Blockchain Trilemma - Crypto Academy / S5W2 - Homework post for @nane15.

(1) Explain in your own words what the Blockchain Trilemma is.
(2) Is the Blockchain Trilemma a Trilemma?
(3) Define the following concepts in your own words:
A. Decentralization
B. Scalability
C. Blockchain Security
(4) Based on your knowledge, explain at least two viable solutions to the challenges posed in the Blockchain Trilemma.
Conclusion.

INTRODUCTION: Good day @nane15 and welcome to my homework post for season 5 week 2. This is a beautiful lecture and you did a good job in making everything understandable. Thanks for imparting knowledge.


Before I go ahead to explain what Blockchain trilemma is, I will like to shed some light into what the two words that made up the term which are the blockchain and trilemma. Understanding these two words will make one have a better grasp of what blockchain trilemma is.
What is blockchain? I know by this time the word blockchain is no longer new to us as the technology has undergone a wide application and with this, I mean the technology is being used to solve several problems or issues around the world today.
Blockchain can be defined as a mode or system of recording information in such a way that makes it very difficult or probably impossible to hack or edit the information recorded. It is a digital ledger of transactions that are duplicated as well as distributed over the entire network of computer systems(nodes) on the blockchain. Several transactions are recorded in each block, and every time a new transaction occurs on the blockchain, the transaction will be recorded and added to every participant’s ledger.
And lastly, Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology in which transactions are recorded using an immutable cryptographic signature called a hash.
What does Trilemma mean? A trilemma can be defined as a situation in which two choices can be made between three options that seem equally undesirable.
Now, what does blockchain trilemma means?
Blockchain technology has brought about a lot of changes to the financial sector majorly. It is with this technology that financial transactions can now be carried out in a more transparent, secured, and fast manner. It eliminated the involvement of intermediaries or anything call central authority while carrying out a transaction and this makes it cost-effective. Despite it being more effective, the blockchain trilemma is a major obstacle encountered by this technology.
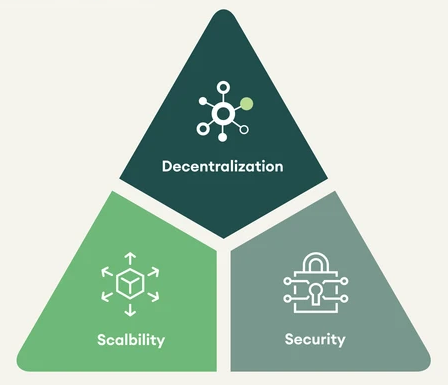
Blockchain technology is characterized by three main features and with this I mean whenever we are talking about blockchain technology, then we must be talking about Decentralization, Security, and Scalability as these are the core features. These three features are what made up the blockchain trilemma.
Blockchain trilemma is a concept or term that was coined by Vitalik Buterin. It can simply be defined as an issue encountered by developers when building blockchains and from some of the blockchains that have been created, we can see that more often than not, developers are forced to sacrifice one aspect of this issue for the sake of the other two aspects.
Blockchain trilemma is simply a word that describes the difficulty encountered by developers in integrating these three main features on the blockchain technology concurrently. It is a situation where they have to pick two out of these three features and I believe the global adoption of blockchain technology depends on if this problem can be resolved. The blockchain trilemma I believe is a problem that that has been in existence ever since the creation of blockchain itself but it was only the evolution of technology that makes it glaring.


From the definition of the Trilemma given above, a trilemma is a situation whereby it will be nearly impossible or let me say impossible to choose or implement the three main options that constitute the trilemma.
In the case of blockchain trilemma, this is not so as due to the evolution of the blockchain technology, the issue posed by this trilemma is being overcome gradually and with this, I can say the word blockchain trilemma was just used to denote the importance and the level of difficulties of these three terms.
Another reason why to me it isn’t a trilemma is that we can have these three features only that one of them will be compromised to some extent.
Though the blockchain trilemma has not been fully resolved by any blockchain network, it is an issue that can be addressed

(A) Decentralization : (B) Scalability : (C) Blockchain Security



Decentralization can simply be defined as this feature that eliminates the essence of third parties in a financial transaction. Looking at the origins of blockchain technology, we can see that the main reason for inventing this technology is for it to be decentralized i.e., to eradicate the involvement of any central institution or authority while carrying out a transaction. In a decentralized market, every user has power based on their assets to make decisions.
To understand what decentralization means and why it is an important aspect of blockchain technology, the following are some things to know.
It eradicates Central authority: The involvement of an intermediary or third party for the authorization of a transaction is no longer needed as this is taken care of by smart contracts.
It enhances transparency: Decentralized blockchain networks are characterized by a ledger in which all transactions are recorded it is open to all. Since it is open for all, then anybody from any part of the world can interrogate or check every transaction detail.
It makes present-day financial transactions permissionless and borderless completely: A decentralized blockchain network is permissionless as nobody signature is needed for the processing or authorization of a transaction since smart contract does the job and also, it is borderless as there is no need for the user to go through any long or series of verification before gaining access to this system and also since they can also be accessed anywhere in any part of the world or by anyone.
It reduces risk: We should know that elimination of the third party is the characteristic of a decentralized blockchain network which helps in reducing risk as there will be no form of error or mistake which might bring about losses of one’s assets. In another word, a decentralized blockchain network is pretty much secured.
It enhances financial inclusion and also brings about fast transactions and low transaction fees.
From what has been explained above, we can see that highly decentralized blockchain networks will exhibit high security, and with this, it is the scalability feature that will be affected just as depicted in the image below.
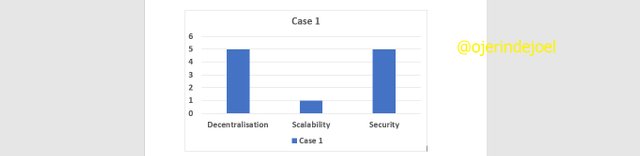


Scalability can be simply be defined as the ability of a system to handle a growing amount of work. It is a measure of how a blockchain network process a transaction. Scalability is probably the most problematic feature to integrate into modern blockchain networks that must be decentralized and why is this so? This is because, in a decentralized blockchain network, there are a lot of nodes (a node is a computer connected to a blockchain network and can perform some functions like creating, receiving, or sending information.) that can initiate a transaction, and the greater the number of nodes, the greater the no of transaction and this affect how scalable the network is.
From the explanation given above, we can say that decentralization and scalability are inversely proportional. Scalability increases as decentralization decreases and vice versa just as depicted in the image below.
Below are the advantages of having this feature incorporated on a blockchain network.
It enables the network to support a higher workload and function normally under perhaps extreme conditions and without charging high fees.
It helps some specific protocols that require support for a high number of transactions such as gaming, social platforms, messaging apps, video streaming platforms, etc.


Security can simply be defined as a condition of not being threatened in any ramifications. Without security, blockchains would be completely useless as everyone would be able to disrupt ledgers and even manipulate them. Blockchain technology makes use of what we call cryptography to ensure security.
What is cryptography? Cryptography can be defined as the study of securing communications from unauthorized individuals.
This cryptography exhibited by this technology entails the following features,
It entails Confidentiality i.e., it is the intended recipient that can only decrypt or access the contents of the sent message.
It entails non-repudiation and with this, I mean that the sender of the message cannot at any time say he didn’t send the message or deny in the long run his reasons for sending or creating the message.
It entails Integrity and this means that data sent using cryptography cannot be manipulated in any way.
Lastly, it entails Authenticity and this means that both the sender and the recipient can verify each other’s identities.
All these features listed above ensures secure transactions.
Cryptography can be divided into three which are the Secret Key Cryptography, Hash Functions, and the Public Key Cryptography. Now let us quickly see what each type is.
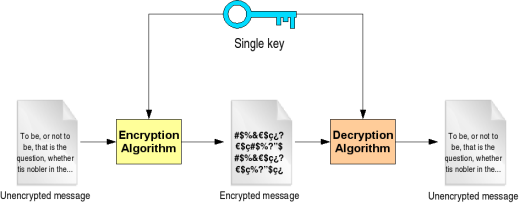
Secret Key Cryptography
This is a type of cryptography that is symmetric, and with this, I mean that only a single key is used for both encryption and decryption and some examples include AES, DES, Caesar Cipher.

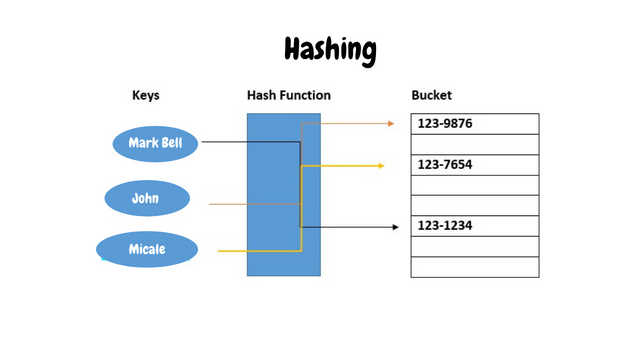
Hash Functions
Hash functions can be defined as the irreversible, one-way functions that protect the information. A hashing algorithm should produce different outputs even when the same thing is inputted and examples include MD5, SHA-1, etc.

Public Key Cryptography
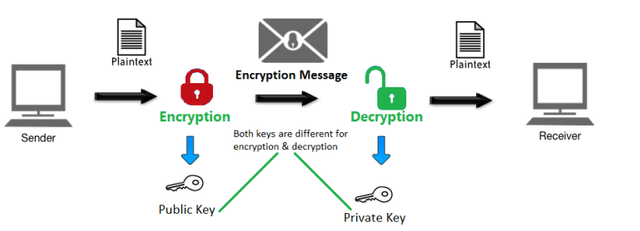
Whenever a transaction is made, it is recorded in an immutable block and this block gets validated based on the type of consensus mechanism. Blockchain technology can only exhibit a high level of security together with either decentralization or high scalability.
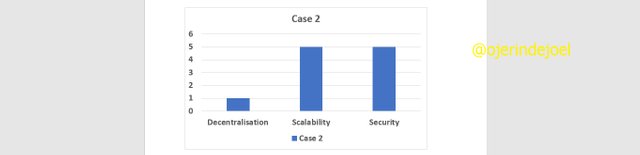
For a Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism which is the mechanism exhibited by the Bitcoin network, Ethereum 1.0, and some other networks, these networks are characterized by a high level of security, high decentralization but with a low level of scalability just as shown below.

For a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism which is the mechanism exhibited by SOL, Cardano network, and some other networks, these networks are characterized with a high level of security, high level of scalability but a low level of decentralization just as depicted in the image shown below.

We should know that security is the only fundamental part that a blockchain network requires to work. Without security, the network can be disrupted by malicious users by controlling a major portion of the nodes or by manipulating the ledger’s data.
The security aspect is that aspect every user of this technology will always look out for as without security, blockchain networks are completely unreliable and also useless and this also makes it a very important aspect that developers cannot just overlook too. Just as already explained above, it is either security and decentralization or security and scalability.


Just as learned in the lesson, the blockchain trilemma solutions can be classified into layer 1 and layer 2. Just as we know that the essence of blockchain technology is decentralization and also without security this technology is useless and with this, most of these solutions that will be explained later are on how to improve the scalability features.


Layer 1 refers to the blockchain protocols like Bitcoin, Litecoin, etc., in the decentralized ecosystem.
Consensus Protocol improvement
Just as stated earlier, the proof of work is the consensus mechanism that is used on popular blockchain such as Bitcoin. Although this mechanism is secure, it is slow i.e., less scalable, and using Bitcoin as a practice case, only seven transactions can be made per second and this is what brought about the invention of Proof of Stake (PoS). Here, instead of requiring miners to compute cryptographic algorithms using computing power, the proof of stake consensus mechanism or protocols determines a validator based on one’s stake in the network and this is to increase the capacity or scalability while increasing decentralization as well as also ensuring security.Sharding
This is one of the most popular layer 1 solutions. Here, transactions are broken into smaller data sets which are called shards, and these shards are simultaneously processed in parallel and this allows numerous transactions to be validated concurrently. Also, instead of having each node hold a copy of every block from the genesis block up to the latest block, this could be split and held by different nodes and this will bring about high scalability.


Layer 2 refers to a network technology that works on an underlying blockchain network just to improve the blockchain network’s scalability as well as its efficiency. Examples include the Lightning network.
State channels
This encompasses two-way communication between a blockchain and off-chain transactional channels using different mechanisms just to improve the transaction capacity as well as speed. Also, State channels do not require immediate miners to validate transactions since it is a network of adjacent resources that make use of a smart contract mechanism.Nested Blockchains
Just as the name implies, this involves building multiple interconnected blockchains while having the main chain or parent chain. Here, the parent chain delegates job to the child chain and on which after completion will be sent back to the parent chain. This distribution of work will therefore increase the level of scalability.Sidechains
Sidechains are regarded to as blockchains adjacent transactional chains that are used for numerous batch transactions. They make use of an independent consensus mechanism that can be optimized for high speed and scalability. The sidechain will help in improving the weaknesses of the main chain and will as well focus on scalability while the main chain will focus on overall security.

CONCLUSION
Blockchain trilemma is an issue that has been in existence ever since the invention of blockchain technology but it was the recent wide adoption of this technology that makes it obvious. The blockchain trilemma is simply a word that describes the difficulty encountered by developers in integrating decentralization, security, as well as scalability on a network.
However, ongoing innovations which is classified as layer 1 and layer 2 are been put in place to tackle this trilemma and in which some have proven efficient though not 100% efficient but they are still subjected to improvements.