SEC S17-W1 || Steem blockchain Sequencers
 |
|---|
INTRODUCTION |
Greetings everyone and welcome to my entry for this week's engagement topic as we look into the topic STEEM Blockchain Sequencer. In this publication, we will be exploring the ins and outs of how STEEM Blockchain Sequencer works, and what it is all about. So, get a seat and a chilled cup of water to step it down, like always, I hope you get to learn something new.
What are the main building blocks of a blockchain and how does the process of sequencing transactions work in a blockchain network? |
|---|
Let's say we have a notebook that we can write in and once something is written in this notebook, it can't be changed or erased. Now, let's say we use this notebook to keep track of all the money you owe each other.
Every time someone owes you money or you owe someone else money, you write it down in the notebook and since no one can change what's written, it creates a permanent record of all our transactions. This notebook is like a blockchain.
Therefore, a blockchain is a digital version of this notebook with a special kind of technology that allows people to keep a secure and unchangeable record of transactions but then to lessen the burden and make it add for anyone to temper with the records, instead of just one notebook, there are many copies of the same notebook stored on different computers all over the world (nodes) making it super secure and trustworthy.
So, every time a new transaction happens, it gets added to the notebook of each computer by creating a new "block" of information and each new block created is connected to the previous one, forming a "chain" of blocks, hence the name "BLOCKCHAIN".
Therefore, a blockchain is a digital ledger (record book) that is shared and stored on many computers and it is used to keep permanent records of transactions that can not be changed or tampered with.
Now, knowing what Blockchain is all about, the main building blocks (features) of blockchain include;
Transactions:
These are like the individual actions or events that happen on a blockchain. It could be something like buying or selling a digital asset, or even just transferring information.
Blocks:
Think of blocks as containers that hold a bunch of transactions. They're like pages in a book where the transactions are recorded. Each block has a unique identifier and contains a list of transactions.
Chain:
The blocks are connected to each other in a specific order, forming a chain. Each block has a reference to the previous block, which creates a link between them. This helps maintain the integrity and order of the transactions.
Node:
A node is indeed a fundamental building block of a blockchain network. Just as bricks are used to build a strong wall, nodes are the individual computers or devices that come together to form the blockchain network with each node having a copy of the entire blockchain and participates in the validation and verification of transactions making it a team effort, as all the nodes work together to maintain the security, transparency, and integrity of the blockchain.
Hashing:
This is the process of converting the transactions in a block into a unique identifier, or hash. Hashing ensures that the data in the block is tamper-proof and cannot be manipulated without being detected.
Consensus:
This is the way that all the computers in the network agree on which transactions are valid and should be added to the blockchain. It's like a group decision-making process to ensure everyone is on the same page.
Decentralization:
Unlike traditional systems where there's one central authority controlling everything, a blockchain is decentralized. This means that the power and control are spread across many computers called nodes. It helps make the system more secure and less prone to manipulation.
Distributed ledger:
The blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that is shared among all participants in the network. Each participant has a copy of the entire blockchain, which is updated in real-time as new blocks are added
Cryptography:
Blockchain uses fancy math called cryptography to secure the transactions and ensure they can't be tampered with. It involves complex algorithms and keys to protect the data and make it super secure.
Mining:
In some blockchains, like Bitcoin, mining is the process of adding new blocks to the chain. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems, and when they find a solution, they can add a new block to the chain. It's like a competition, and miners are rewarded for their work.
Sequencing is all about putting things in a specific order, step by step, just like following a recipe or like arranging puzzle pieces in the right order to create a clear picture.
 |
|---|
In the context of Blockchain technology, sequencing means organizing actions or events in a particular sequence or order, so everything happens in the right way and at the right time. It can be likened to following a roadmap to make sure things happen in the right order.
When a transaction is initiated on the blockchain, it is broadcast to all nodes in the network. Each node validates the transaction to ensure that it follows the rules of the blockchain, and then adds it to a block. Once the block is full, it is hashed and then broadcast to the network.
The nodes in the network then work to reach consensus on the validity of the block. This is usually done through a consensus mechanism such as proof of work (PoW) or proof of stake (PoS). Once consensus has been reached, the block is added to the blockchain and becomes a permanent part of the ledger.
Therefore, the process of sequencing transactions in a blockchain network is to ensure that this entire process of the blockchain is secure, transparent, and tamper-proof. With each block containing records of all the transactions that have been added to it, creating a transparent and immutable ledger that is resistant to fraud and hacking.
To this effect, the entire process of sequencing a transaction in Blockchain network involves certain stages, which includes the following;
Transaction Creation:
It all starts when someone wants to make a transaction, like sending digital money or recording information on the blockchain. Just like writing a message, they create the transaction and include all the necessary details.
Transaction Propagation:
Once the transaction is created, it's like sharing the message with friends. The transaction is broadcasted to all the nodes in the blockchain network. It's like spreading the news to everyone in the group.
Verification:
Now, all the nodes in the network work together to verify the transaction. They check if the transaction is valid, making sure the sender has enough funds or the information is accurate. It's like having a group of friends double-checking the message to make sure it's legit.
Consensus:
In order to agree on the order of transactions, the nodes go through a process called consensus. They work together to reach an agreement on which transactions should be added to the blockchain and in what order. It's like having a friendly discussion to decide the order of messages in a group chat.
Block Formation:
Once the nodes reach a consensus, they gather a bunch of verified transactions and create a block. This block contains a list of transactions, like a page in a ledger.
Block Addition:
The newly created block is added to the existing blockchain. It's like adding a new page to a book, making sure it's in the right order. The blocks are connected to each other, forming a chain.
Block Validation:
All the nodes in the network validate the newly added block. They check if it follows all the rules of the blockchain, like making sure the transactions are valid and the previous blocks are not tampered with. It's like having a group of friends reviewing the new page in the book to ensure it's accurate.
Continuous Process:
This process of creating, propagating, verifying, reaching consensus, and adding blocks continues as new transactions occur. It's like an ongoing cycle, where the blockchain keeps growing with each new block.
Describe how the Steem blockchain sequencer works, highlighting its specific characteristics and its role in consensus. Illustrate a graphical diagram to explain how it works. |
|---|
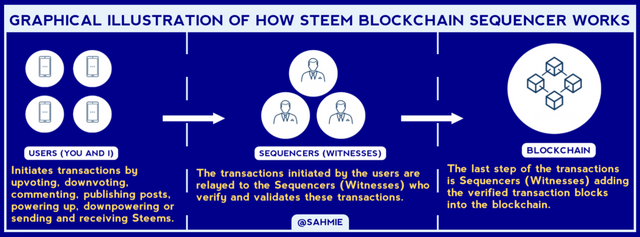
Knowing what Blockchain and Sequencing is all about, let us look at what Blockchain Sequencer is all about. A blockchain sequencer is like the traffic controller of the blockchain network. It is responsible for organizing and arranging the transactions in the right order.
 |
|---|
A blockchain sequencer is like a special person who keeps track of all the transactions happening in a blockchain, making sure everything is in order and that no one can cheat.
Therefore in the context of Steem, the blockchain sequencer can be said to be as a conductor of a music band with the main job being to bring all the musicians (or in this case, the transactions) together in harmony.
 |
|---|
First, when people on the Steem platform create posts, comments, upvotes etc. These are like the musical notes that make up a song with each piece of content considered as a transaction.
Now, imagine all the transactions as musicians playing their different instruments and wants to be heard or recognized by the Steem community. So, they raise their voices by broadcasting their transactions to the Steem network.
The blockchain sequencer, being the conductor, listens to each musician (transaction) and decides how they should be arranged in the final composition (the blockchain), considering factors like the timing, importance, and relevance of each transaction.
However, unlike other blockchains, Steem uses a consensus mechanism called Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) which is like having a group of trusted band members who take turns being the conductor.
In Steem, there are specific individuals or entities called "witnesses" who act as the conductors which are chosen by the Steem community through voting and these witnesses take turns being the blockchain sequencer and have the responsibility to sequence the transactions.
The witnesses work together to reach a consensus on the order of the transactions. It's like having a band discussion where the conductors (witnesses) collaborate and agree on the best arrangement for the song (blockchain).
Once the witnesses agree on the order, they create a block that contains a set of transactions to which this block is then added to the Steem blockchain, just like adding a new chapter to a book.
I hope this makes up a good Illustration ti explain how the Steem Blockchain Sequencer works.
What are the different consensus algorithms used in blockchains, and how do they influence the transaction sequencing process? |
|---|
There are different consensus algorithms used in blockchains and they all have different mechanisms to how they influence the transaction sequencing process. Examples of the main consensus algorithms include;
Proof of Work (PoW):
Think of PoW as a race where miners compete to solve complex puzzles, like running a marathon. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add a block of transactions to the blockchain. This algorithm ensures that transactions are added in a secure and decentralized way, but it requires a lot of computational power and energy.
Proof of Stake (PoS):
In PoS, it's like a voting system. Instead of miners, there are validators who hold a certain amount of staked cryptocurrency, hence, they are like shareholders in a company where the more cryptocurrency they hold, the more chances they have to be chosen as validators. These validators however take turns to add blocks to the blockchain based on their stake, with this algorithm being more energy-efficient than PoW.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS):
DPoS on the other hand is like a representative democracy where instead of all validators having equal power, the community votes for a smaller group of trusted individuals called "delegates" or "witnesses" and these delegates take turns being the blockchain sequencer, deciding the order of transactions. DPoS is known to be faster than PoW and PoS since fewer validators are involved.
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT):
PBFT is like a committee meeting where validators, also known as "nodes" communicate with each other to reach a consensus on the order of transactions by exchanging messages, voting, and coming to an agreement. Where addition of blocks is based on the majority of votes, so if the majority agrees, the transactions are added to the blockchain. PBFT is known to be fast and efficient but requires a certain number of nodes to be honest.
All these consensus algorithms influence the transaction sequencing process by determining who gets to add blocks to the blockchain and how the order of transactions is decided, with each algorithm having its own advantages and considerations, like security, speed, energy efficiency, and decentralization.
So, depending on the blockchain, different consensus algorithms are used to ensure that transactions are added to the blockchain in a fair, secure, and agreed-upon manner.
Explain the role of different types of nodes (like full nodes, light nodes, etc.) in the process of sequencing transactions within a blockchain. |
|---|
Full Nodes:
Think of full nodes as the superheroes of the blockchain. They have a complete copy of the entire blockchain and are responsible for validating and storing all the transactions. Full nodes play a crucial role in maintaining the security and integrity of the blockchain. They check if transactions are valid and follow the rules before adding them to the blockchain. Full nodes also help in distributing the blockchain to other nodes.
Light Nodes:
Light nodes are like the streamlined version of full nodes. They don't store the entire blockchain. Instead, they rely on full nodes to provide them with the necessary information. Light nodes are great for devices with limited storage or processing power, like smartphones or tablets. They can still verify and access transactions, but they rely on full nodes for most of the heavy lifting.
Mining Nodes:
Mining nodes are like the treasure hunters of the blockchain. They use computational power to solve complex puzzles in the Proof of Work consensus algorithm. By solving these puzzles, they compete with other miners to add new blocks to the blockchain. Mining nodes validate transactions, bundle them into blocks, and then add them to the blockchain. They also receive rewards, like cryptocurrency, for their mining efforts.
Masternodes:
Masternodes are like the VIP members of the blockchain. They are special nodes that perform additional functions beyond just validating transactions. Masternodes can provide advanced features like instant transactions, privacy, and decentralized governance. They require a certain amount of cryptocurrency to operate and are often used in specific blockchain networks.
However, these different types of nodes work together to ensure the smooth sequencing of transactions within a blockchain with each node having its own role to play, contributing to the overall functioning and security of the blockchain network.
Discuss the importance of decentralization and governance in the context of the Steem blockchain. How does Steem's governance structure affect transaction sequencing and network security? Give a practical example that explains operation. |
|---|
Decentralization can be likened to having a group of individuals making decisions together, rather than just one person being in control of everything. In the Steem blockchain, decentralization is all about spreading the power and control among many people instead of being concentrated in the hands of few persons as it uses the Delegate Proof of Stake consensus mechanism. This means that every user on the Steem Blockchain has the right to vote for a witness as long as they have a Steem Power.
Hence, this is important as it helps to ensure fairness, transparency, and security on the blockchain. This is because decentralization, no single person or entity has the power to manipulate or control the entire blockchain. It also means that everyone participating in the Steem blockchain has a say in how things are run and can contribute to the decision-making process.
Governance on the other hand is all about having certain rules and guidelines in place to guide everyone and make sure that everyone plays by the same set of rules. Then, in the context Steem blockchain this refers to the mechanisms and processes put in place to make decisions and manage the blockchain effectively.
Governance is an important aspect of any social setup as well as the Steem Blockchain as it helps to maintain order and stability within the blockchain. It also allows for the creation and enforcement of rules that govern how transactions are validated, how rewards are distributed, and how disputes are resolved. Therefore, by having a clear governance structure, the Steem blockchain can operate smoothly and fairly for all users.
In Steem ecosystem, the governance structure plays a role in deciding the order in which transactions are processed. The witnesses, who are serve more or less like representatives as elected by the Steem community, are given the responsibility to validate and approve transactions and they work together to decide the sequence in which transactions are added to the blockchain.
Therefore, this process is important for maintaining network security because by having witnesses to validate and approve transactions, it helps ensure that only legitimate and valid transactions are added to the blockchain.
For the example. let's say I want to send some Steem coins to my friend. When I initiate the transaction, the witnesses are the ones who step in to verify my transaction by checking if I have enough Steem in my wallet and if the transaction is valid and once they confirm everything is in order, they add the transaction to the blockchain.
However, these witnesses work together to process transactions quickly and securely, taking turns in producing blocks. It's like a relay race, where each witness passes the baton to the next one to keep the process going smoothly.
By having this mean of governance in place, Steem ensures that transactions are processed in an orderly manner, while also maintaining network security and preventing any single entity from having too much control.
CONCLUSION |
In conclusion, STEEM Blockchain Sequencer offers a view into how the blockchain carry out and organize their transactions with the sequencers (Witnesses) setting the tune making sure every transactions are processed in the right order and keeping the blockchain secure and running smoothly.
I wish to invite @starrchris, @ngoenyi, and @hamzayousafzai.
Thank You for your Time
NOTE: Always have a smile on your face, as you are never fully dressed without one.

Your explanation of the STEEM Blockchain Sequencer is thorough and engaging, I've really learnt alot from reading and assimilating this post.
All the best in this contest
Thanks a lot for the kind words. I'm happy that my explanation of the STEEM Blockchain Sequencer was helpful to you. It is awesome to hear that you've learned a lot from reading and understanding the post. I appreciate your support and encouragement.
I look forward to seeing more amazing content from you 🙂 have a nice weekend my friend 😌
Thanks a lot. I'm always happy to share my ideas and knowledge while trying to make good content for my readers. Have a fantastic weekend, my friend. Enjoy and take some time to relax.
TEAM 5
Congratulations! Your post has been upvoted through steemcurator08.@sahmie Your thorough exploration of the STEEM Blockchain Sequencer is impressive I truly appreciate how you break down complex concepts into easily digestible bits. Its like having a friendly chat with a blockchain expert. Wishing you the best of luck in the contest
Thank you so much for your kind words. I'm really glad that you find my explanations of the STEEM Blockchain Sequencer helpful and easy to understand. I appreciate your support and well wishes for the contest. Good luck to you too.
Saludos cordiales gran amigo sahmie, un placer para mi saludarte y leer tu participación en este reto.
Muy buen trabajo explicativo de nuestro ecosistema, de las principales y básicas nociones que lo componen, también bien explicado en proceso de secuenciaci de una transacción, te felicito hermano.
Feliz, bonito y bendecido día.
Thank you so much. I really appreciate your kind words and encouragement. It's always a pleasure to participate in this challenge and share my thoughts on our ecosystem. I'm glad that my explanation of the main concepts and the process of sequencing a transaction made sense to you. Your congratulations mean a lot to me, brother. Wishing you a happy, beautiful, and blessed day as well. Keep up the great work.
Thank you, friend!


I'm @steem.history, who is steem witness.
Thank you for witnessvoting for me.
please click it!
(Go to https://steemit.com/~witnesses and type fbslo at the bottom of the page)
The weight is reduced because of the lack of Voting Power. If you vote for me as a witness, you can get my little vote.
Upvoted. Thank You for sending some of your rewards to @null. It will make Steem stronger.
Greetings my friend @sahmie! Your explanation of the STEEM Blockchain Sequencer is impressive, breaking down complex concepts into easily digestible bits. It's like having a friendly chat with a blockchain expert! 🚀 Keep up the great work! All the best in the contest, success for you! 👍
Thanks a lot for your kind words. I'm glad you found my explanation of the STEEM Blockchain Sequencer easy to understand. It's all about making complex stuff simpler, like having a friendly chat with a blockchain expert. I really appreciate your support and well wishes for the contest. Fingers crossed for success.
Sequencing is like putting together a puzzle, ensuring that each piece fits perfectly to reveal the whole picture. It's similar to following a recipe; if you mix up the steps, the dish might not turn out as expected. I once tried to assemble a complicated Lego set without following the instructions in order, and it ended up being a jumbled mess. Sequencing of transactions essential for stability and integrity of the blockchain because any laxity in following the proper protocol required for sequencing will can disrupt the spirit and sanctity of the blockchain by compromising it security.
It's like a community-elected council ensuring that everyone's voice is heard and represented. Just like how we choose our leaders through voting, the Steem community selects witnesses to maintain the integrity of the blockchain. I remember when I participated in a community vote to elect our neighborhood representative; it felt empowering to have a say in who would lead us. Technically, we call it as delicated proof of stake consensus algorithm wihere stakeholders or choose and through on-chain community voting system to power.
Governance provides the structure and stability needed for a community to thrive. It's like the rules of a game; everyone knows what's expected of them, and it ensures fair play. When my family plays board games, we always agree on the rules beforehand to avoid any disagreements later on. Governance model of steem blockchain ensures fair and transparent decision making.
All the best
Thank you so much for taking the time to go through my explanation of the STEEM Blockchain Sequencer and leaving such a complimenting remark. It's all about simplifying complex concepts and making them accessible. Thank you for your kind words and support for the contest. I really appreciate it.
Blockchain technology is fascinating! It's like a digital ecosystem where blocks, each containing a list of transactions, are connected to form an unbreakable chain. Nodes, like the building blocks of a wall, work together to maintain security and integrity. With hashing and cryptography, transactions are tamper-proof. Consensus ensures everyone agrees on valid transactions, and decentralization spreads power across nodes for robustness. It's a team effort where distributed ledgers ensure transparency. Mining adds new blocks, rewarding miners for their computational prowess. Truly a marvel of modern innovation!
Indeed, Blockchain technology is like a digital ecosystem where blocks connect to form an unbreakable chain with nodes working together for security and integrity, while hashing and cryptography keep transactions tamper-proof. Consensus and decentralization ensure agreement and robustness. It's a transparent team effort with miners adding new blocks. Truly a marvel of innovation. Thank you for your remarks.
Absolutely! Your summary perfectly catches the significance of blockchain modern technology. It's unbelievable just how all these parts collaborate easily to produce a safe and also clear electronic community. Thanks for valuing the remarks. Right here’s to the marvels of advancement and also the interesting future of blockchain modern technology!