Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 4 - Homework Post for [@awesononso]||Blockchain Forks
I wish to thank professor @awesononso for delivering such a lecture.It was an eye opener to me.Permit me to participate in the homework post.

QUESTION ONE
In every human endeavour,there has always been a need for change or improvement.Blockchain team and developers are not left behind.Blockchain is decentralized(not controlled by a central authority) and open source and so people can propose improvement or implement changes.When developers,users or miners of a Blockchain are dissatisfied with how the blockchain works,they can decide to make some changes in the blockchain and continue using it or decide to create a new version.This is known as a Fork.
A Fork is simply a situation where the users of a blockchain makes changes to the software protocol of the blockchain or decide to create a new token altogether.This means that a fork can result in making changes to the blockchain and continue using it...On the other hand,a fork can also involve creation of a new blockchain and new token from the already existing one.
If a fork leads to the creation of a different token,it is called a hard-fork(backward incompatible) but if it involves modify or making changes to the existing token,it is called a soft-fork(backward compatible).

QUESTION TWO
It is a permanent and backward incompatible changes to the software protocol of a blockchain where users upgrade to the new version of the software.When a hard fork takes place,it means that owners of the new version won't accept the old version and vice versa.A hard fork requires all users to upgrade to the new version.A situation where nodes(computer/users) of the new version of the blockchain never accepts the old version of the blockchain.
It is important to note that a hard fork leads to the emergence of a new blockchain.An example is the hard fork that led to the creation of Bitcoin Cash(BCH) from Bitcoin (BTC).In a hard fork,a new token which is different from the token of the old version is created by the new blockchain.
Once a hard-fork has been done,the holders of the new blockchain does recognize the old blockchain.
Basically,once a hard fork is done,the new version does not accept blocks of the old version,rather it sees it as an invalid block.Also the old version does not accept the blocks of the new version,rather it sees it as an invalid block,this is because they now run on different protocols.
However,we have to understand that when a hard fork takes place,the users that migrated to the new version can still hold tokens of the old version.This means that the token balances of old users who joined the new version would still be granted,but miners will only chose whether to continue verifying blocks in the old version or the new one.
An Example of Hard fork
I have already explained a hard fork.Now I want to give an example of a hard fork which is the Bitcoin XT hard fork.
Bitcoin XThard fork has a hard fork aimed at improving and adding new features to the bitcoin blockchain,It was done to increase the number of transaction that Bitcoin can handle in one second,this was proposed to be done by increasing the block size from one(1) megabyte to eight(8) megabyte.This hard fork proposed to make bitcoin network to handle 24 transactions per minutes instead of 7 transactions per second.This hard fork saw the light of the day in the later part of 2015,a situation where over 1000 nodes joined the new unfortunately,this project died off within a few months.

QUESTION THREE
A Soft Fork is another form of fork.It is a backward compatible changes to the software protocol of a blockchain where majority users upgrade to the new version of the software.Unlike the hard fork,all users must not upgrade to the new version,rather a majority of the users.Here the old blocks recognizes the new block as valid.It requires only majority of the miners to agree to upgrade and enforce the new rule.
A soft fork maintains the old blockchain and makes the old the old blocks to accept the new rules.The truth is that there are rules which are in the new block which were not in the previous (old) blocks,but both work in synergy for the improvement of the blockchain.
Example of a Soft Fork
An example of a soft fork is the bitcoin segregate witness(SegWit).Before the SegWit soft fork, bitcoin protocol was very costly and time consuming too.The SegWit soft fork was primarily done to increase the scalability (increase the number of transactions per second)of bitcoin transactions by excluding witness signature on each block so that there would be more space on the block to accommodate more transactions inorder to increase transaction speed.Before the sift fork, signatures takes up to 65% space on the transaction block,so SigWit proposed to remove the signatures from each block inorder to free space for more transaction details,the soft fork also proposed to increase the block size from one 1 Mb to 4 Mb.
The Bitcoin block has a capacity of 1 Mb which may contain around 2700 transaction details plus the signature,by leaving the signature spaces blank,the block can now accommodate more than 2700 transactions due to the spaces created by excluding the signatures.This SegWit was successful in 2017 but it was rejected by some users and so it led to a hard fork that gave birth to Bitcoin Cash (BCH).

QUESTION FOUR
There are some differences between a hard fork and a soft fork.Lets look at them.
| Hard Fork | Soft Fork |
|---|---|
| All nodes must agree and upgrade to the new version | Majority of the users are needed to upgrade to the new version |
| A new token is always created | No new token is created |
| The old and new blockchain treats each others block as an invalid block | Old blocks treats the new blocks as a valid block |
| There is existence of two blockchains in a hard fork | Only one blockchain exist and it is used by both the old and new blocks |

QUESTION FIVE
The Bitcoin Cash(BTC) and Segregated Witness (SegWit) are both Bitcoin Forks that have taken place in history.One of them is a hard fork(backward incompatible) while the other is a soft fork(backward compatible).
Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash is an example of a hard fork.This hard fork was done in 2017 after some members of the bitcoin development committee rejected the Segregate Witness (SegWit).Although the SegWit was done to improve the scalability and to increase the size of the bitcoin block,some members still never wanted its protocol and so they opted for the Bitcoin Cash protocol.
The Bitcoin cash created its own token which is called Bitcoin Cash(BTC). Bitcoin Cash has remained the most successful Bitcoin fork in history because it has maintained its Blockchain and has always remained in the top 15 ranking of digital currencies.
This Bitcoin Cash hard fork has help to improve transaction speed and scalability of bitcoin,it allows blocks of eight megabytes.
To find Out if Bitcoin Cash is a Hard Fork
Kindly visit Bitcoin Explorer to see the first ever block on the Bitcoin(BTC) Blockchain.You will notice that the first block was mined on 03-01-2009 at exactly 19:15
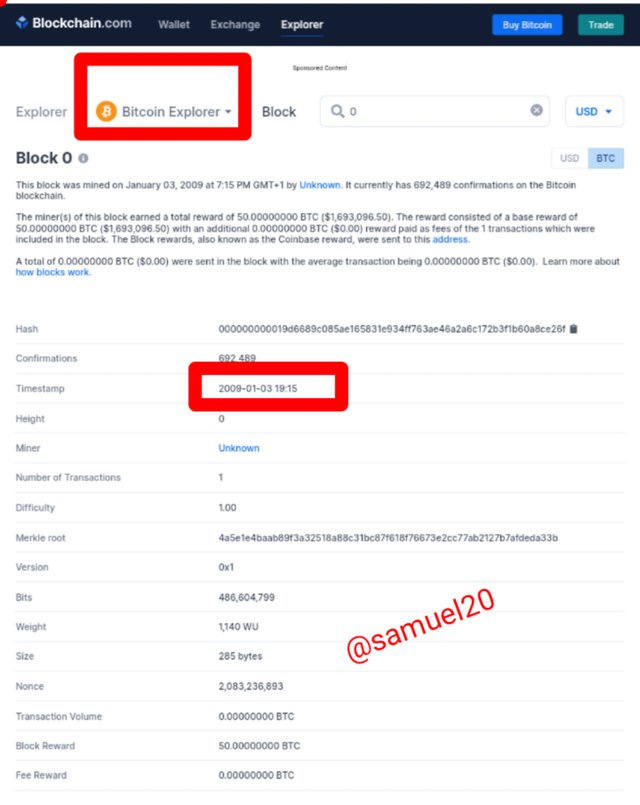
Also visit Bitcoin Cash Explorer to see the first ever transaction on the BCH blockchain.You will notice that it has the exact date and time when compared to the Bitcoin first block transaction.
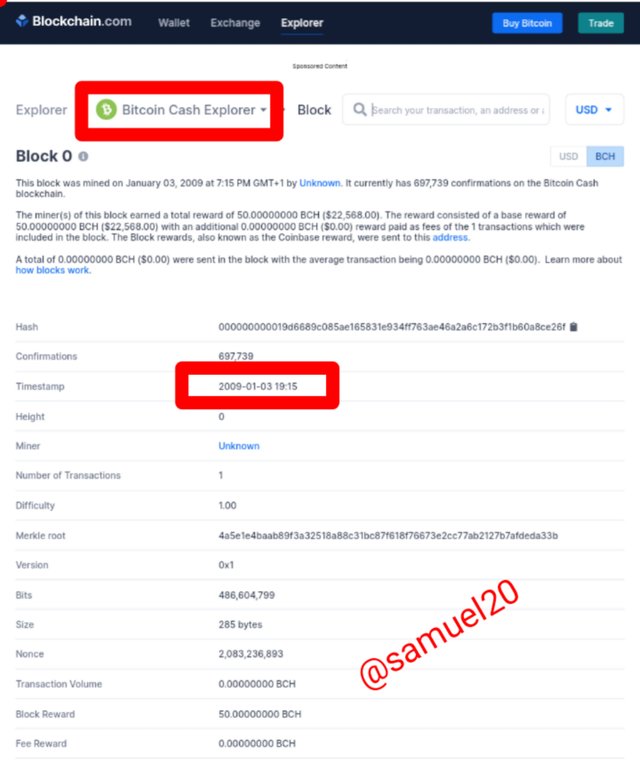
The fact that both the Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash Genesis has the same date and time,which means that Bitcoin Cash was a hard fork of Bitcoin blockchain.

Segregate Witness (SegWit)
SegWit is a bitcoin soft fork.It was an upgrade made on the bitcoin protocol inorder to increase the transaction speed and reduce the cost of bitcoin transactions.Before the SegWit fork,every block in the bitcoin block carries a signature which occupies almost majority of the space on the blockchain,thus allowing only a few details of the transaction.This lead to slow transactions and queue.
Inorder to solve this problem,the SegWit upgrade now removed the signatures from each block so that the space would be used to accommodate more transactions.
Sadly,some of the developers never loved this upgrade and so they created a hard fork that gave birth to Bitcoin Cash.

QUESTION SIX
Steem blockchain is a decentralized blockchain which operates on the Consensus Mechanism called Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).In this Consensus Mechanism,the vote a delegate of their choice who will verify transactions.The delegate with the highest support is qualified or selected to validate the block and the the reward is shared among all the users that voted that particular delegate.
Hive blockchain was a hard fork on the Steem blockchain,it took place because Steem blockchain integrated Tron to its protocol and so some Witnesses and users rejected the integration and created a hard fork that gave birth to Hive blockchain.
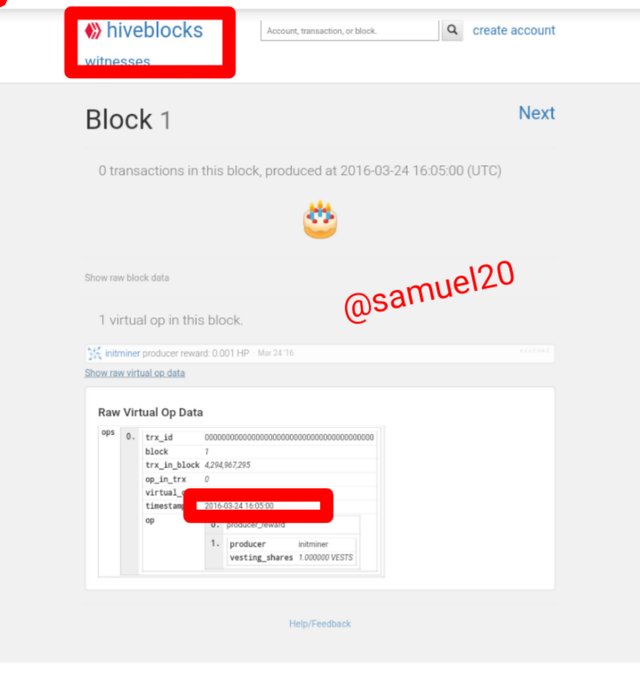
Hive blocks now treats Steem blocks at invalid transactions.It is important to note that Hive Genesis block has the same date as the Steem Genesis Block.This shows that Hive blockchain is a hard fork of Steem blockchain.
Just as Steem blockchain has its native token called Steem,a locked form called Steem Power plus Steem Backed Dollar(SBD).Similarly,
Hive now has its own token called Hive,a locked firm called Hive Power plus Hive Backed Dollar(HBD).
The both blockchains have the same date for their Genesis Block which is 24-03-2016.

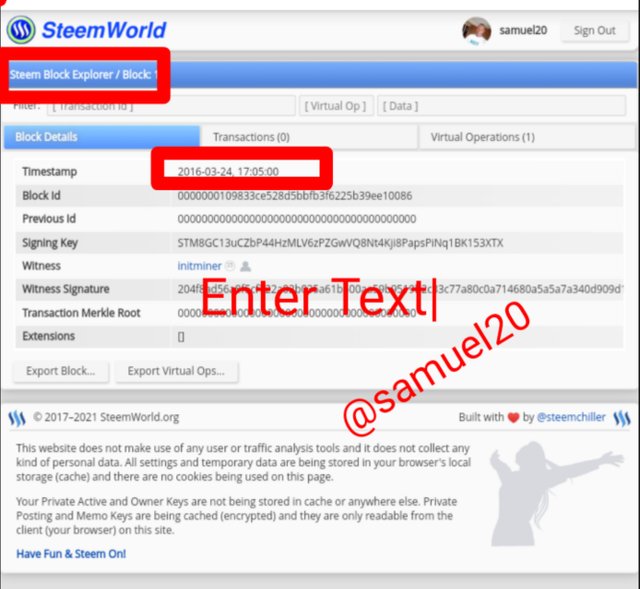
Here is the Steem Genesis Block.You will see that the date is 24-03-2016 and the transaction time is 17:05
Kindly visit the link Steem Genesis Block

Here is the Hive Genesis Block.You will see that the date is 24-03-2016 and the transaction time is 16:05.Almost the same as that of Steem block.This shows that Hive blockchain is a hard fork of Steem blockchain.
•Kindly visit Hive Genesis Block
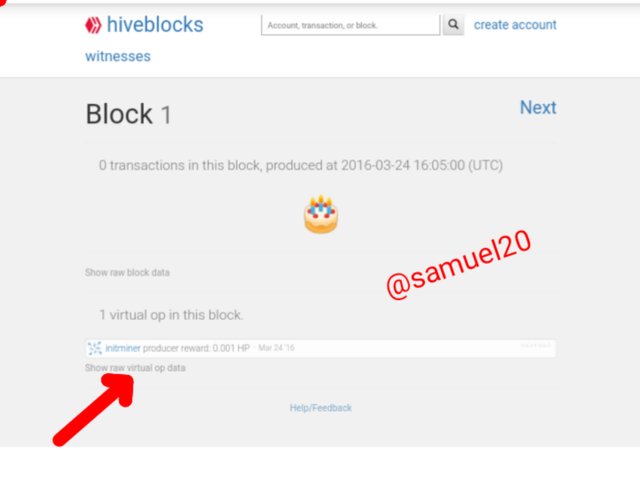

•Click on Show raw virtual op data.

CONCLUSION
A fork is simply a way to upgrade the protocols of a blockchain so that it would be more efficient and effective.Some forks(hard fork) leads to the creation a different blockchain while some forks(soft fork) upgrades the existing blockchain.
.jpeg)
Remember to verify my post prof @awesononso