Crypto Academy Season 2 Week 7. Topic: Exchange Orderbook, its use and How to Place Different Orders - By Professor @yousafharoonkhan
 Image: My own work.
Image: My own work. Hey, everyone. Great to be here again. Finally found the time to go through the lectures for the week and I am excited to be able to study the materials and to share the lessons i have learned by writing about them. Today, I will be writing about professor @yousafharoonkhan's lesson on Exchange Orderbook, its use, and How to Place Different Orders.
The crypto orderbook is perhaps one of the scariest parts of an exchange user interface. There are so many numbers that are all changing simultaneously in split seconds, so much that it can be hard for beginners to wrap their heads around.
However, the orderbook is perhaps the most important part of a crypto exchange's interface, because it represents the buy and sell orders and literally the activities of the market. So let's start by understanding what Orderbooks are and how they work.
Q1: What is an Orderbook, and how does a crypto Orderbook differ from our local market?
An order book is simply a real-time record of open and pending buy/sell transactions showing the prices at which a choice asset is bought and sold by traders (buyers and sellers). For cryptocurrencies, an Orderbook is an electronic record of the various prices at which trades on a certain asset pair are executed. It is usually displayed in two colour-coded segments, representing the buy(green) and sell(red) Orderbooks, respectively.
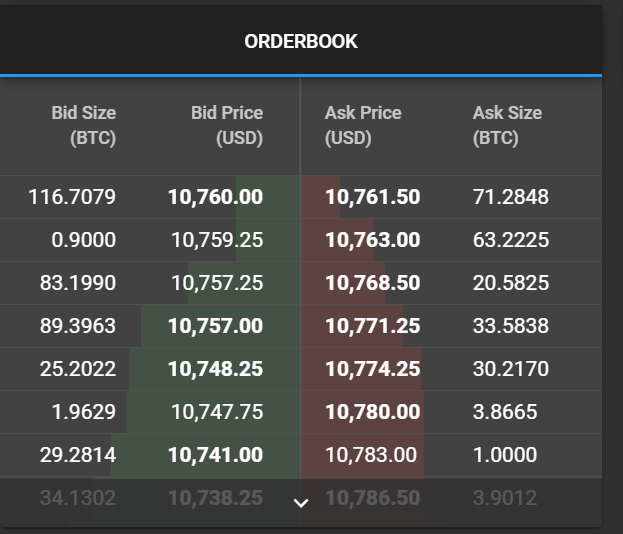
The Buy Orderbook captures the various prices at which buyers are willing to buy a particular asset pair, while the Sell order book records the various prices at which sellers are willing to offer a particular asset pair for sale. For some exchanges, the buy orders are known as Bids, whereas the sell orders are known as Asks.
Unlike the local market order books, the crypto Orderbook differs in the following aspects:
Information Assymetry:
In traditional markets, market information like an Orderbook is not readily available to all market participants at the same time, whereas, the crypto Orderbook is a publicly available and easily accessible piece of information on exchanges, that can be utilized by any market participant to make informed market decisions. This availability is because of the digital nature of a crypto exchange's orderbook.
An Orderbook is especially important in connecting buyers directly to sellers in a free market. For instance, a seller in a traditional shop dealing in gadgets might manipulate the prices of some items because the buyers don't get to interact with the Orderbook directly. They could end up buying stuff for an inflated amount.
The crypto Orderbook, however, is publicly available to every user on an exchange. Hence, both buyers and sellers have similar privileges at negotiating prices.
High volatility:
Unlike traditional markets where prices remain fairly constant over time, the crypto market is known for its high price volatility. The crypto Orderbook presents a concise record of buyers'/sellers' behaviors towards an asset pair captured by their price preferences at different points in time.
Flexible options:
The traditional market presents limited trade options- trade is either cash for the product (in a buying scenario), or product for cash (in a selling scenario), whereas, the Crypto market's Orderbook offers varied options, that is; trades can take place between numerous asset pairs. For instance, the traditional market can only trade tomatoes for cash; while the crypto market can have an asset like Bitcoin (BTC) trading against a wide range of other assets/currencies like USDT, BNB, ETH, etc.
Pending Orders:
Crypto Orderbooks make provision for traders' expectations on price. I bet it'd be practically impossible to pull a conversation like "Hey, I'm getting these tomatoes at $2 by 4pm," in a traditional market. Such expectations won't even get an ounce of consideration in the local market Orderbooks. But crypto Orderbooks makes room for traders to transact based on their expectations of what the price movement would be in the next moments. You can set conditional buy/sell orders for an asset pair, which, executes when those predefined conditions are met.
Q2: How to find an Orderbook in any exchange (with graphic emphasis).
Binance has always been my choice exchange for crypto trading. This is partly because of its popularity on a global scale, and also efforts put in by the team to enhance the user experience on their platform. For me, I think it is safe and much easier to navigate Binance through the mobile app, which is available for download on google playstore. Hence, my explanations will come from a real-time user feel of the Binance mobile app.
Assuming you already own an account on Binance, click on the app icon to launch and log in to your account. Once logged in, you land on the Home screen (which shows the trending Market for a time period (usually the past 24hrs)).
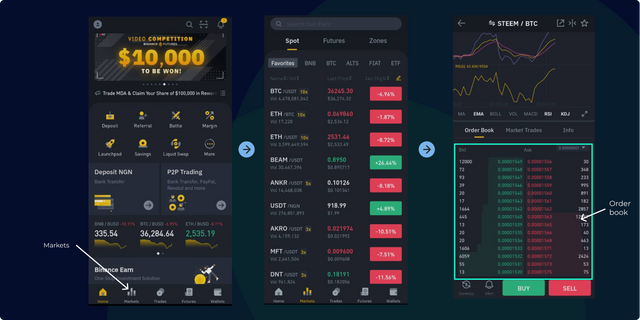 Image: The Homepage, Markets (with trade pairs), and Orderbook.
Image: The Homepage, Markets (with trade pairs), and Orderbook. At the bottom of the exchange interface, you will find five options which are Home, Markets, Trades, Futures, and Wallet. To locate an orderbook, we must first select a "Market" or Trade pair. Hence, you have to tap on the "Markets" button. This takes you to a page with lots of trading pairs and market options like spot, futures, and zones. I will use the spot market for my analysis.
Tap on your choice trading pair.
N/B If your choice pair is not on the list, simply do a manual search by clicking on the search icon and inserting the symbols for your chosen pair. Binance, as at the time of writing has just two STEEM pairs listed (STEEM/BTC and STEEM/ETH). I will proceed with the STEEM/BTC pair because it's quite popular and should have a robust order book.
Once you've searched out your desired pair and clicked on it, the trade interface for that pair will load up. On this screen, you will find the chart for the STEEM/BTC trade pair, the price, and other market metrics such as the percentage gained or lost, the volume of trade, and some indicators. You will also find the Orderbook at the bottom of this page. It is identifiable by a chunk of colour-coded numbers. The colour codes green and red simply differentiates the "Buy" orders from the "Sell" orders.
PAIRS.
In the financial market (Both crypto and Traditional markets), assets are displayed in terms of their relative value. That is, the value of an item (maybe currency, stock, commodity, etc.), is quoted in relation to another commodity (usually in price or quantity). Trades are executed based on traders' preconceived bias on which direction prices would go. The combination of both commodities in this way are called Pairs or Trade Pairs.
In the Crypto market, a pair is just an asset expressed in terms of another. For instance, the STEEM/BTC pair could be explained as STEEM expressed in terms of BTC.
A pair consists of two assets which are functionally classified as a "base" asset and "quote" asset. In our example, STEEM is the base asset while BTC is the quote asset. This implies that the price of STEEM will be "quoted" in terms of BTC.
For example, it can be confusing to beginning traders when the price of STEEM/BTC is displayed as (0.00001668). What this means is that 1 STEEM is worth 0.00001668 BTC. These pairs act to reconcile market transactions. That is, for a buy trade, you're literally selling some STEEM to stack up some BTC, and for a sell trade, you sell BTC to stack up some STEEM (Cause you to feel STEEM is about to moon).
This is the same concept for a trading pair such as STEEM/USDT with a price of say, $10.56. It is simply interpreted as
1 STEEM = 10 USDT.
SUPPORT AND RESISTANCE
In very simple terms, these are market zones that hold the largest amount of orders. It is that point where buyers or sellers are at their peak performances, and they easily come off as inflection points that determine if a market move would continue or change direction.
The support zone acts as the lower limit of the market while the resistance is the upper limit of the market for the period it holds. It is common knowledge that "sell" pressure gets exhausted around support zones, hinting at a possible reversal into an uptrend, and "buy" pressure oftentimes gets exhausted around resistance zones, hinting at possible reversal into a downtrend.
Q3: Important features of an Orderbook with (screenshots).
My Verified Binance Acccount
The order book is made of two obvious segments coded in two colours - red and green. These two segments hold records for the "BUY" and "SELL" orders prevailing in the market in a particular trading period.
The red coded order book is the "SELL" order book and contains information such as:
- Prices: This shows the various prices sellers are willing to take for the various quantities of the asset demanded.
- Amount: The various amount of STEEM that sellers are willing to sell at various prices.
- Time: The time at which these orders were placed. (Some exchanges do not always include the time )
This segment also contains details of the average selling price and the total market value of 'SELL" orders in the segment.
The green coded Orderbook is the "BUY" Orderbook and it contains information such as
- Prices: This shows the various prices buyers are willing to give for the various quantities of the asset demanded
- Amount: The various amounts of STEEM that buyers are willing to buy at various prices.
- Time: The time at which these orders were placed. (Some exchanges do not always include the time )
This segment also contains details of the average buying price and the total market value of 'BUY" orders in the segment.
Q5: How an Orderbook helps in trading for profit and protects from loss.
An order book is a very useful tool in trade analysis. Here are a few ways the order book can help one make better trading decisions and stay profitable:
Support and Resistance zones:
An order book can reveal the price at which most buying or selling activities are clustered. These points would always pose as inflection points where the market changes direction or breaks forth to new levels. Large volumes of Buy or Sell orders around a price cause a phenomenon known as "BUY/SELL walls." These points also help reinforce the presence of a strong point of inflection at those prices, because orders that are below a BUY wall won't execute until the orders in the buy wall have been depleted. With a proper interaction with the Orderbook, traders will have a much clear picture of the price zones with the most intense market activities, and make more profitable trade decisions as a result.
Supply and Demand conditions:
The order book holds information on the various prices at which buyers and sellers are willing to engage in trade on a particular asset. This can solve the trader's mystery of making unrealistic price predictions at levels that a greater majority of the market participants are not looking at. Which may lead to such traders not having the desired result.
Entry and Exit:
Having a knowledge of the information presented in the order book could help a trader know when to jump into a trade and when to exit the same. For instance, the demand and supply conditions can act to reveal those that are in charge of the market at certain points in time. As the laws of demand and supply, if it turns out that buying (demand) pressure is more than selling(supply) pressure, then there's a tendency that prices will go up in order to mop up the excess demand.
At such a point, a trader that looks into his order book would close his short positions and look for some favorable entries for a long trade.
Spot fake market moves:
With the order book, one can escape the trap of random indicator trade calls by looking up to see if the actual market interaction between buyers and sellers supports the signal suggested by indicators. For example, if trade volumes on the Orderbook are thin, it could indicate that such a trend is not sustainable and it would be wiser if the trader stays out of such a trade.
CONCLUSION
The Orderbook is not just a bunch of real-time trade records to keep track of the various buying and selling prices of an asset, it is also a useful tool that traders can utilize both to aid a less stressful trading adventure, and to make more profitable trading decisions.

It's a wonderful homework! Illustrations are very neat. I have thing or two to learn from you 😉
Thank you.