Bitcoin's Trajectory - Crypto Academy S4W5 - Homework Post for @imagen

Source: canva.com
It is always a pleasure to read @imagen posts because they have been very beneficial for me when it comes to a basic understanding of cryptocurrency and the complexities surrounding it. Hope to contribute the limited knowledge that I came across during the course of research of this assignment in the most coherent manner possible.
Question number 1
How many times has Bitcoin been "halved"? When is the next expected? What is the current amount that Bitcoin miners receive? Mention at least 2 cryptocurrencies that are or have halved.
Bitcoin halving

Source: euronews.com
Ever since it was created in 2008 by an anonymous cryptographer known by the alias of Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin (BTC) has bewildered traditional stock market investors. Scarcity lies at the very core of Bitcoin. There will only ever be 21 million Bitcoins minted. The bulk of the supply has already been created 18.7 million, with the remainder to be mined until the year 2140.
The process of mining involves wrapping up a 1 megabyte’s worth of transactions into a block and accumulating the transaction fee; an associated “block reward” is unlocked with every new block. Block rewards are how new Bitcoins are minted. Blocks are created roughly after every 10 minutes, and this will continue as long as the miners are willing to process transactions to earn transaction fees and block rewards.
Block rewards started out at 50 BTC per block. Every 210,000 blocks (roughly every 4 years) the block reward gets cut in half. This is referred to as “The Halving” On November 28, 2012, the block reward was cut to 25 BTC per block. On July 9, 2016, the block reward was cut in half again to 12.5 BTC per block. And finally, on May 11, 2020, the latest halving of the block reward occurred. The current block reward is 6.25 BTC per block meaning they are getting 6.25 BTC for mining bitcoin with their computing power. The next halving will occur on the 26th of March 2024, when the block reward will be reduced to 3.125 meaning the miners will be getting 3.125 BTC for mining one block.
Litecoin

Source: blockgeeks.com
Litecoins halvings are similar to that of bitcoin. Litecoin is created when miners add new transactions to blocks. The miner who added the block receives a certain amount of Litecoins as a reward for doing that. This amount consists of a fixed number of new Litecoins and transaction fees included in the block. Unlike the Bitcoin network, where new blocks are added approximately every 10 minutes, on the Litecoin network, blocks are added a little faster. Once roughly every 2.5 minutes. After every 840,000 blocks are mined, the block reward is halved. Considering the average block mining rate of 2.5 minutes, this occurs approximately once every 4 years. This event is called Litecoin block reward halving or simply Litecoin halving, and it's pre-programmed in the Litecoin algorithm. When Litecoin was launched, the block reward was 50 LTC. Now, after two halvings, the Litecoin block reward to the miner is 12.5 LTC. The next LTC halving will take place on 6th August 2023. During that event, the block reward to miners will drop to 6.25 LTC.
Z cash

Source: marketcheasier
Next on the list of halve coins is the ZEC coin pronounce as Zee cash, which is another hard fork of Bitcoin. It was initially launched in October 2016 to provide enhanced privacy for the users.ZEC transactions are verified without sharing details like amount, sender, and receiver identifications. Like Bitcoin, this coin halves every 4 years and its maximum supply is 21 million ZEC. The first halving event of 2020 removed the Founders Reward. Also, block rewards were reduced from 6.25 ZEC to 3.125 ZEC. The next halving will further reduce Zcash miners’ block reward to 1.5625 ZEC and will occur at some point in 2024.

Question number 2
What are consensus mechanisms? How do Proof-of-Work and Proof-of-Staking differ?
Many of the blockchains we witness these days have a lot of things in common and operate in similar ways, but one of the ways, how blockchains can be distinctive is the way consensus or in simple words agreement is reached. Which transactions are legitimate and which transactions are added to the blockchain?
Blockchains do this using various consensus mechanisms. Consensus mechanisms are protocols that make sure all nodes (device on the blockchain that maintains the blockchain and (sometimes) processes transactions) are in harmony with each other and agree on which transactions are legitimate and are added to the blockchain. These consensus mechanisms are crucial for a blockchain to operate correctly. They make sure everyone uses the same blockchain. Everyone can submit things to be added to the blockchain, so it’s necessary that all transactions are continuously checked and that the blockchain is always audited by all nodes. Without a good consensus mechanism, blockchains are at risk of various attacks. There are many ways to reach a consensus. Two of the widely used consenses mechanism widely used are proof of work (POW) and proof of stake (POS).
Proof of work

Source: alexlwitt.medium.com
Proof Of Work (POW) is the first blockchain consensus mechanism and was and is still used by Bitcoin. Many cryptocurrencies have followed Bitcoin’s example and have also adopted this consensus mechanism. The Proof Of Work process is known as mining and the nodes are known as miners. Miners solve complex mathematical puzzles which require a lot of computational power. The first one to solve the puzzle gets to create a block and receives a reward for creating a block. These mathematical problems carry some interesting properties. First of all, they are disproportionate, meaning it takes a lot of time to find the answer, yet it’s easy to prove if an answer is correct. Secondly, the only way to solve these puzzles is to ‘guess’ the answer. It is not possible to solve the puzzles quicker using any other method than trial and error. This also means that if one wants to find the solution to the puzzle faster, they would need more computational power, which can get very costly.
Lastly, the difficulty of these problems changes depending on how fast blocks are mined. To maintain a consistent supply of new coins, blocks have to be created within a certain time frame which is roughly 10 min in the case of bitcoin. If blocks are created too fast, the problems get harder, and if they are created too slow, the problems get easier
Proof of stakes

Source: medium.com
Proof Of Stake (POS) is the more environmentally friendly alternative of the Proof Of Work consensus mechanism. Proof Of Stake makes use of the foundation that those whosoever own most coins in a network have a bestowed interest in keeping the network maintained and the value of it is the value of the coin goes up the ladder.
In a system that uses Proof Of Stake, a randomized process is used to determine who gets to produce the next block. Users can stake their tokens to become a validator (someone who can produce blocks), which means they lock their tokens up for a certain time. After doing so they are eligible to produce blocks. The process that decides who gets to produce the next block takes a couple of dynamics into account, what are these dynamics is dependent on the design of the blockchain, but in general, the person who has the biggest stake has the highest chance to produce a block. An example of another critical aspect that can be taken into account is how long the coins have been staked. Validators are also rewarded for their work. The reward that the validator receives for creating the next block depends on the design of the blockchain yet again. Usually, they either receive all, or part of, all the transaction fees of all the transactions in the block they created, or they receive a fixed amount of coins (generated through inflation). Proof Of Stake is not only much more energy-efficient than the Proof Of Work system, but it also has another major distinction. In a Proof Of Work system, a miner may own none of the coins they are mining, meaning they only seek to maximize their profits without actually improving the network but in a Proof Of Stake consensus mechanism system, validators have a much bigger incentive to maintain the network as they hold the coins of the blockchain on which they are validating.

Question 3
Enter the Bitcoin explorer and indicate the hash corresponding to the last transaction. Show Screenshot.
To get the answer to this, I choose to visit the blockchain.com. The website indicates different metrics of bitcoin such as price and latest transaction etc. To get the latest transaction hash I click on the latest transaction hash option displayed in the bottom right of the screen.
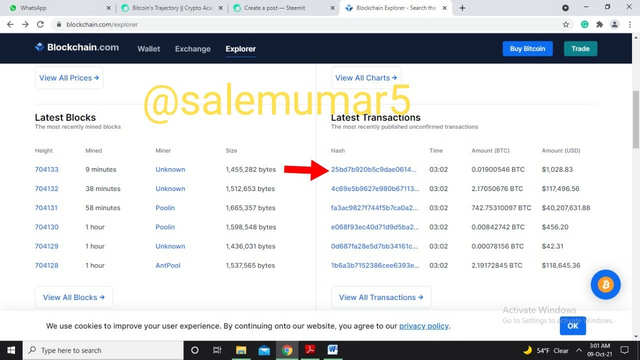
Source: blockchain.com
The option will land us on the further breakdown of the information of the hash 25bd7b920b5c9dae061471083b4ff4816fd99063b11f90abd681f101c59edd43 This transaction was of 0.01900546 BTC and the fees of it was 0.00001040 BTC. This transaction was first broadcast to the Bitcoin network on October 09, 2021 at 3:02 AM GMT+5. The transaction is currently unconfirmed by the network at the time of writing this post. At the time of this transaction, 0.01900546 BTC was sent with a value of $1,028.83 as shown in the below picture.
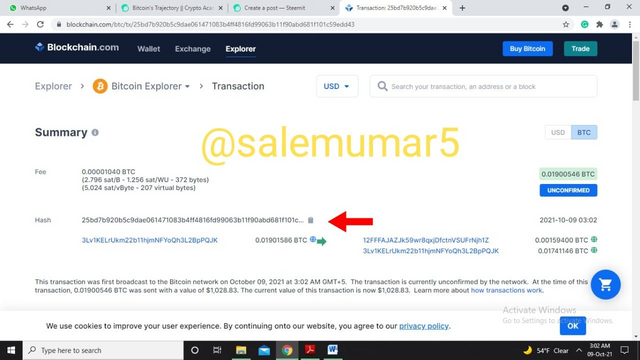
Source: blockchain.com

Question number 4
What is meant by Altcoin Season? Are we currently in Altcoin Season? When was the last Altcoin Season? Mention and show 2 charts of Altcoins followed by their growth in the most recent Season. Give reasons for your answer.
Altcoins are cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin. They share similar characteristics with Bitcoin that is they store and transfer monetary value but are also different in other ways such as they carry smart contracts on their blockchain. Some altcoins use a different consensus mechanism either proof of work (POW) or proof of stake (POS) to produce blocks or validate transactions. As of October 2021, there are over 12,000 cryptocurrencies. According to CoinMarketCap, altcoins accounted for nearly 60% of the total cryptocurrency market in October 2021 because they are derived from Bitcoin, altcoin price movements tend to follow Bitcoin's trajectory.
There is no perfect indicator of an incoming alt-season. However, Blockchain Center provides a tool for assessing market sentiment and determining whether the market is in Bitcoin or alt-season. The website follows metrics that if 75% of the Top 50 coins performed better than Bitcoin over the last season 90 days it is Altcoin Season. The below screenshot indicates that currently, we are not in the altcoin season and bitcoin has been dominating over them.
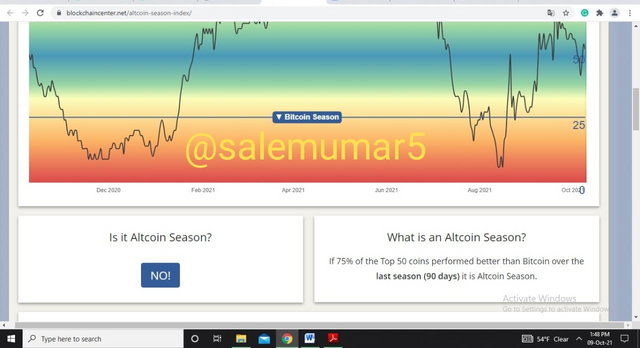
Source: blockchaincenter.net
Perhaps the longest alt-season to date is the one we have previously witnessed from December 2020 to April 2021. It follows nearly the same pattern as 2018’s altcoin season, with many new coins launching and hitting record highs in a matter of weeks and months. From a historical 70% dominance, Bitcoin’s dominance levels at that time dip below 50% further elevating the dominance of the altcoin over bitcoin. Below chart depict the start of the last altcoin season in December 2020. This shows that at the the start of the season the total market cap of the altcoin was at $221,830,134,316.
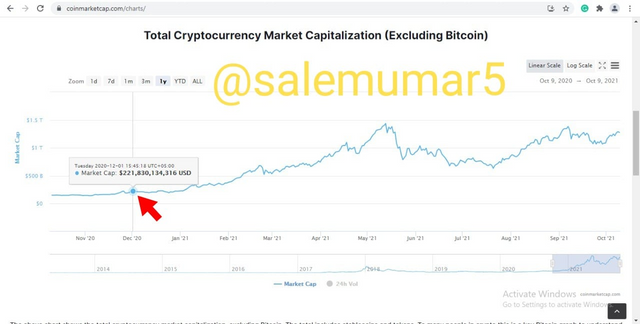
Source: coinmarketcap.com
When the altcoin season came to its end in April 2021, the total market cap of all the alt coin was at $1,104,277,391,214 which was an increase of 398% when the season was started in December 2020 as shown in the below screenshot.
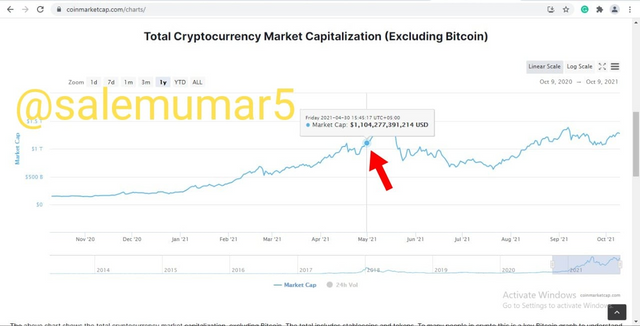
Source: coinmarketcap.com
This can further be substantiated by the example of the following altcoins.
Polygon
At the start of the season in December 2020, polygon which is currently at 21 in the coinmarketcap, the price of polygon was at $0.01872 as shown in the below screenshot
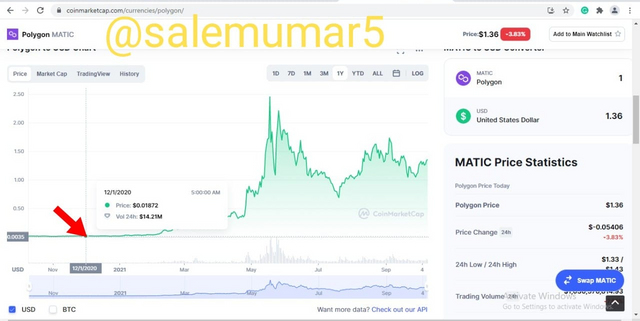
Source: coinmarketcap.com
By the end of the season the polygon enjoyed a astronomical rise in its price and came to point of $0.8206 which is a rise of 4,283% as shown in the below screenshot.
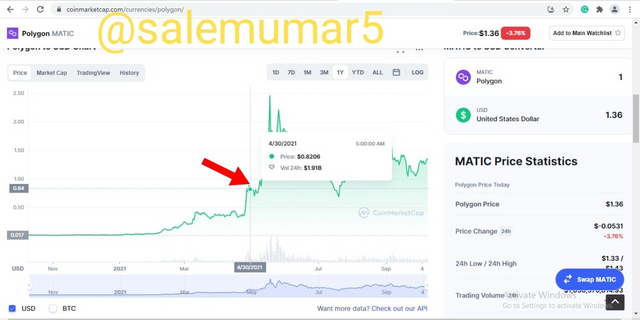
Source: coinmarketcap.com
Vechain
Vechain which is at the position of 27 on coinmarketcap, also follows the same trajectory of abnormal rise thanks to the altcoin season of the dec 2020 in which it price was initially recorded at $0.01476 as evident from the below picture.
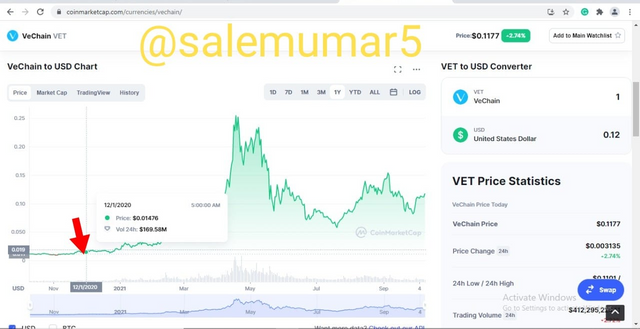
Source: coinmarketcap.com
Then by the end of the season the price of the Vechain stood rock solid at the price of $0.2011 which was a rise of 1,262% from its initial price recorded at the start of the season as visible from the below screen shot.
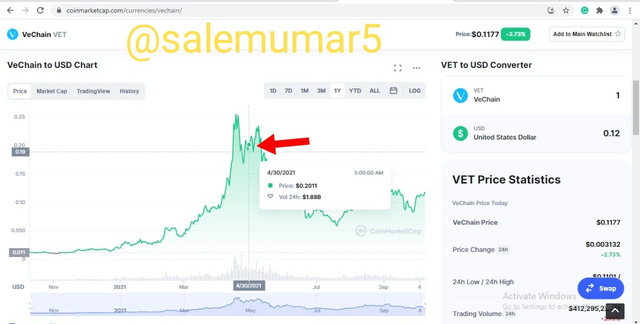
Source: coinmarketcap.com

Question number 5
Make a purchase from your verified account of the exchange of your choice of at least 15 USD in a currency that is not in the top 25 of Coinmarket (SBD, tron or steem are not allowed). Why did you choose this coin? What is the goal or purpose behind this project? Who are its founders / developers? Indicate the currency's ATH and its current price. Reason for your answers. Show Screenshots.
To answer this I tend to bought EOS (Electro-Optical System) coin from my binance account.
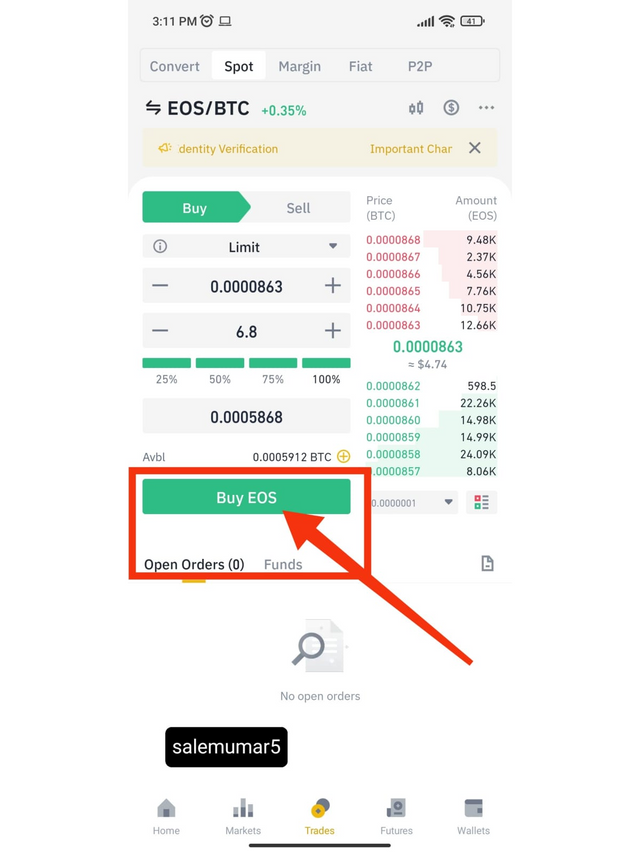
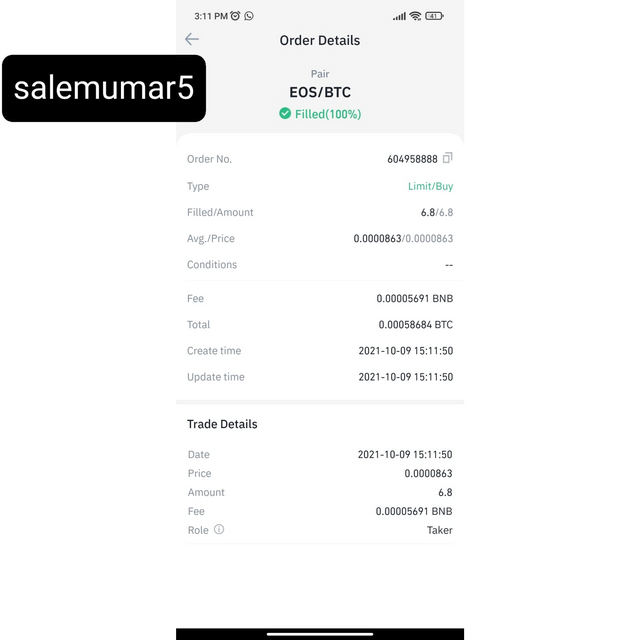
because of the wide range of utility that the EOS coin offered and to me it seems to return good amount on investment if it ts done for the longer period. Other reason of choose this coin is that it is a blockchain-based, fully decentralized network that enables the development, accommodating, and implementation of commercial-scale decentralized applications or commonly known as a smart contract.EOS main goal is to supports all of the core functionality required to allow businesses and individuals to create these apps in a way that is nearly identical to how traditional web applications are created. EOS can provide secure access and authentication, data hosting, usage management, permissions, and communication between dApps and the internet in a much more efficient way than any coin can do. EOS holders can lock or stake their tokens to participate in various processes. The users that stake EOS can vote and carry out decisions to alter the software’s rules, or participate in the blockchain validation process. The EOS protocol was founded in 2017 by a company called Block.one. The company was led by Dan Larimer but is now led by Brendan Blumer.

Source: bytemaster.medium.com

Source: en.wikipedia.org
EOS reached its all time highest of $19.21 on may 5, 2018 as seen in the below screenshot.
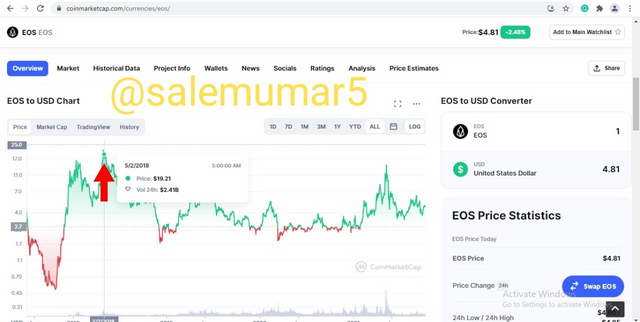
Source: coinmarketcap.com
Whereas the current price of the EOS at the time of writting this post is hovering at $4.80 as seen in the below screenshot
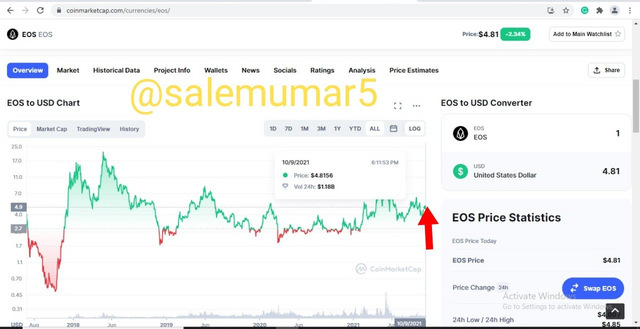
Source: coinmarketcap.com

Conclusion
The emergence of Bitcoin has sparked a debate about its future and that of other cryptocurrencies that have been competing with it. Despite Bitcoin’s recent issues with high transaction fees, its success since its 2009 launch has inspired the creation of alternative cryptocurrencies (altcoin) such as Etherium, Litecoin, and Ripple. A cryptocurrency that aspires to become part of the mainstream financial system would have to satisfy very different criteria. While that possibility looks remote, there is little doubt that Bitcoin’s success or failure in dealing with the challenges it faces may determine the fortunes of other cryptocurrencies in the years ahead. The current state of affairs in the altcoin markets is unlikely to consolidate into a single cryptocurrency. But it is also likely that a majority of the altcoins listed in crypto markets will not survive. The altcoin market will blend around a bunch of altcoins those with strong utility and use cases that will dominate the markets. For investors looking to diversify within crypto markets and to whom the high price of bitcoin seems too high, altcoins are an inexpensive way to expand their horizons beyond Bitcoin. Rallies in cryptocurrency markets have produced returns that are multiples of those produced by Bitcoin. But there are risks involved in altcoin investing, not least of which is the absence of regulation. The maturation of cryptocurrency markets will likely bring more intricacy and capital into the industry, paving the way for rules and regulation-making them less volatile

Este Post contiene Contenido Plagiado
Fuentes:
CC: @sapwood
Total | 0/10