Homework-Task 1 || Blockchain Wallet- Chapter-1 (@sapwood) - Tarea 1 | Blockchain Wallet- Capítulo 1 by @pablo1601
#
[English]
Good evening everyone! Here I am doing the first assignment from the teacher @sapwood from the Crypto academy!
After a very useful and dynamic lecture I am about to complete the task.
How do I find (or what is the easiest way to find) the block explorer of any Blockchain? Examples
Before I start answering the first question I will start by defining what is meant by Block explorer and this is valid for any blockchain, be it Bitocoin, Steemit, Cardano, Etherum, Tron, etc.
A Block Explorer is a public auditing tool where users can verify each and every transaction that takes place on a Blockchain. This is very important because one of the characteristics of this technology is that all transactions are verifiable.
There is a famous phrase that says:
"Don't trust, verify!
These search engines are the heart of a blockchain.
The easiest way to find a blockchain explorer is through CoinMarketCap which is the site that lists all cryptocurrencies through a constant crawl of the crypto market.
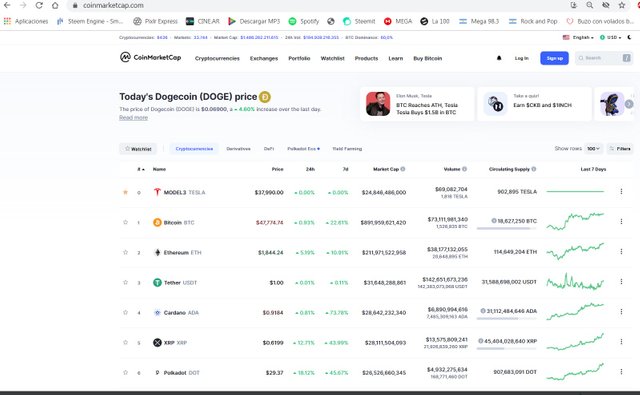
To find the explorer that allows to verify the transactions made in each of the blockchain of the cryptocurrencies just select the crypto that we want to consult, go to the Explorers option and there it will show us which are the Explorers and Blocks for the different Cryptos whose transactions we want to consult.
As an example I show you those of the Steem and Cardano cryptocurrencies.
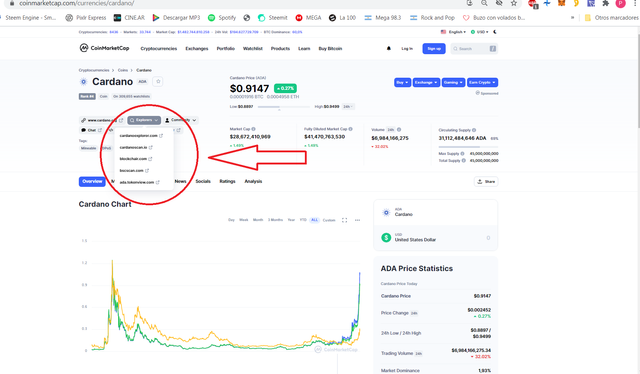
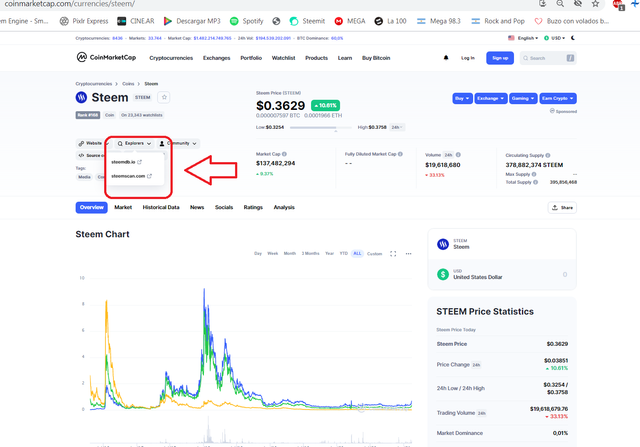
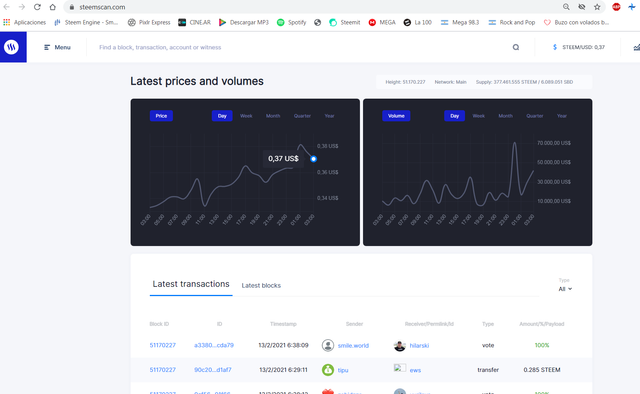
So we can verify transactions of the different currencies
How do I verify the number of commits?
Again to explain how I verify the number of confirmations I first have to explain what confirmations are within a blockchain.
In bitcoin, in order for a transfer to go from pending to processed, the transaction needs to be confirmed. This means that our transaction has been included in a block in such a way that the transaction is irreversible.
Remember that the blockchain is made up of blocks which include thousands of transactions and until that block is mined (included in the blockchain) the transaction is not completed.
The people in charge of adding these blocks to the blockchain are the miners through their computers connected to the Bitcoin network.
Confirmation is then when transactions are included in a block and for each block that follows it, which means that each block that is added to the chain reduces the risk of the transaction.
For example to check the number of confirmations of a transaction in Bitcoin we must go to a Bitcoin block explorer and put the hash of the transaction in the search engine and we will get a detail of the block in which it was included, the status of the operation and the number of confirmations of the block.
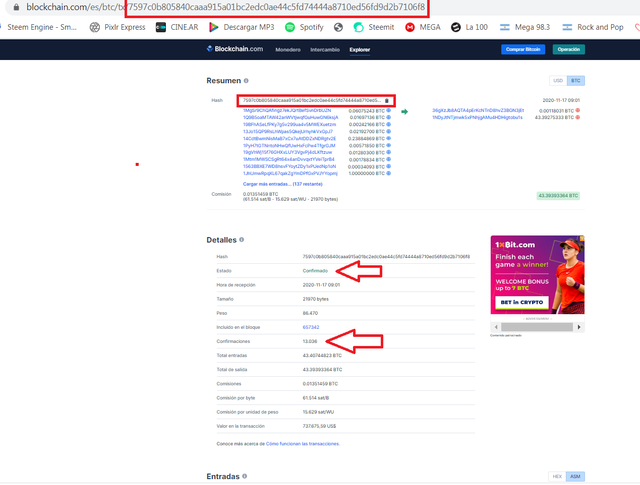
As more blocks are generated within the chain, the number of confirmations will increase.
How do I find the transaction hash, sender address, recipient address, network fees for a particular transaction?
When we make a bitcoin transaction, the exchange or wallet we use issues us a hash of the block in which the transaction was included. If we search in one of the Block Explorers for the Hash of the block, it will issue us a report containing all the information we need.
The hash is the cryptographic cipher and is a unique and unrepeatable number within the blockchain and is the key data to be able to verify operations within the blockchain.
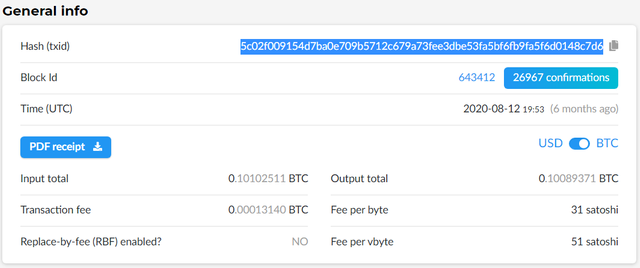
Another basic piece of information for transactions within a blockchain is the addresses of the sender and the recipient. These are the wallet addresses of the sender and the receiver of the bitcoin. These addresses are public.

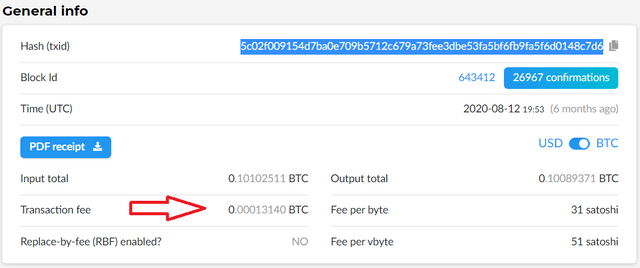
The network fees of a transaction are the fees charged by the miners for the work they do to validate the transactions and mine the blocks of the chain and this is shown in the detail of the block that we have verified.
How do I verify if a wallet address is valid for a network or not (using Block Explorer)? Examples
To verify the validity of a wallet address we do it through the same Block Explorer, entering in the search engine the address of the bitcoin wallet in this case as seen in the following image.
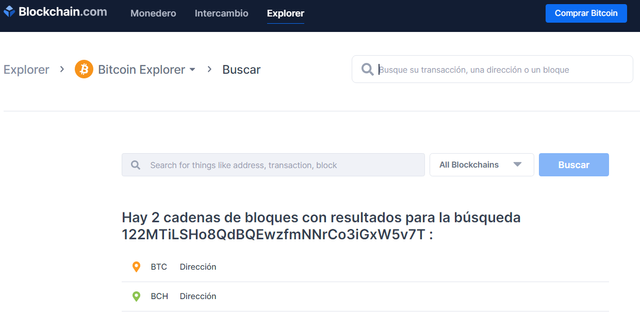
Here I searched for the following wallet address (122MTiLSHo8QdBQEwzfmNNrCo3iGxW5v7T) and got the results shown in the screenshot above. This indicates the validity of the wallet address.
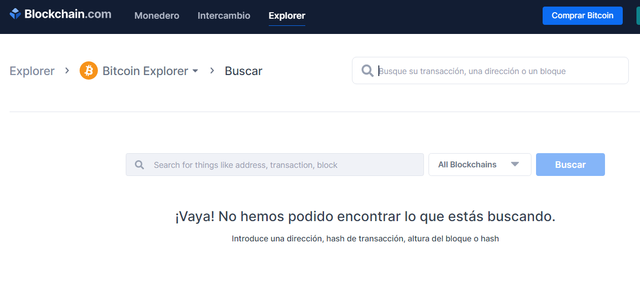
If I change the last letter of the address (122MTiLSHo8QdBQEwzfmNNrCo3iGxW5v7y) and do the search I get the following result:
Thanks to @sapwood for this very clear and didactic class where he allowed us to investigate a little more about already known topics.
Regards
Follow @steemitblog to keep up to date with the latest news.
Thanks @steemcurator01 and @steemcurator02 for the support they constantly give to the whole community.
[Español]
Muy buenas noches a todos! Aquí estoy realizando la primer tarea de l profesor @sapwood de la Crypto academia!
Después de una clase muy útil y dinámica me dispongo a completar la tarea.
¿Cómo encuentro (o cuál es la forma más fácil de encontrar) el explorador de bloques de cualquier Blockchain? Ejemplos
Antes de comenzar a dar respuesta a la primer pregunta comenzaré por definir que se entiende por Explorador de bloques y esto vale para cualquier blockchain, sea Bitocoin, Steemit, Cardano, Etherum, Tron, etc.
Un Explorador de Bloques, en una herramienta de auditoria publica en donde los usuarios pueden verificar todas y cada una de las transacciones que tienen lugar en una Blockchain. Esto es muy importante porque una de las características de esta tecnología es que todas las transacciones son verificables.
Hay una famosa frase que dice:
"No confies, verifica!
Estos motores de búsqueda son el corazón de una blockchain.
La forma más sencilla de encontrar un explorador de bloques es a través de CoinMarketCap que es el sitio en donde se lista todas las cryptomonedas a traves de un rastreo constante del mercado crypto

Para encontrar el explorador que permita verificar las transacciones realizadas en cada una de las blockchain de las cryptomonedas basta con seleccionar la crypto que deseamos consultar ir a la opción Explorers y allí nos mostrará cuales son los Exploradores e Bloques para las diferentes Cryptos cuyas transacciones queramos consultar.
A modo de Ejemplo les muestro las de las moneras Steem y Cardano.




Así podemos verificar transacciones de las diferentes monedas
¿Cómo verifico el número de confirmaciones?
De nuevo para explicar como verifico el número de confirmaciones primero tengo que explicar que son las confirmaciones dentro de una cadena de blockchain.
En bitcoin para que una transferencia que nos han hecho pase del estado pendiente a procesado, es necesario que la transacción sea confirmada. Esto significa que nuestra transacción haya sido incluida en un bloque de tal manera que esa transacción sea irreversible.
Recordemos que la cadena de bloques está compuesta por bloques los cuales incluyen miles de transacciones y hasta que ese bloque no es minado (incluido en la blockchain) la transacción no se ha completado.
Los encargados de agregar esos bloques a la blockchain son los mineros a través de sus computadoras conectadas a la red de Bitcoin.
La confirmación es entonces cuando las transacciones son incluidas en un bloque y por cada bloque que sigue a el, lo que hace que cada bloque que se agrega a la cadena reduce el riesgo de que la transacción.
Por ejemplo para verificar el número de confirmaciones de una transacción en Bitcoin debemos ir a un explorador de bloques de Bitcoin y colocar el hash de la transacción en el buscador y obtendremos un detalle delo bloque en el cual fue incluido, el estado de la operación y la cantidad de confirmaciones del bloque

A medida que se generen más bloques dentro de la cadena el número de confirmaciones irá en aumento.
¿Cómo encuentro el hash de la transacción, la dirección del remitente, la dirección del destinatario, las tarifas de red de una transacción en particular?
Cuando realizamos una transacción de bitcoin, el exchange o la wallet que utilicemos nos emite un hash del bloque en el que fue incluida la operación. Si nosotros buscamos en uno de Exploradores de Bloques el Hash del bloque nos emitirá un informe que contiene toda la información que necesitamos.
El hash es la cifrado cryptográfico y es un número único e irrepetible dentro de la cadena de bloques y es el dato clave para poder verificar operaciones dentro de la blockchain

Otro de los datos básicos a la hora de las transacciones dentro de una blockchain son las direcciones del remitente y del destinatario. Serías las direcciones de las billeteras de quien envía y quién recibe los bitcoin. Estas direcciones son públicas.

Las tarifas de red de una transacción son las comisiones que cobran los mineros por el trabajo que realizan al validar las operaciones y minar los bloques de la cadena y esta figura en el en el detalle del bloque que hemos verificado.

¿Cómo verifico si una dirección de billetera es válida para una red o no (usando Block Explorer)? Ejemplos
Para verificar la validez de una dirección de wallet lo hacemos a través del mismo Explorador de Bloques, introduciendo en el buscador la dirección de la billetera de bitcoin en este caso como se ve en la siguiente imagen.

Aquí busque la siguiente dirección de wallet (122MTiLSHo8QdBQEwzfmNNrCo3iGxW5v7T) y me arrojó los resultados que indican la captura anterior. Ello me indica la validez de la dirección de la billetera
Si en cambio le modifico la última letra a la dirección (122MTiLSHo8QdBQEwzfmNNrCo3iGxW5v7y) y hago la búsqueda me da el siguiente resultado:

Gracias a @sapwood por esta clase tan clara y didáctica donde nos permitió investigar un poco más sobre temas ya conocidos.
Saludos
Segui a @steemitblog para enterarte de las novedades que se vayan sucediendo
Gracias @steemcurator01 y @steemcurator02 por el apoyo que dan constantemente a toda la comunidad
Excellent. I really loved reading this piece. Very precise and to the point. Awesome. Keep it up!
Very well said, that is unique to a particular transaction.
Thank you.