SteemitCryptoAcademy [Beginners’ Level] | Season 3 Week 4-HOMEWORK for Professor @awesononso | Blockchain Forks by @Phenomenal1052
1.What is a Fork? (In your own Words)
2.Explain in details what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
3.Explain in details what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
4.What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
5.Explain the following Bitcoin Forks and explore the blockchain where necessary. Indicate if they are hard forks or soft forks;
- Bitcoin Cash
- Segregated Witnesses
6.Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks(Provide screenshots).
Note: All Screenshots should have your username as a watermark on it.
Image from professor post
What is a Fork?
We all know the Cryptocurrency world is a decentralized world, and one of the things that makes it decentralized is the open source code, this means that a Cryptocurrency source code is available and can be accessed by the public.
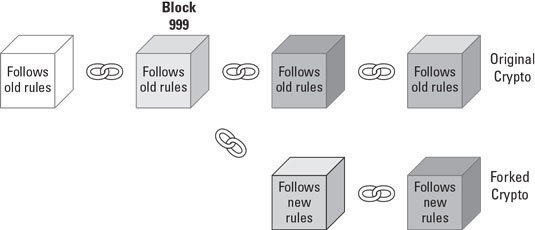
So a fork can easily be defined as a change in a blockchain network protocol.
This can occur when someone or a developer feels and decide to make a change in a network. This can cause also can a permanent split.
There are two types of Fork, “Hard & Soft fork”.
Explain in details what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
A Hard Fork is simply a new update on a blockchain network node that is incompatible with the existing blockchain protocol, and this will cause a permanent split of the network into two separate network.
Hard Fork create a permanent change in a network protocol making the two version to have their own different transaction blocks. Like I said in the definition above, this new changes will cause incompatibility problem, and will force miners to make a decision either to update to the new version or the old version of the network.
Hard Fork usually occurs if a need to add new feature to a blockchain network protocol in order to make it function well or meet the standard of other network. Some people might think why not just a simple upgrade, instead of a complete overhaul of the network protocol, but sometimes just ordinary upgrade might not be enough to get the result needed, so a thorough change is needed sometimes. There are different reasons why hard Fork is done, like security reasons, new feature and lots more.
The are lots of examples and cases but the one I will be talking about is the Ethereum hard Fork that brought about Ethereum Classic.
Ethereum Classic
This is the very first hard Fork that Ethereum had and it is mostly described as being controversial.
Ethereum Classic was formed in 2016 as one of the split version of the first Ethereum after the creator decided that carrying out an hard Fork is the best way to check one of the biggest hack in the history of Cryptocurrency. After the Ethereum system was hacked and millions of dollars was stolen, the creators of Ethereum decided that creating a new version is the best way to get the stolen money and also secure the network. Not everyone agreed to this, some people felt that this decision would go against the principle of decentralization in the crypto world, so they decided to keep the original source code and rename the currency to what we have today as Ethereum Classic.
The goal was to keep the original source code and maintain a perfect decentralized system and continue running smart contracts. The Ethereum Classic network allows developers to build and run smarts contract on the network.
Since Ethereum Classic kept the old source code it is referred to as the original Ethereum.
Explain in details what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
Soft Fork is a backward compatible change in the software protocol of a network, where only previously valid transaction blocks are made invalid and the old nodes will only recognize new blocks as valid.
Soft Fork is just like a system update, but can only work if majority of the miners update to the new version.
Soft Fork does not cause the network to split into two different currency, instead it create two lanes that can coexist with each other. The old nodes can still verify transactions as long as it follows the rule of the new one.
There are different reasons while soft Fork is carried out, just like a building needs renovation, so does a network also needs new update to it system protocol, for reasons like bug issues, security checks, and addition of new feature to make the network more secure and sustainable to use.
There are different example of soft fork that one can refer to, but the one I will be talking about is :
Ethereum 2.0
Is a set of system upgrade currently in progress that would make the network more efficient, secure for users.
There are lots of upgrade that will come with the version
The Beacon Chain
The beacon chain is the first among the upgrade and it is already live. According to the Ethereum team, It aim is to bring staking to Ethereum, and also lay the front work for future updates and coordinate this new system.The merge
The merge update is all about merging the mainnet Ethereum being used with the new beacon chain, and this will improve staking for the network more efficient and save high intensive energy used in mining.
The summary of the updates in the Ethereum 2.0 is the transition from using the popular Proof of work to the Proof of Stake. The aim is to move from a high energy consuming, time consuming proof of work to the Proof of Stake to reduce the amount of time, energy consumed in processing transactions and also reduce the amount of transaction fees charged, plus when the updates is fully done, the Ethereum system will be able to complete over 100,000 transactions per second and keep the network secure.
What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
| Hard fork | Soft fork |
|---|---|
| * A hard Fork always results into two permanent, complete splits of the block chain | A soft Fork does not result into two complete splits, but instead it creates two lanes or branches that can co-exist with each other and one blockchain remains. |
| * It is a complete and thorough overhaul of the network system protocol | It is more like an update of the network system protocol. |
| * It is always backward incompatible and cannot work together | It is backward compatible and can function together. |
| * It requires all nodes to upgrade and agree to use the new version. | It only requires only a majority of the miners upgrading to enforce the new rules of the system. |
| * It makes previous transactions and blocks either valid or invalid | Only previous valid transactions Block are made invalid. |
Explain the following Bitcoin Forks and explore the blockchain where necessary. Indicate if they are hard forks or soft forks;
Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash Is a Bitcoin Hard Fork, it was created in August 2017 by Bitcoin miners and concerned developers who felt the soft fork named Segwit deos not fully address the real problems of scalability and does not fully follow the way laid and the initial idea of Bitcoin creator Satoshi Nakamoto which is the principle of decentralization, so they created Bitcoin Cash in 2017 with the aim of solving the issue of scalability and a bigger Block size.
The were able to create Bitcoin Cash and it solves some of the problem of Bitcoin like having a bigger Block size of 32mb instead of the Bitcoin 1mb, it also process transactions faster than Bitcoin and lots more.
Key difference between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash
- Bitcoin Cash process transactions faster than Bitcoin.
- Transactions fees in Bitcoin Cash is lower than Bitcoin.
- Bitcoin Cash can handle more transactions per second than Bitcoin.
Similarities in Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash - They both has a fixed number of coins in supply at 21 million.
- They both makes use of proof of Work in processing transactions.
Segregated Witnesses
Segwit is a BitcoinSoft Fork created to solve the problem of block size.
The idea was brought by a Bitcoin developer named Peter wuille at a Bitcoin conference in 2015, but was activated in 2017.
It was design to increase Bitcoin Block size by removing signature data from transactions, to free up space to be able to add more transactions to the Block. The idea is just like someone wants to send lots of file to another person on xender but the space isn't enough, so the receiver will have to remove some unimportant Giles to free up space for the important files.
It increases the Block size from 1 megabite to nearly 4 megabite. The name segwit was gotten from the words “segregated witness”.
The segwit has it pros and cons so let look at it.
| PROS | CONS |
|---|---|
| * It saves users more on transactions fees using Bitcoin segwit | It increases resources usuage |
| * It process transaction faster by increasing the amount of data in 1 block | Not all wallet or Cryptocurrency exchange platform support Bitcoin segwit. |
Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks(Provide screenshots).
Steem Hard Fork
Steem is also a popular crypto blockchain, that rewards users for sharing content and growing communities. Steem is run in the Steemit platform.
Some conflict emerge during argument on the issues on the steem platform, so a hard fork was done which resulted in the creation of a separate blockchain called hive. Hive is run on hive.blog and it has it own token called HBD.
Since it was hard forked from steem, they both share things in common.
Homepage Design
The first and obvious similarity is the resemblance home page, they both shared the same design and build up of the home page.
You can see that in this screenshots.
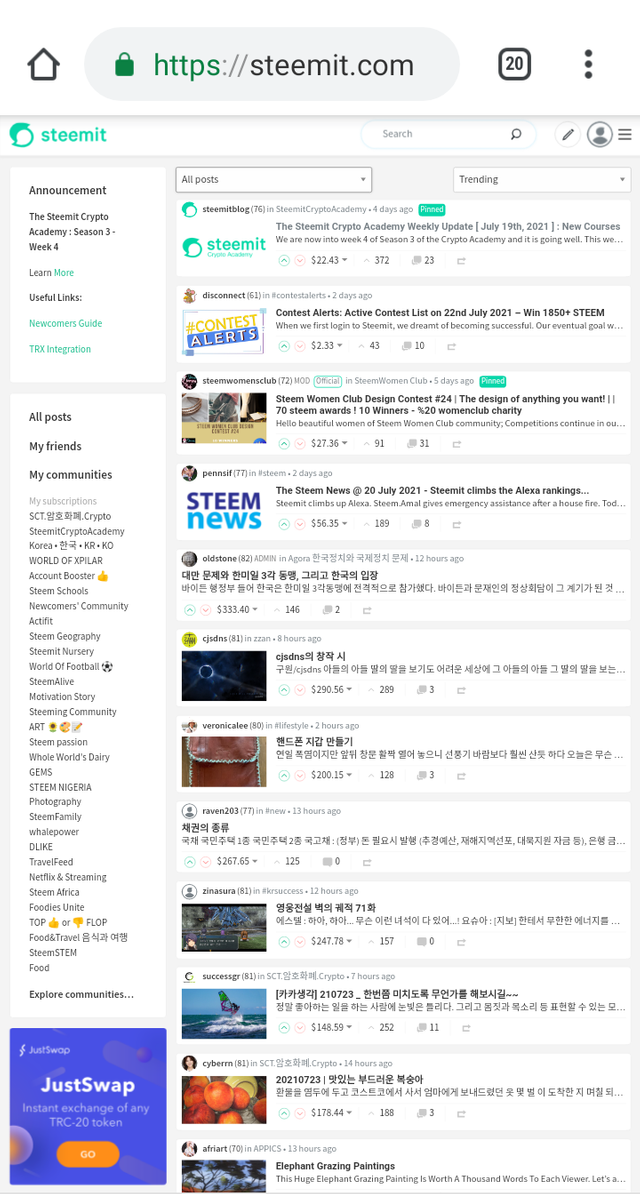
Screenshot of steemit homepage
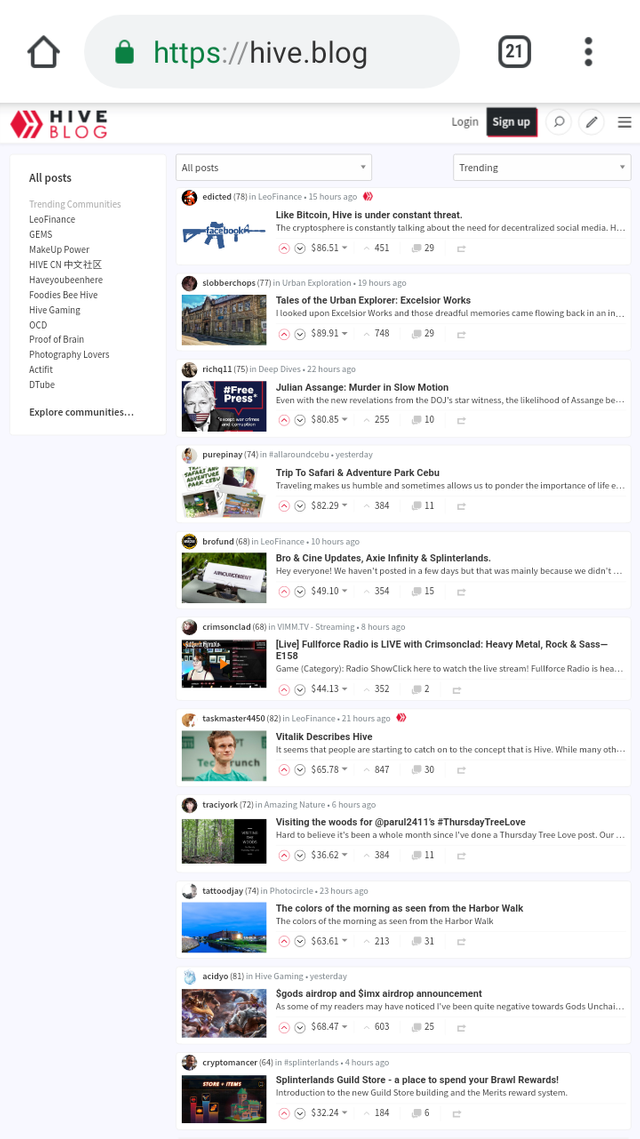
Screenshot of hive homepage
We can see the clear similarities in the homepage design.
Genesis Block
They also share similarities in their Genesis Block.
Here is the Genesis block of Steem.
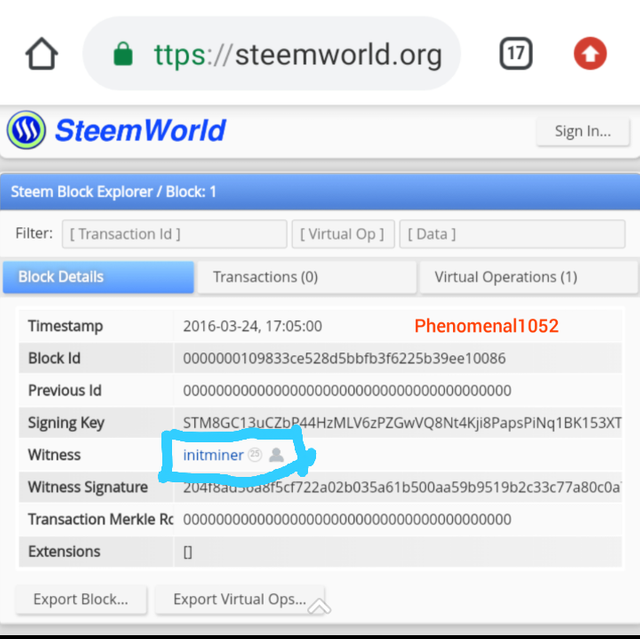
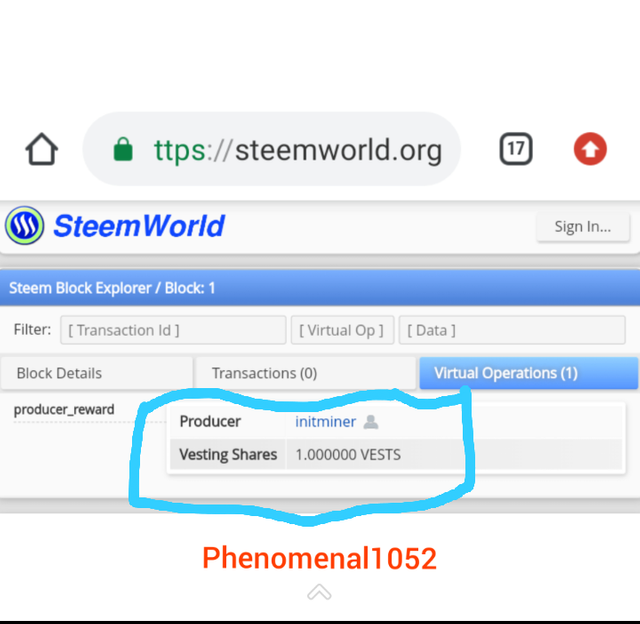
Screenshot from Steem block.org
Here is the genesis block of Hive.
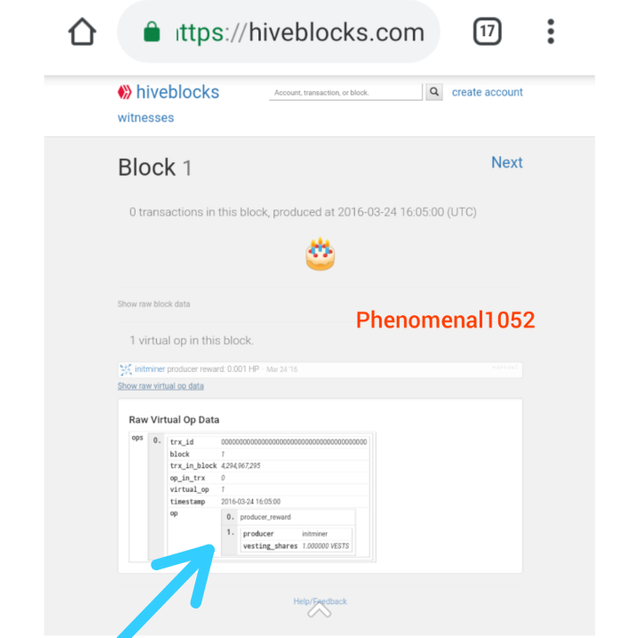
Screenshot from Steem block.org
The witness and vesting shares are the same in both blockchains.
I took another block to prove the similarities. Here are the screenshots of the Block 3000 of both blockchains.
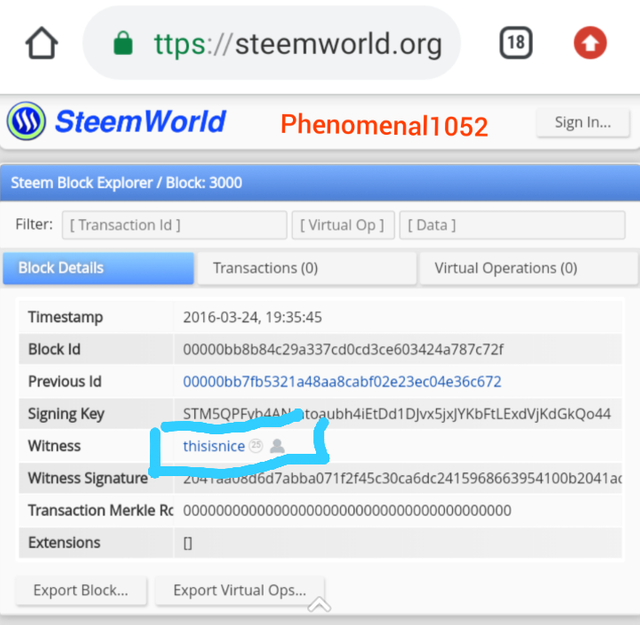
The witness of Steem block 3000 is @thisisnice and vesting shares is 1.000 VESTS.

The witness of Hive block 3000 is @thisisnice and the number of vesting shares is 1.000 HIVE.
Conclusion
Developers are human being, so they are not perfect. We all know human want is unlimited and cannot be satisfied, plus human opinion or ideals differs from each other, that is the case with decentralized blockchain, that is why forks, either hard or soft fork always occur.
We all learn, want and advance everyday, as long as new ideals comes, update on system protocol is inevitable. Thank you professor.
Cc. @awesononso