Crypto Academy Season 3 Beginners’ Level - Homework Post for WEEK 4: [BLOCKCHAIN FORKS] by @reddileep for Professor awesononso
HOMEWORK WEEK 4
Entire Question
1.What is a Fork? (In your own Words)
2.Explain in details what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
3.Explain in details what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
4.What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
5.Explain the following Bitcoin Forks and explore the blockchain where necessary. Indicate if they are hard forks or soft forks;
- Bitcoin Cash
- Segregated Witnesses
6.Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks(Provide screenshots).

- INTRODUCTION TO THE FORK

- HOW IT WORKS
Here I have selected Bitcoin as an example to define the Fork deeply. Actually, bitcoin is a decentralized system and a single person can't decide the upgradations of the Bitcoin system. Because it is controlling by every user in the system. However, bitcoin miners are doing a significant contribution to the bitcoin system and they are the ones who make the decisions regarding the upgradations of the system. If more than 95% of the miners agree to this update, the developers will perform this update. So sometimes the value of bitcoin changes due to these upgrades and this process is called Fork.
Further, developers always inform about this upgrade to the cryptocurrency users and users should have the responsibility to upgrade their software according to the upgrades of developers.
So, according to this phenomenon, there are two types for Fork mainly.
Below I have included an image created by me through MS PowerPoint Program

- INTRODUCTION TO THE HARD FORK

- HOW IT WORKS
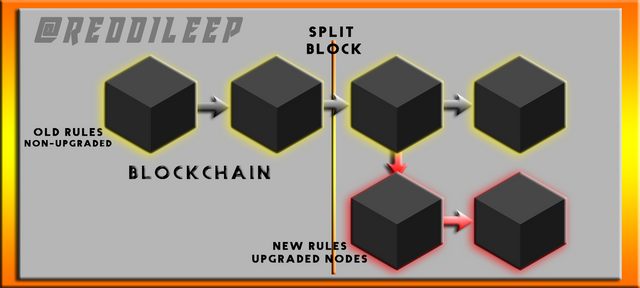
If we suppose there is an old blockchain it name is B1. Now it is updated to B2. It means B1 become B2. So, after the update, if the user still uses B1 Blockchain to do their transactions can be disappeared.
If I go to the deep of my example, B1 block has 2MB data and the upgraded B2 block has 4MB of data. It means B2 block is created with additional data to the B1 block. Now we can see the B2 Block is bigger than B1 and we can't copy the B2 data to the B1 Block. Therefore, we can't use B1 block after the update and we must do the update if we want to use the coin correctly.
Below I've attached an image to explain the idea of Hard Fork which was created by me from Photoshop Program

- EXAMPLES
- SIMILARITIES BETWEEN ETHEREUM CLASSIC AND ETHEREUM
Below I've proven it by exploring them from the Blockchain.
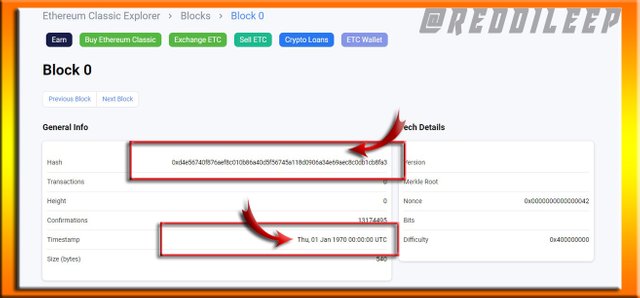
Here I've explored Genesis Block of Ethereum classic (BLOCK 0) using the below hash code.
0xd4e56740f876aef8c010b86a40d5f56745a118d0906a34e69aec8c0db1cb8fa3
Now I've explored Genesis Block of Ethereum (BLOCK 0) using the same hash code.
0xd4e56740f876aef8c010b86a40d5f56745a118d0906a34e69aec8c0db1cb8fa3
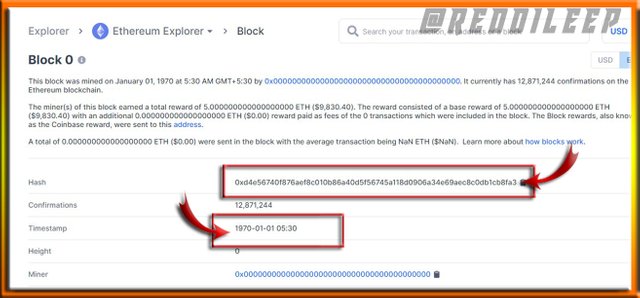
Now we can realize that there are some similarities of both Blocks like Date and Hash code. Because even they have upgraded the Block, the history of the block can't be changed.
Finally, we can see some more Hard Forks like Expanse (EXP) and Quorum. These Hard Forks are also created through the Ethereum codebase.

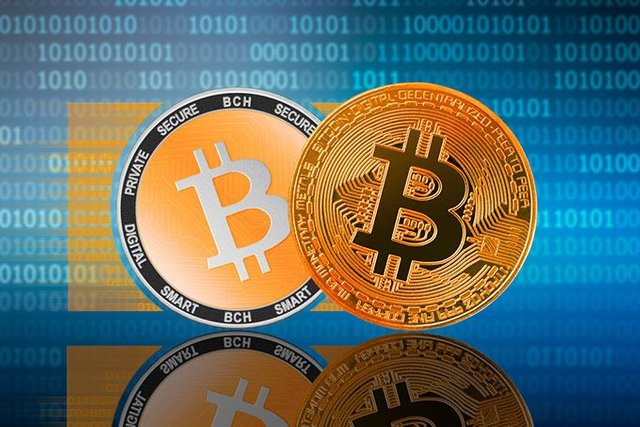
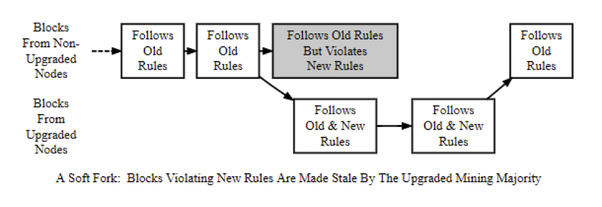
- INTRODUCTION TO THE SOFT FORK
Soft Fork is also an upgrade of the system. But this time it isn't dangerous like Hard Fork. Because the users have some specific time duration to be updated to the newer version. Till then, they can do the transaction without upgrade as the new version is backwards compatible with the older version. Basically, this upgrade is known as Soft Fork. Below I have explained it deeply including process and examples.

- HOW IT WORKS
If we suppose B1 is the previous version and an upgrade has happened now using Soft Fork. So, now the upgraded version is B2. But some of the users don't know about the B2 upgrade. Then we know we have the blockchain with distributed ledgers. B1 has the Public Ledger and B2 have another Public Ledger as it is upgraded. Now half of the persons use B1 ledger as they don't know about the upgradations and other persons use B2 ledger. However, both people can do the transactions without fail as both ledgers are compatible and those ledgers can work together.
If I go to the deep of my example, B1 block has 2MB data and the upgraded B2 block has 1MB of data. It means B2 block is created by removing additional data from the B1 block. Now we can see the B2 Block is smaller than B1 and we can copy the B2 data to the B1 Block without failing. Therefore, we can use B1 block even it is upgraded to B2 for a specific duration of time. This phenomenon is known as Soft Fork.
Further, there are two types of Soft Forks
Miner-activated soft fork (MASF)
It means rules created according to the majority of Miner's voting. Here decisions are taken by minersUser-activated soft fork (UASF)
It means rules created according to the users in the system like exchanges, wallets
Further, we can get a better idea from the below attached image.

- EXAMPLES
Further, developers informed every user to upgrade their software for Segregated Witness (SegWit) upgrade. However, Unupgraded users were also able to transact without any problems as Segregated Witness supported for Backward compatibility.
Below I've included the logo of the SegWit. There are several factors that we need to consider regarding this logo. Let's move to the behind factors of this logo.

Image Source
We can see the word "SEG" is from black colour and the word "WIT" is from white colour. The reason for black and white apart in this way is to point out the purpose of separation.

Hard Forks and Soft Forks look like the same as both are upgrades according to the willingness of miners or users. But actually, it has some of the differences. Below I have included them in a table to give a clear idea.
| HARD FORK | SOFT FORK |
|---|---|
| We may lose our money if we do transactions without an upgrade. So it is very risky. | As both upgrades are compatible, we can do any transaction without risk. |
| We can't do any transaction without upgrading | We can do any transaction for a specific period. |
| Prices can be reduced after an Upgrade | Prices do not change because it does not affect sellers or buyers |
| Privacy of the Hard Fork is better | Privacy is less as compared to Hard Fork |
| Only Miners have the majority of taking decitions | Miners and users both can take decisions |

- BITCOIN CASH
Actually, before this upgrade, we had to wait for a certain time to accomplish our transaction as the Block size was limited to 1MB. Then, after the upgrade size of the blocks had increased to between 8 MB and 32 MB.

Below I've explored Bitcoin Cash through the blockchain.
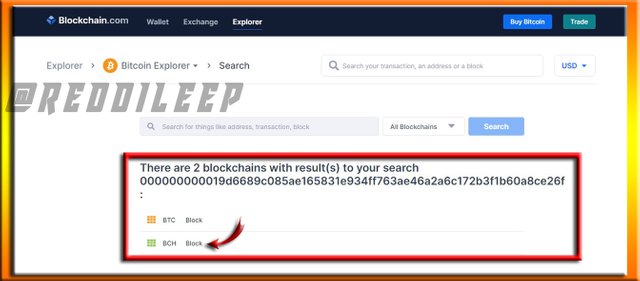
Above we can see there are two blocks for the same hash code. So, below I've selected BCH (Bitcoin Cash Block) among them.
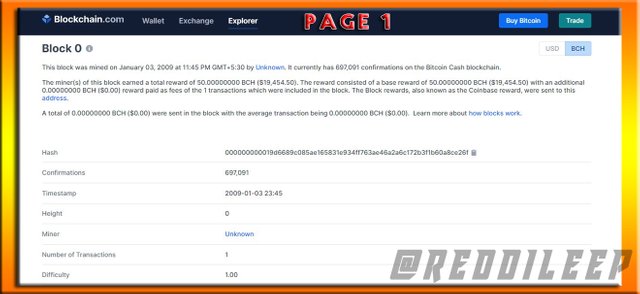
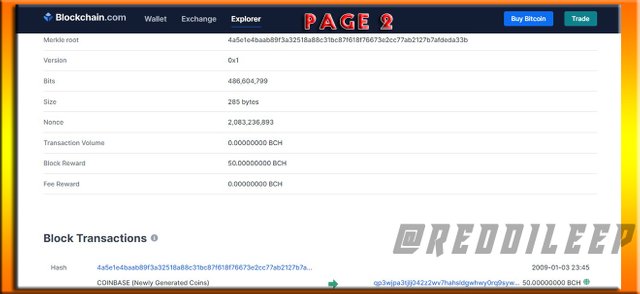
- TYPE OF FORK - BCH is a HARD FORK as an upgrade for BTC

- SEGREGATED WITNESSES
Finally, Dr. Pieter Wuille brought a concept to create a separate block by removing signature data in 2015. So, according to the SegWit update, we can see only Public Keys and Transaction messages in the Block. Then, the ID (Digital signature) and the Public key of the sender is recorded in a separate block and Hard coded into the system. Therefore, the load of the bitcoin network was reduced and Transaction speed was increased.
Further we can get a better idea from the below attached image.
- TYPE OF FORK - Segregated Witness is a SOFT FORK as an upgrade for BTC

- Introduction to STEEM & HIVE

- STEEM HARD FORK
After the announcement of TRX (Tron) integration with Steem blockchain, all the Steem Blockchain users didn't agree to that integration. Therefore, they were separated and created a new Blockchain called Hive Blockchain. If we compare both platforms we can see a lot of similarities between Steemit and HiveBlog.
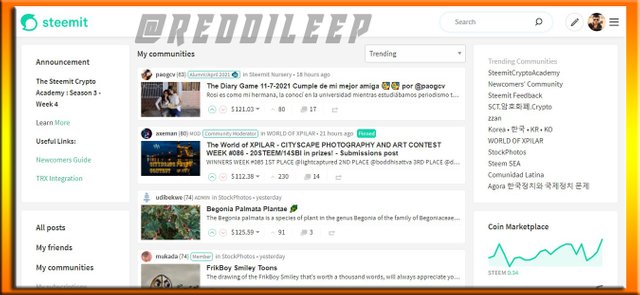
Below I have attached Screenshots of both platforms interfaces and we can see the appearance looks the same at a certain level.
Screenshot taken through Steemit.com
Screenshot taken through Hive.blog
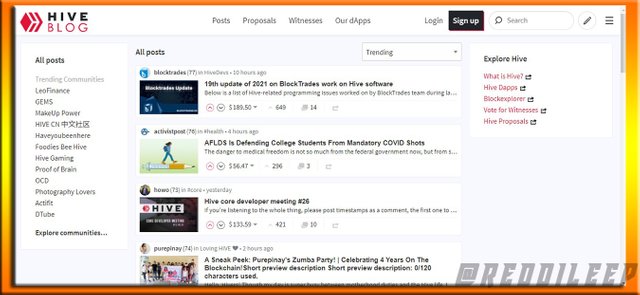
Above we can see the interface similarities very clearly.

- SIMILARITIES THROUGH THEIR GENESIS BLOCKS
GENESIS BLOCK of Steem
Here I've used https://steemworld.org/ to explore Steem Genesis Block and I've selected Block Explorer, Block 1.
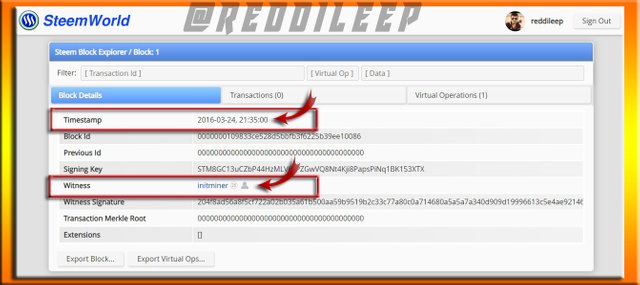
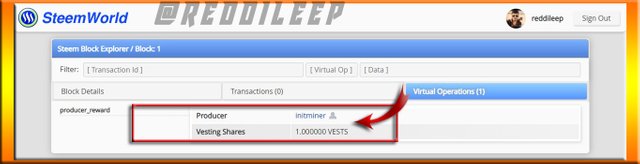
We can see above highlighted points in Steem Blockchain are very similar to the Hive Blockchain. Below I've proven it by exploring Hive Blockchain.
Here I've used https://hiveblocks.com/ to explore Steem Genesis Block and I've selected 1 from the search bar to explore the Block.
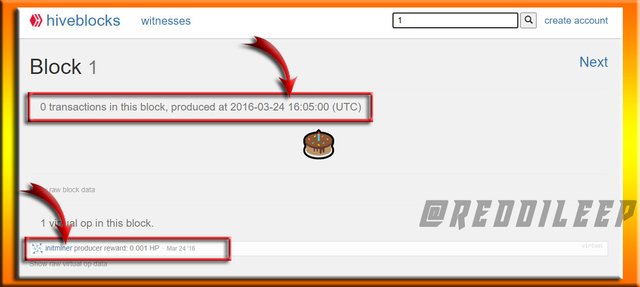
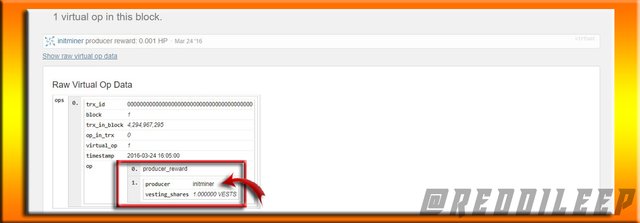
Now we can clearly realize that the block produced to date and time are exactly the same as the Steem produced to date and time. Also, the producer name @initminer and the number of vests are the same as the Steem.
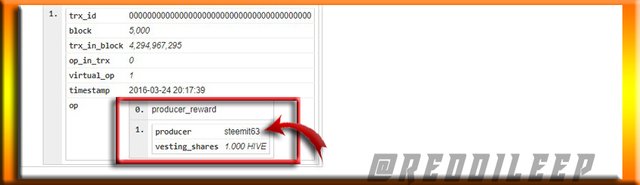
Below I've explored block 5000 on both Blockchains. Let's examine their similarity also.
Block 5000 from Hive Blockchain
Block 5000 from Steem Blockchain
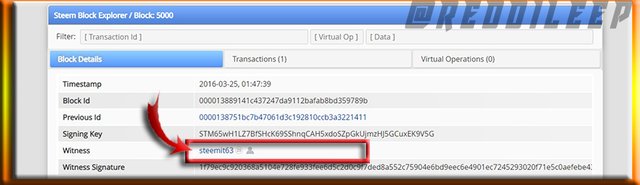
Above we can clearly see the miner @steemit63 is similar for both Blockchains. Now we can realize that even with two Blockchains, the history of the blockchain can't be changed as both depend on a common history.
Both Hard Forks and Soft Forks are very important for users. So, users have the responsibility to attend to the developer's alerts. If we don't do it, we have to lose our coins, especially on a hard fork. Even Soft Fork, developers have fixed some bugs to speed up the system. Therefore, if we upgrade our software to the new version, we can do any transaction for any coin without any interruptions.
This is all about my homework and I really appreciate Professor @awesononso for your valuable lesson and your dedication to creating a very essential lesson for us.

Thank you..







.png)
