Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 4 - Homework Post for [@awesononso] Blockchain Forks
It is a good day for me, and I am happy to be here again. Today, without wasting much time, I will be writing on the assignment by @awesononso. In this assignment, I will be explaining in detail the work Blockchain Fork. I hope you enjoy the entire ride.

What is a Fork? (In your own Words)

A fork is an upgrade/change to the protocol in a blockchain. I have heard of the word Fork in several scenarios ranging from a simple upgrade in a chain(soft fork) to a split in a chain as a result of a disagreement between miners/witnesses(Hardfork). In some cases also, when a new blockchain starts using the same protocol of a previously existing blockchain, it is often regarded as a fork of the blockchain (codebase fork).

Explain in detail what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).

The change in rules, protocol updates leading to an irreversible action on the entire blockchain protocol causing a split whereby blocks produced in the old blockchain are regarded as invalid while the blockchain regards blocks produced following the new rules as valid. In other for nodes/witnesses/miners, to participate in the validation of blocks in the new blockchain, they need to upgrade their software to the new software. Once the rules have been created and nodes have applied the upgrades, other miners who do not follow the upgrades will be immediately considered as invalid miners while new miners will not be able to mine in the old blockchain as well.
Example: Ethereum Classic
Ethereum is regarded as Bitcoin's sister coin since it is the second blockchain to exist after Bitcoin experienced a Hardfork which led to the birth of Ethereum Classic. Ethereum Classic was created after the hack on Ethereum which caused the Dao to lose $50M in ETH. The Hardfork occurred on 15 July 2016 at the 1,920,000 block creating the new blockchain ETC. Ethereum Classic still uses "0x" at the beginning of its address and both Ethereum and Ethereum Classic share blockchain history until the block of the split.

Explain in detail what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).

Soft Fork is the most frequent type of fork but it doesn't get the news presence like the hard fork, this is because it doesn't require a split in the blockchain. Soft Fork is an upgrade on the blockchain protocol/chain that can be reversible. Most times, it is aimed at increasing speed and scalability, or for improvement of security. With a soft fork, all new blocks are regarded as valid and the majority of miners/witnesses upgrade to the new protocol. With a soft fork, both nodes that have been upgraded and nodes that haven't been upgraded can communicate with themselves validating blocks on the chain.
Example: Bitcoin SegWit
Segregated Witness is a very good example of a soft fork in a blockchain. SegWit is an upgrade done on the Bitcoin Blockchain and it was aimed at improving the way transactions are in the Blockchain. The upgrade is an improvement to separate witness signatures from inside the block so as to increase the number of transactions that can be held in a block.

What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?

Although both Hard Fork and Soft Fork have to do with an upgrade on the blockchain, they differ in so many ways and this includes:
Hard Fork upgrade creates a new blockchain while Soft Fork is an upgrade that doesn't create a new chain.
In Hard Fork, all blocks from the parent/old blockchain is rendered invalid in the new blockchain, but Soft Fork validates the blocks continually.
Upgrades in Soft Forks are reversible while upgrades in Hard Fork are irreversible.
Hard Fork Requires nodes to agree to the protocol in other to validate blocks but for Soft Fork not all nodes have to agree, it is a matter of Majority.

Bitcoin Cash

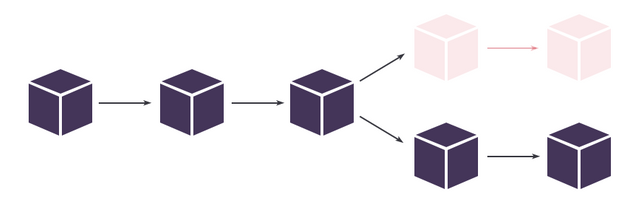
Bitcoin Cash Hardfork is a fork of Bitcoin which occurred in August 2017 with the aim of increasing the block size of the blockchain from 1MB to 8-32MB. The Bitcoin network was very slow and this led to suggestions of increasing the block size. Size it required a consensus, a few miners agreed to it while the rest didn't like the idea. This led to a split in CHAIN creating two chains with the new chain having a new currency BCH.
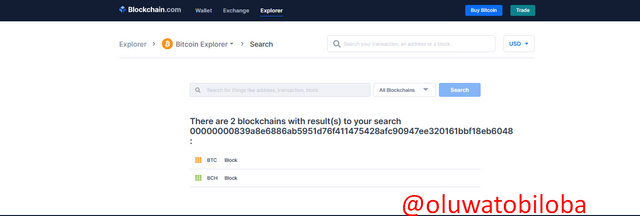
Both chains share history in the past until the Fork which caused a split in both chains. With this, blocks and transactions will be the same; for example the transaction ID 00000000839a8e6886ab5951d76f411475428afc90947ee320161bbf18eb6048 can be found on both BTC and BCH.

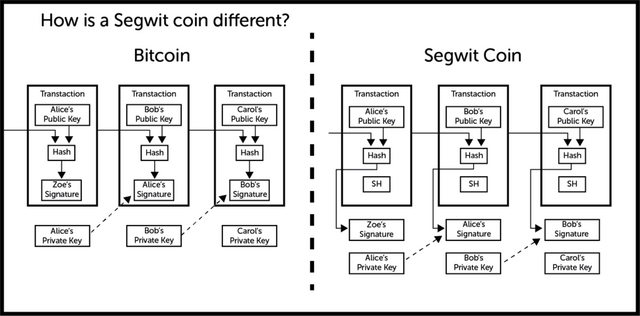
Segregated Witnesses

Segregated Witness (SegWit) is a soft fork that occurred after the hard fork of BCH. It was implemented in 2017 after it was proposed by Pieter Wuille in 2015. Contrary to Bitcoin Cash, SegWit still functions on the Bitcoin blockchain and although the address is different from the Legacy Bitcoin, they still co-exist on the same blockchain. With SegWit, the block size is increased.

Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks(Provide screenshots).

Steem is a blockchain that uses the Delegated Proof of Stake protocol. Founded in 2016, it was one of the major blockchains in the social media industry but after a change in ownership of stake and the partnership of Steem and Tron, Witnesses started to question the transfer of ownership and the purpose of the stake transferred. After a long heated to and fro with the Witnesses, a few Witnesses decided to create a fork chain known as HIVE. Both chains look alike and they both share history together until the fork. Both have interfaces that look alike, to visit the Steem interface, click on https://steemit.com and to check the hive interface, click on https://hive.blog.
To check for the genesis blockchain of both chains, you need to visit their block explorers. To check for Steem, you visit https://steemworld.org/ and to check that of Hive, you visit https://hiveblocks.com/
- To check the genesis block of Steem, click on https://steemworld.org/, log into the website.
- Click on Block Explorer to get to the Block Explorer page
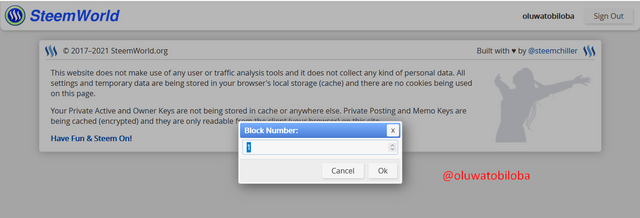
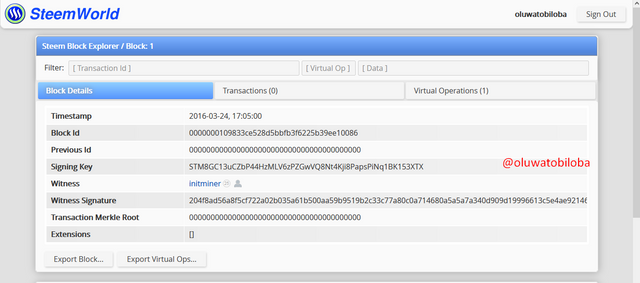
- To search for the first block, search for 1 and the block will show up.
To check the Hive genesis block, click on https://hiveblocks.com/
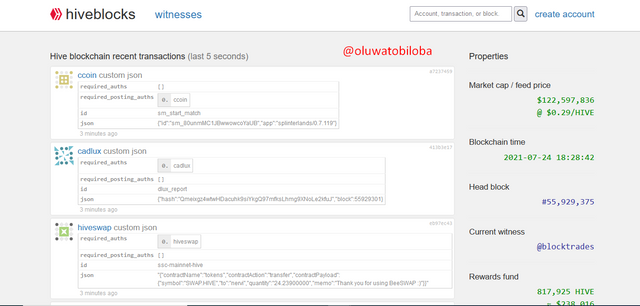
- On the search page, you click on 1 and the block shows up.
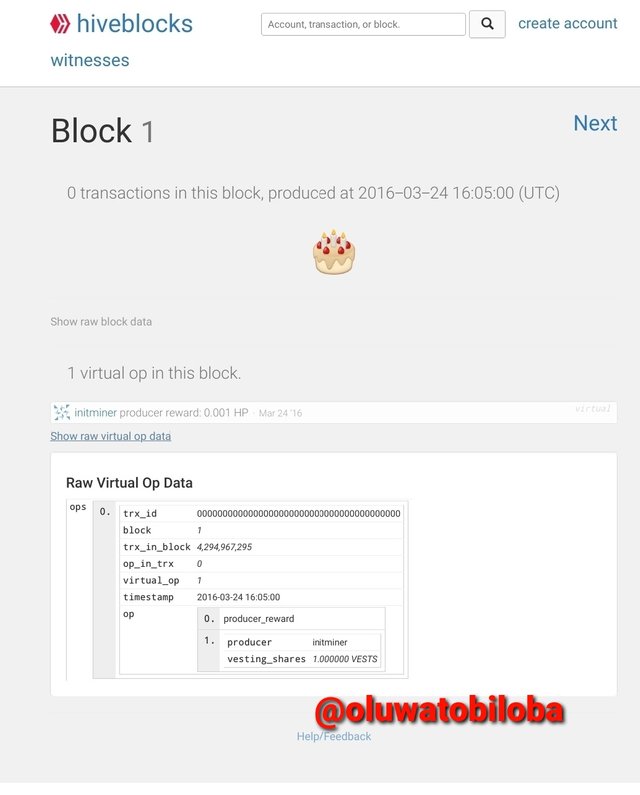
There are major similarities between the both chain ranging from the miner/Witness that mined the first block @initminer, then the ID of the block which is 0000000000000000000000000000000000000000, and Block 1.

Conclusion

Forks are a very important part in a blockchain as it is required to implement upgrades on the blockchain and in some cases, it could be the split of a blockchain (Hard Fork).
Both could be beneficial and some cases detrimental but when soft Forks are a failure, it can be reversible but when fork chains are a failure, the project dies and it is irreversible.
Hello @oluwatobiloba,
Thank you for taking interest in this class.
Unfortunately, this account has been blacklisted and therefore is not eligible to perform tasks in the academy.
Hello, I rectified the issue of account being owned by one person last week and I have written posts after this that has been validated. Please confirm again.
Thanks