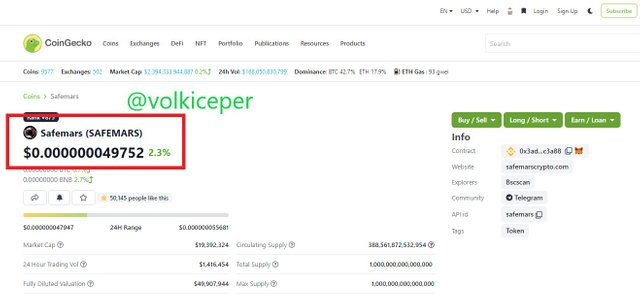
I bought Safemars for a total of $ 36.91 in 2 transactions. Screenshots of both processes are available below.


Below, there is the number of Safemars I have now and the current value of total Safemars I have.

The current value of 1 Safemars coin is $0.000000049752 now.
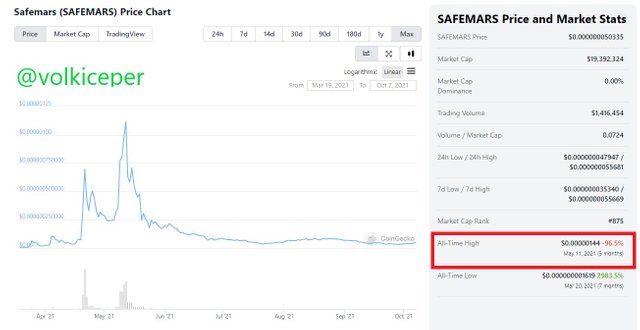
The all time high value of Safemars coin was $0.00000144 at May 11, 2021.
My purpose in buying Safemars was that I could buy a lot of Safemars for a small price.
If its value rises, the potential return will be enormous. If its value does not rise or fall, my loss will be very small as I have already spent so little money.
And, I think the price will increase when the nft staking feature on the roadmap on the Safemars website comes. I think the value of projects that contain NFT supporting elements will increase. I bought Safemars for these reasons.
Conclusion
As a result, we refreshed some of our knowledge in our brains and learned some new information. Thank you @imagen for providing such an opportunity.
I hope safemars gains a lot of value as soon as possible and I will be sp on steemit platform with most of that money.
Gracias por participar en la Cuarta Temporada de la Steemit Crypto Academy.
Continua esforzandote, espero seguir corrigiendo tus asignaciones.
Thank you Prof @imagen :)