CRYPTOACADEMY SEASON3 WEEK2 ASSIGNMENT POST FOR @pelon53 BY @tymes2
INTRODUCTION
Hello steemians, I am very delighted to write my homework post for this week and also using this opportunity to say a very big thank you to prof @pelon53 for this wonderful lecture this week.

Picture DESIGNED by myself

Question number 1
Explain What does collision resistance mean? And what does resistance to preimage mean?
What does the resistance to collision mean?
The collision resistance ; This is to oppose any impact circumstance so on the off chance that we talk around two distinct contributions there won't ever be a crash, an alternate yield should be created however we should comprehend that an impact assault in more intricate terms is "nearly" difficult to accomplish. What happens then we can say that the Collision Resistance is the main property of the hash work. In numerical insights it is practically difficult to get two unique information sources that have a similar yield, hence it tends to be said more or less that this is difficult to occur.
We can also say that crashes can happen after numerous years this is because of experimentation techniques and this happens when two (2) information sources produce a similar hash code, however it can require years. for this to occur, so we can say to be exceptionally clear there is no crash free capacity just that the likelihood that this can happen is incredibly extremely low.
What does preimage resistance mean?
Preimage resistance can be resolved as an essential property of the hash, this is guaranteed on the grounds that the capacity can't be turned around, I imply that when attempting to settle the info beginning from the hash previously produced, it is practically difficult to tackle on the grounds that the more mind boggling it is the higher information will be the protection from the preimage, which shows that it's anything but conceivable to return the yield to the first information just utilizing the yield esteem. this ensures and makes protection from preimage.

Question 2
USE TRONSCAN AND ETHERSCAN TO VERIFY THE HASH OF THE LAST BLOCK AND THE HASH OF THAT TRANSACTION. SCREENSHOT IS REQUIRED FOR CHECKING.
With ETHERSCAN below are the steps to follow in verifying the hash of the last block and the hash of that transaction.
- first of all you can navigate to the etherscan website using this link (https://etherscan.io/)
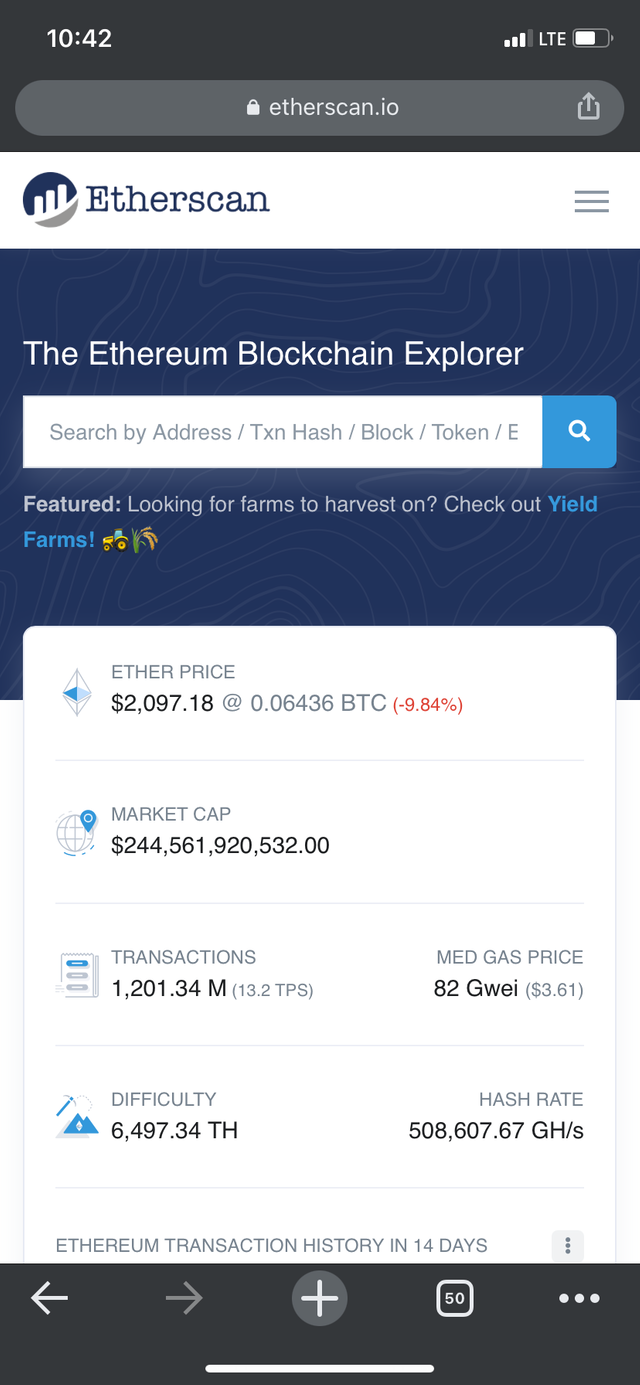
- There are two options available, i.e. Latest blocks and latest transactions.
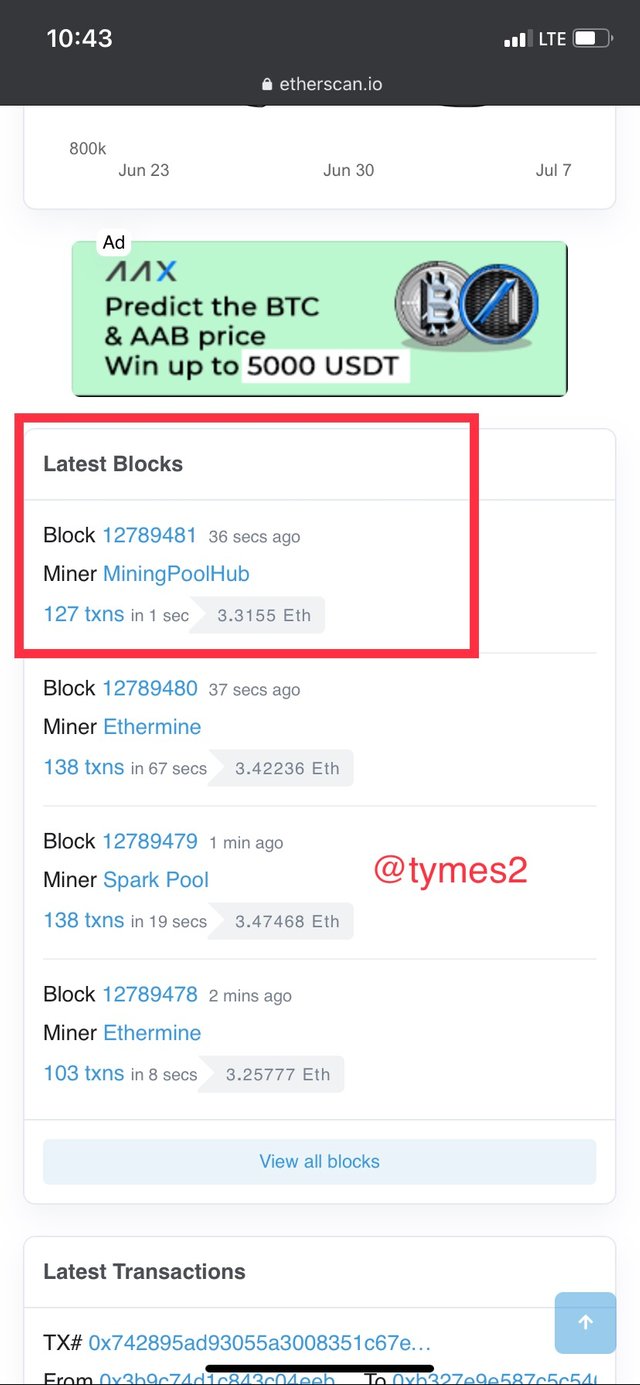
- After clicking on it several details will be showed since we are interested in the hash of that block scroll down and locate the hash.
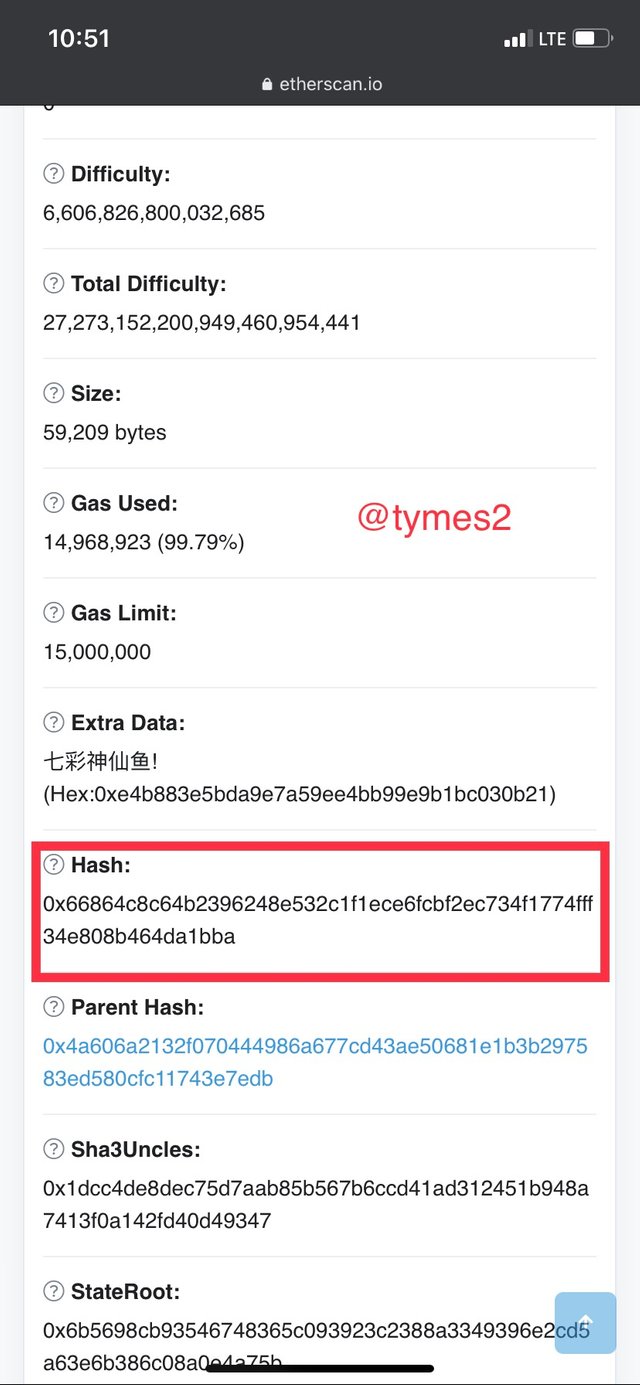
- For the hash of this block we have
0x66864c8c64b2396248e532c1f1ece6fcbf2ec734f1774fff34e808b464da1bba
- Now, if you want to check the transaction hash of that block on that same page scroll up and click on transactions
- click on the first transaction
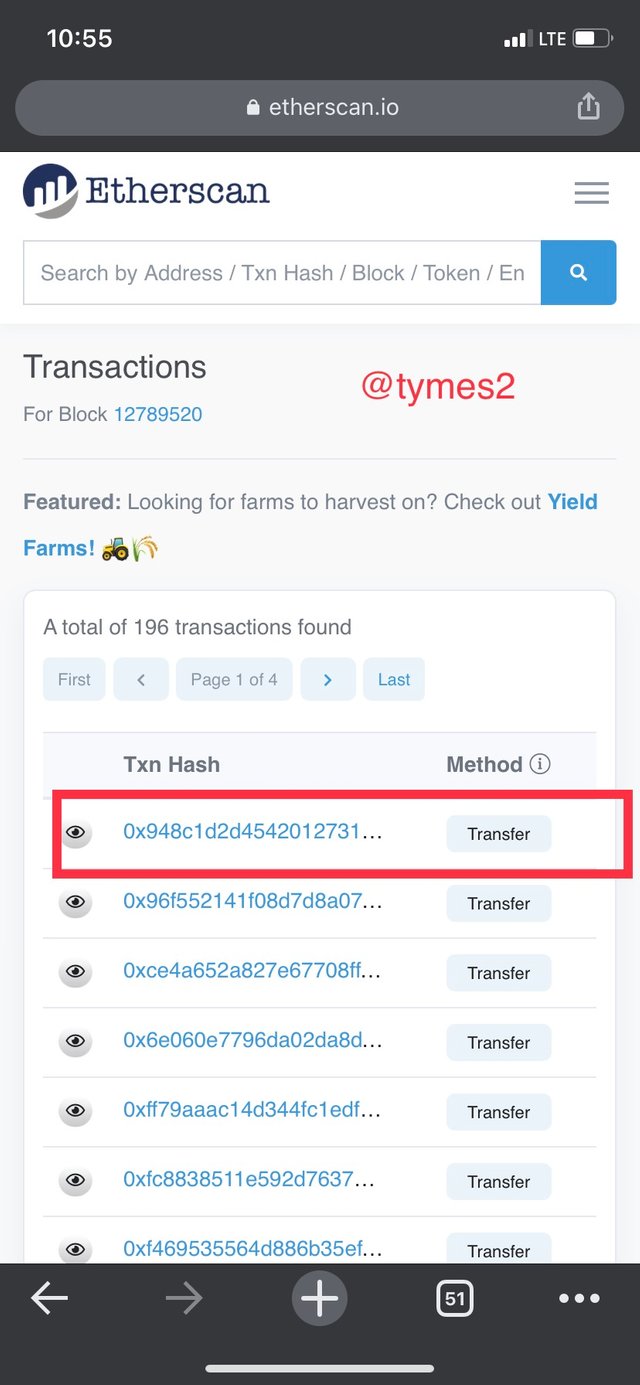
- after you have click one the first transaction, the transaction hash will be shown
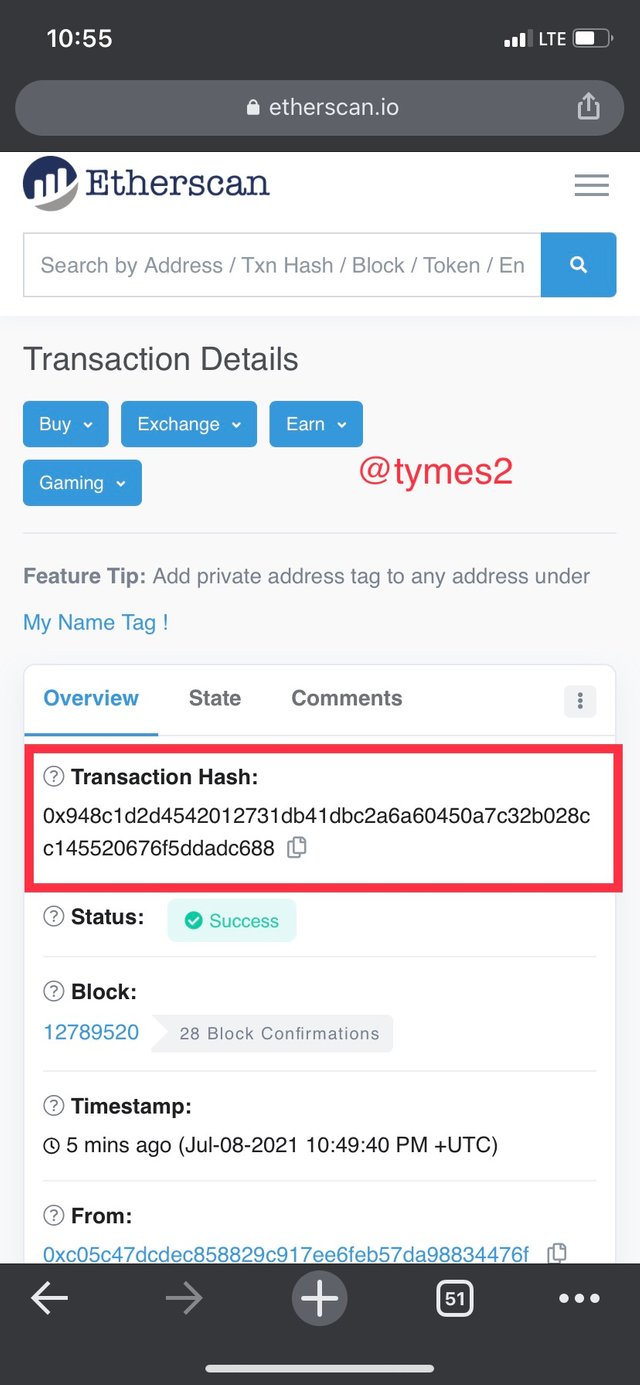
0x948c1d2d4542012731db41dbc2a6a60450a7c32b028cc145520676f5ddadc688
TRONSCAN
Below are the steps one can follow to verify
- Visit their website. And you can do that by using this LINK(https://tronscan.org/#/block/31770718)
- click on the last block to revel its details
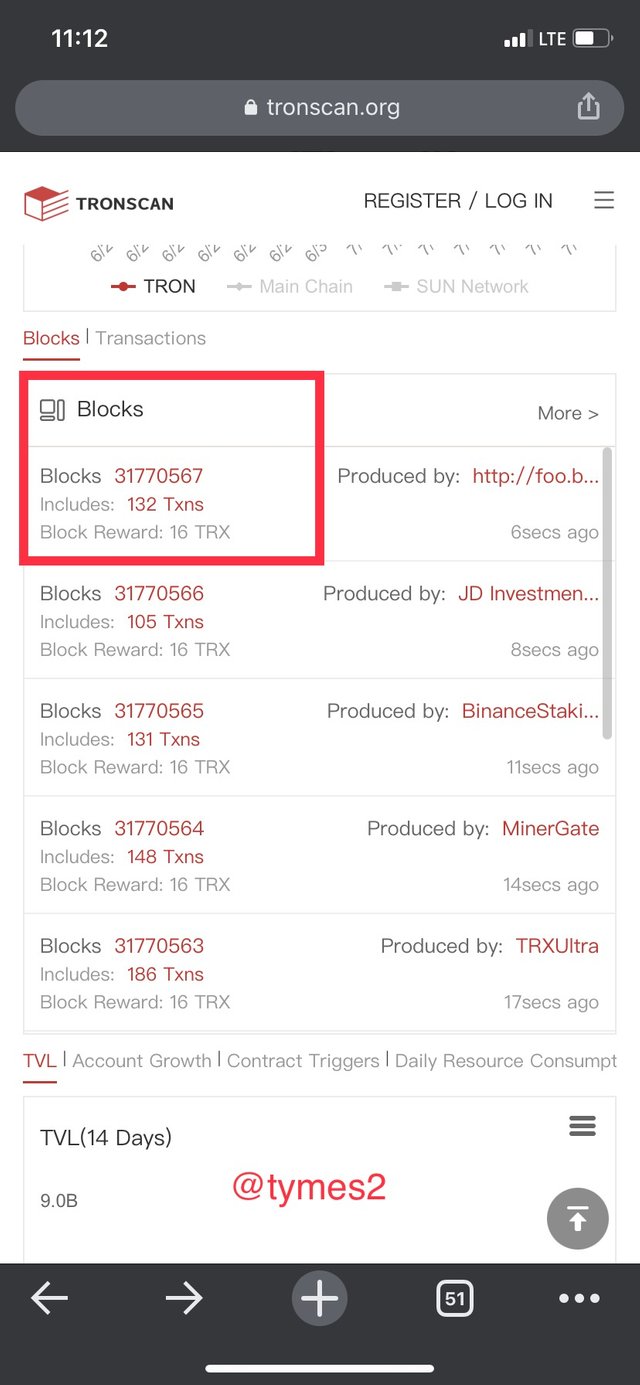
- Just below the block height we can find out block hash which is
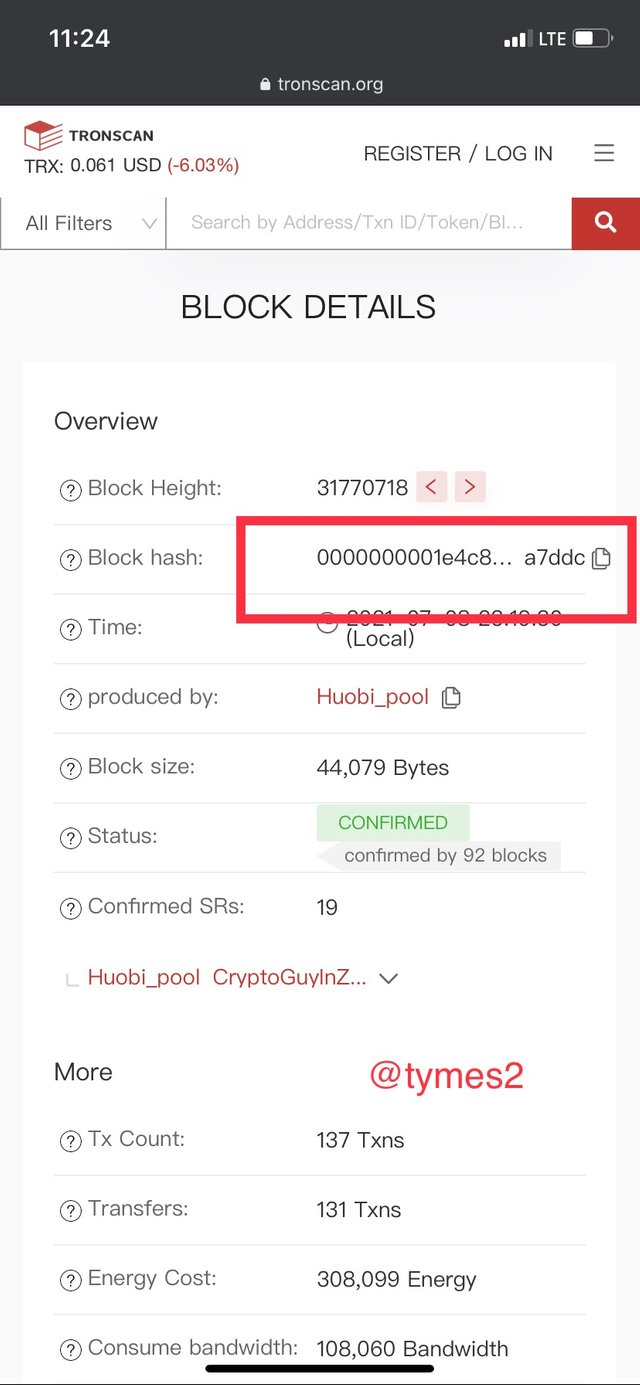
0000000001e4c85e268ae9471fe15f1b5e6771b2dcc6db1de631a4108d7a7ddc
- To find out your transaction hash, still on the same page, scroll down you will see it so you can select the labeled transaction.
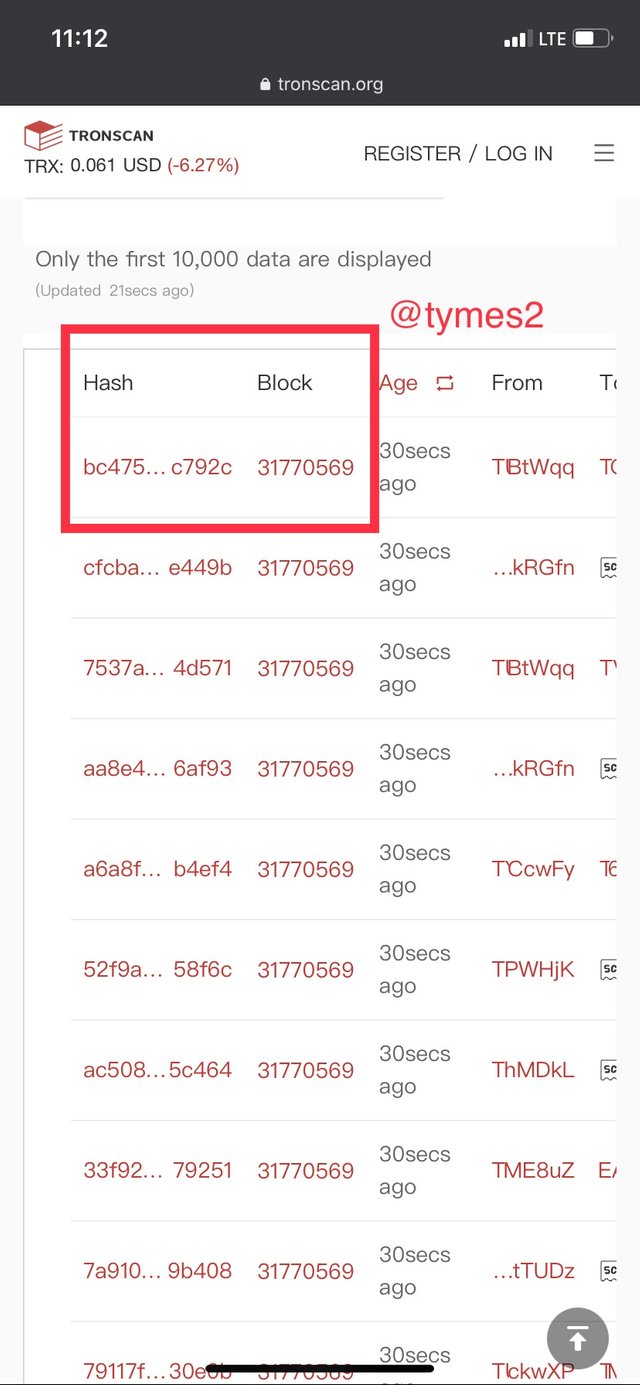
- select the latest block and click on it to view the details
- The transaction hash is first on the details as
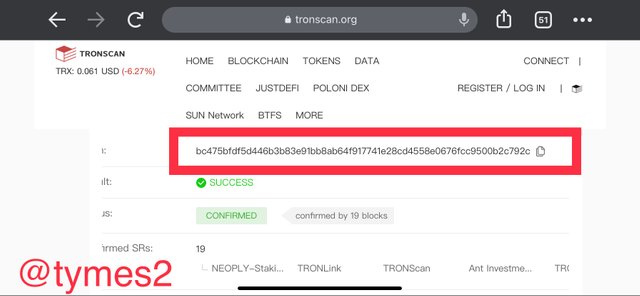
bc475bfdf5d446b3b83e91bb8ab64f917741e28cd4558e0676fcc9500b2c792c

QUESTION 3
To go with this task, you can use this link
- go to this website
(https://passwordsgenerator.net/sha256-hash-generator/)
- type ‘CryptoAcademy’ and click on generate
the hash of the word ‘CryptoAcademy’ is
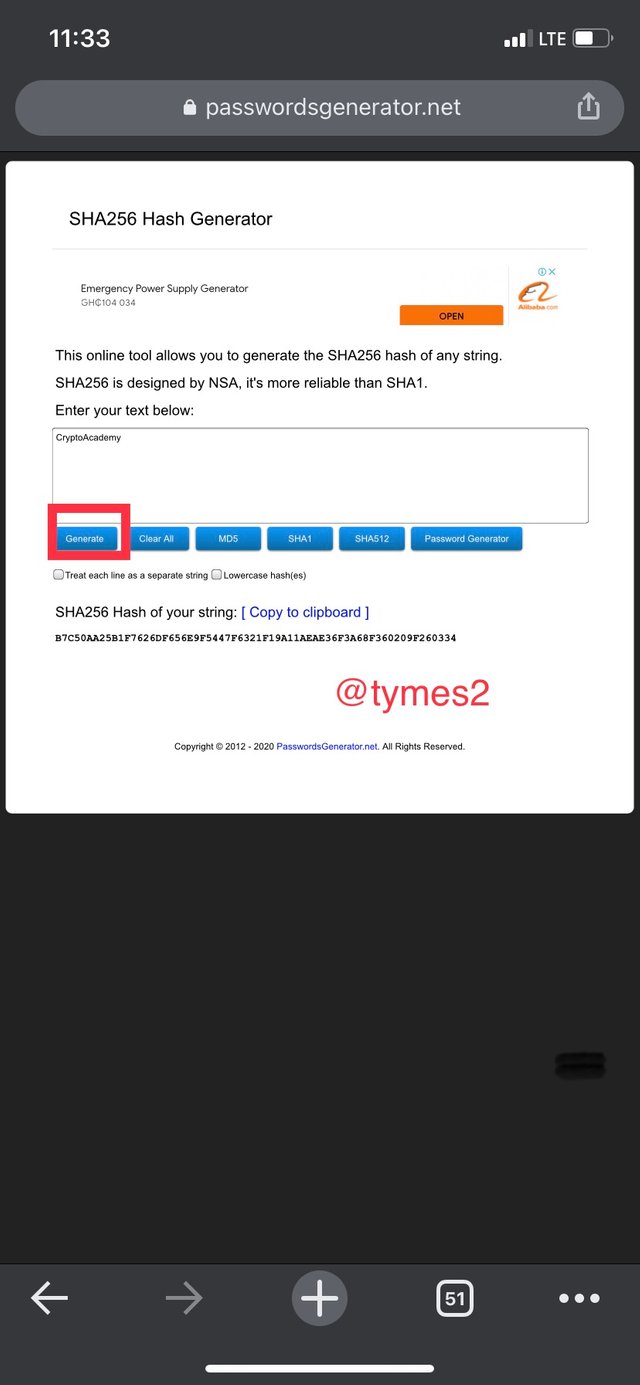
B7C50AA25B1F7626DF656E9F5447F6321F19A11AEAE36F3A68F360209F260334
the second case we will be using
‘cryptoacademy’
- go to this website
(https://passwordsgenerator.net/sha256-hash-generator/)
- type the word ‘cryptoacademy’ and click on generate.
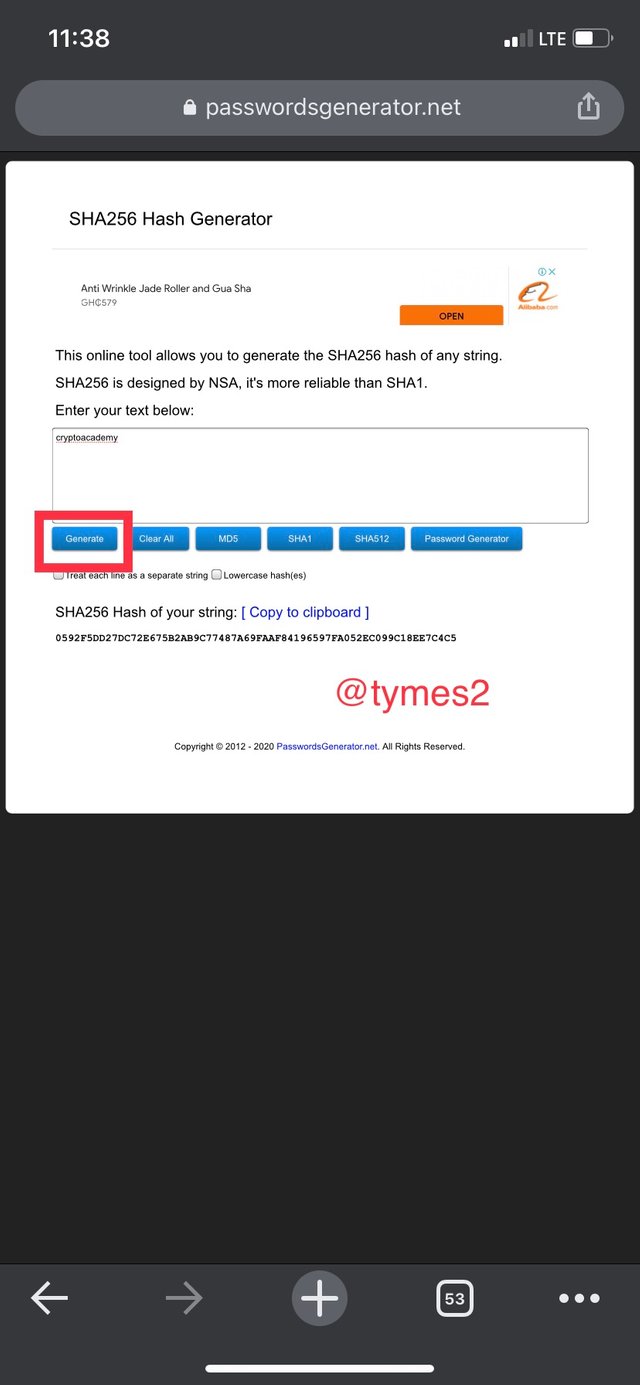
- the hash for the word ‘cryptoacademy’ is
0592F5DD27DC72E675B2AB9C77487A69FAAF84196597FA052EC099C18EE7C4C5
DO YOU SEE ANY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE TWO WORDS? EXPLAIN.
The intelligent clarification for this situation is that these two sources of info don't have a similar substance so they will produce two distinct yields in light of the fact that the SHA-256 is impervious to impact, that is, with a PC that we use today we would never crash as clarified above, it would require millennia to create an impact, this hash work was grown so this impact can't happen in this very nearly two data sources can't produce a yield since it has a high protection from impact.

Question 4
In your own words explain the difference between hashing and cryptography.
What I understand is that the SHA-256 have an extraordinary protection from impact so two distinct information sources will sensibly produce two unique yields despite the fact that they mean exactly the same thing, they are composed in an unexpected way, in other words that sha-256 was created to keep a high protection from crash so a basic processor would require millennia to accomplish an impact so the thing that matters is that in cryptography everything is a hash work, hashes are fixed characters for a hash work.
Cryptography
This is the little I understand about Cryptography:
Does not have Fixed characters
The data encrypted can be reversed.
cryptography uses algorithms like RAS, DES, AES
the size of the encryption code depends on the data
CONCLUSION
Thanks to all for reading and passing by my post. I would like to appreciate the good efforts of prof @pelon53 for this great lecture taught this week.
