Crypto Academy Season 3 Beginners' course - Task 2: Blockchain, Decentralization, Block explorer
Write the definition of blockchain. And how our data on Blockchain is protected from hackers. ? And write details about Data, Hash and Previous Hash tag and explain through screenshot.
Greeting everyone,
I am delighted to be back to present my homework task 2. I am trying to be as real as i can be from what i have understood about the Blockchain.
Introduction to BLOCKCHAIN
Blockchain technology was first introduced by Staurt Haber and W. Scott Sternetta in 1991. However, no such real world application was brought in use until the launch of bitcoin in 2009.
Blockchain is a specific type of database which never sleeps. It gets its name by combining two words. i.e Block and Chain. A block is a storage of data or information. Since blocks have certain storage capacities, when a block get full, another block will be created by the system for storing data. It keeps continuing as long as the new data persist evolving. And, all these blocks with verified information are joined togather in an organised way and chronological order, thus creating a chain of blocks.
If we are engaged in cryptocurrency one way or another, we might notice that it is taken by storm. This is where we come across the blockchain. And, we cannot deny the fact thatmost blockchain use cases can be seen in cryptocurrency market for recording and storing the monetary transaction. In addition, not only it can be used for cryptocurrency transaction, but also it can be brought in use to store other kinds of transaction too. At present, we can see different blockchain based projects moving forward to implement the blockchain for the sake of societies and the entire world as a whole.
How our data on blockchain is protected from hackers?
I would like to start this by explaining the decentralisation nature in the blockchain. Meaning that it executes itself according to the respective protocol in which no single person/organisation has control over, rather all users collectively retain the control.
In a blockchain, there are thousands or more of computers in a network. These computers are operated by different person or group of people in a various geographical locations are termed as Nodes. Each node consists a full record of the data right from the beginning of the blockchain. And every new block is added to the previous block linearly and chronologically such that the new block contains its own hash, along with the hash of preceeding block. Besides, each block is given an exact timestamp when added to the blockchain.
Lets consider a scenario where a hacker tries to alter data. If the data is changed, their single copy will no longer align with the copies of other nodes. At this point, all the other nodes will cross-refer against each other and easily figure out the node with wrong data. And, the single copy with different data stands out alone against all the other nodes being same. With no procrastination, it will be considered as invalidated.
Under certain circumstances, if a node happens to make an error in its data, it will take all the other nodes in the network as a reference point to correct itself. This is how, no nodes can change the data contained within it in the network.
Altering data in a blockchain when implemented in a decentralised way is an impossible process. It can be viewed and verified by thousands of nodes from everywhere and stored inside the blocks.
And, every block when added to the chain is given an exact timestamp which makes it even more secure.
The goal of blockchain is to allow information to be recorded and distributed, but not edited. In such a way, it can also be considered as a safe and secure online distributed system.
Having said all this, still the contents in a block can be altered if it is in the best interests of the mojority of the nodes. For this, the majority in the decentralised network needs to agree on mentioned changes and reach a consensus to do so.
Someone might be wondering if it is so, how can our data be protected from a hacker. As i have mentioned above, the majority plays a pivotal role so as to change the data in the blockchain. In order to succeed with such a hack, they must simultaneously control and alter at least 51% of the copies in the blockchain, thus, gaining the majority of the copies. Furthermore, such act needs to redo all the blocks which cost tremendous amount of money and resources.
For the verification of the information in each block, there are three elements associated with them in order to form the blockchain. These are:
- Data
- Hash Tag
- Previous Hash Tag
Data:
Every block consists of data. Data could be any kind of information. Basically, it contains the information about monetary transaction such as the transfer of cryptocurrency from sender to reciever when it comes to the certain cryptocurrency like bitcoin. It explicitly clarifies on how much tokens were sent from who to whom, including the exact point of time.
As far as Steemit(social media blogging platform) is concerned, the steem blockchain also records the non-monetary transactions such activities like post, edit, comment, replies, votes, reblog.
All these kinds of transactions are recored and stored in the form of verified data in blocks which is impossible to change.
Hash Tag:
Hash Tag is one of the important elements in a block. It stands unique as it is created differently in each block by the system. These are created by a math function that turns digital information into a string of numbers and letters.
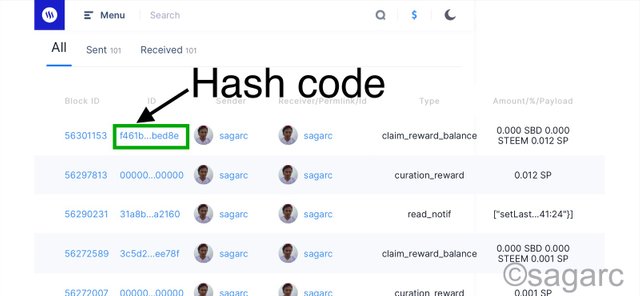
Let me show you one of the transactions with corresponding hash code from my steemit account in steemscan.
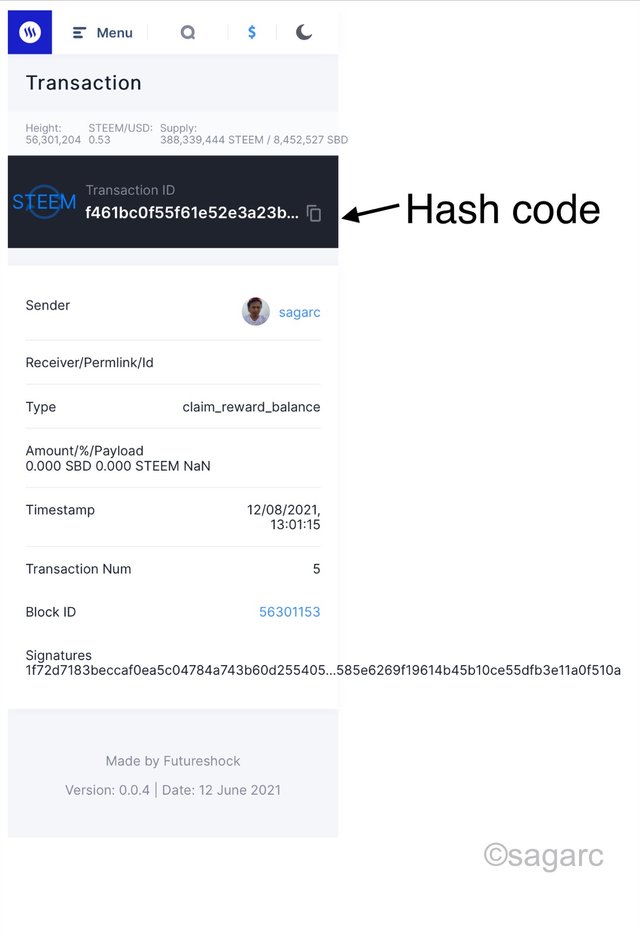
When i click the hash code, a new page opens up showing all the details about the transaction such as sender, reciever, type of transaction, timestamp and digital signature. We can see the hash code displayed on top.
The full size of the hash code looks like this:
In addtion, the hash code is the only way in order to verify the authenticity of the information. It is also considered as an identification number of any block. Comparing it with the fingerprint of human beings would make it more precise.
If that information is edited in any way, the hash code changes as well. This helps us to identify any malicious act occuring in the blockchain. This is a feature what makes the blockchain in a decentralised nature irreversible.
Previous Hash Tag:
What makes all the blocks chained togather is the previous hash code. The creation of each new block is the consequences of new data being entered into the blockchain.
As i have mentioned before, every block is assigned with a hash tag by the system. When a block is filled with the data. New block will be created so as to contain the incoming data in the block. At this moment, the hash code of the previous block is entered into the fresh block. And also, this new block gets an another hash code. This is how all the blocks in the blockchain are interconnected in such way that not a single information can be altered.
Thanks you for your attention.
@yousafharoonkhan
@steemcurator02
@wahyunahrul
Kind regards
@sagarc





Hello @sagarc , I’m glad you participated in the 2nd Task of the Beginner’s class at the Steemit Crypto Academy. Your grades in this task are as follows:
Recommendation / Feedback:
Thank you for submitting your homework. task 2. We hope to see the rest of your submissions.
@reminiscence01 Thank you professor.