Steemit Crypto Academy | Season 3: Week 8 | Homework post of @stream4u || Let's Open The CryptoGraphy
From our esteemed professor @stream4u's article yesterday, I studied blockchain cryptography, private and public keys, digital signatures, encryption and decryption by keys, and other topics, here's my work task in this aspect. So, without further ado, let's get going.
QUESTION NO 1
Explain the Blockchain CryptoGraphy and mention few names which are the Blockchain Platforms (Few names of the Blockchain Platforms)?
Blockchain.
The word "blockchain" is made up of two different concepts, "block" and "chain." Blockchain is a peer-to-peer system. A block is an analysis of information, also known as data files, and a chain is a public database of these blocks that are kept as a collection.
Cryptography
Cryptography is used to connect these lists, making it the most important and essential prerequisite for building a blockchain. Cryptography is a methodology for establishing strategies and methods to prohibit someone else from obtaining and learning data from personal conversations during a communication. Kryptos and Graphein, two ancient Greek words that mean "hidden" and "to write," respectively, are also used in cryptography. Cryptography is defined by a number of concepts mentioned below.
Encryption is the transformation of unencrypted (ordinary text) into ciphertext (random sequence of bits).
Decryption is the procedure of converting ciphertext to plaintext in the opposite direction of encryption.
Cipher: A cryptographic technique that converts plaintext to ciphertext using a mathematical function.
Key: A little quantity of data is necessary to trigger the cryptographic algorithm's output.
Blockchain platforms.
A few of the blockchain platforms are mentioned below.
EOS blockchain
Binance Chain
Bitcoin Blockchain
Ethereum Blockchain etc.
Q2
Explain the Public Key CryptoGraphy.
Public Key CryptoGraphy.
In digital communications, public key infrastructure (PKI) is used to handle individuality and stability. Public key cryptography, an encryption process that depends on the use of two related keys, a public key and a private key, is at the heart of PKI. To encrypt and decrypt a text, these two keys are combined. Asymmetric cryptography is the pairing of two cryptographic keys in this way. Encryption keys are used in public key cryptography to safeguard identities and data from unwanted access or usage.
- Cannot be made available to the general public since any violation could mean a loss of revenue.
- Because of its existence in the network, it is asymmetric, requiring only one key validation step.
- It's where the purchase is sent and signed.
Explain the Private Key CryptoGraphy.
Private Key
A private key, also called a secret key, is a cryptographic parameter which is used to encode and decode data using a method. Only the key's producers and those authorized to decrypt the encrypted should have access to the private key. In symmetric cryptography, asymmetric cryptography, and cryptocurrencies, private keys are crucial.
A private key is important non-guessable pattern of bits generated arbitrarily or pseudo-randomly. The complexity and length of the private key define how easy it is for an attacker to carry out a fearsome attack, in which they try out several keys until they find the appropriate one.
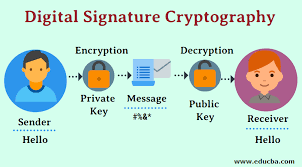
Explain the Digital Signatures CryptoGraphy and what is Singing Of Transaction/Message?
The public-key primitives of message authentication are digital signatures. Hand signatures on written or written texts are prevalent in the material world. They are used to tie the text's signatories.
A digital signature, on the other hand, is a method of tying a person or organization to digital files. The recipient, as well as any foreign entity, can authenticate this commitment.
A digital signature is a crypto number computed from information and a secret key that only the signatory has access to.
Signing of transaction/message:
- Transaction Signing is a new safety step that measures and validates money transfer credentials by using a Digital Protected Key or Secure Key to generate just one confirmation code for a financial exchange.
- It also verifies that whether transaction was initiated by the appropriate entity. The trade is said to be legitimate if all of these conditions are met.
Explain what is Symmetric and Asymmetric cryptography?
Symmetric encryption
Symmetric encryption is a type of encryption in which digital data is encrypted and decrypted using only one key (a secret key). The key must be exchanged between the organisations interacting using symmetric encryption so that it may be utilised in the decryption. This encryption method varies from asymmetric encryption, which encrypts and decrypts data using a key pair, one public and one private.
Data is changed to a state that nobody can understand unless they have the secret key to decrypt it using symmetric encryption methods.
few of famous symmetric cryptographic algorithms are as follows,
Data encryption standard (DES).
Triple data encryption standard (3DES).
Advanced data encryption standard (ADES).
Asymmetric cryptography
Asymmetric cryptography, often referred to as public cryptography, encrypts and decrypts a text and protects it from unwanted entry or use using a pair of linked keys — one public key and one private key. A public key is a cryptography key that may be used by anybody to encrypt messages such that only the rightful owner can decrypt it using their secret key. Only the key's originator has access to a private key, also known as a secret key.
some asymmetric cryptography algorithms are,
- Rivest Shamir Adleman (RSA)
- the Digital Signature Standard (DSS), which incorporates the Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA)
- Elliptical Curve Cryptography (ECC)
- the Diffie-Hellman exchange method.
- TLS/SSL protocol.
How Blockchain Wallets Cryptography works and explains the available types of Crypto Wallets.
Asymmetric-key algorithms and hash functions are the two types of cryptographic algorithms used in blockchains. Hash values are employed to give each user with the capability of a complete image of the blockchain. The SHA-256 hashing method is commonly used as a hashing algorithm in blockchain systems.
A crypto wallets is a safe virtual area where you may store your private keys as well as all of your resources and crypto currency. It is nearly difficult to access your wallets without any of the key once it is misplaced. A private key is used to transfer or move funds in the exchanges wallet and is kept hidden, but the public key is accessible with any device in the network.
The basic categories of exchange wallet are as follows;
1 Hot Wallet.
2 Cold Wallet
Hot Wallet:
A hot wallet is a currency employee's tool for receiving and sending tokens. There have been no designated banks or actual purses for storing cryptocurrency assets, including digital banks. Cryptocurrency wallet are instruments which are routinely used it to store and secure network data, and they exist in a variety of shapes and sizes.
Cold Wallet:
Because it is not connected to wifi, this bitcoin wallet could be hacked. The cold wallets, also known as a "hardware wallet" or "offline wallet," holds the recipient's account and secret address and interacts with appropriate computer operating system. In contrast, a "hot wallet" resides just on user's tablet or smartphone, or in an internet service, which are all hooked up to The internet and potentially vulnerable to hacking. Look into a cryptocurrency wallet.
Types Of Blockchain Wallet:
There are three types of blockchain wallets which includes;
1 Software wallet.
2 Hardware wallet.
3 Paper wallet.
Software wallet.
A software wallet is a bitcoin software that works on your portable hard drive and gives you total reliability and management since each coin you possess is only available on your computer. The Cryptocurrency Organization creates and supports this software, known as Core Processor.
Hardware wallets
Hardware wallets differ form software wallets in that they actually keep your keys and cryptocurrency assets, or on a hard disc, USB drive, and other device. Hardware wallets are ones that don't rely on an internet access to obtain your key.
Paper wallets
Paper wallets are physical wallets that allow you to write both secret key on papers and store them in a safe place. You can also write your keys down on paper and keep them in a safe place. That's also insecure so if the paper is lost, the codes typed or written on this are also lost.
What is the Merkle trees and What its importance in blockchain?
Merkle Tree:
Merkle trees are a data structure commonly utilised in computer engineering. Merkle trees are used to encrypt ledger data more effectively and safely in cryptocurrencies such as bitcoin.
A block of activities is passed through a mechanism in the bitcoin network to produce a hash, which is a sequence of bits and symbols that can be used to verify that even a particular piece of statistics is much like the initial transaction database but not to obtain the original number of data.
Bitcoin's technology, on the other hand, doesn't really run the full block of customer information, on example, represents 10 to 15 minutes' worth of transactions—through the hashing algorithm at once.
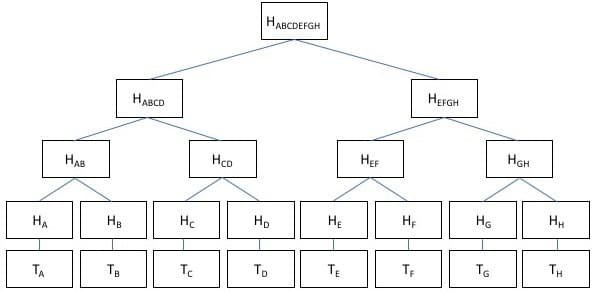
If you looking from the above image of the merkle tree, we can see there are eight activities, as well as the hashing of such eighth exchanges, that are referred to as the leaves.
Merkle tree mixes the hashes of activity A and event B to produce Hash AB, Hash C and transaction D to produce Hash CD, Hash E and incident F to produce Hash EF, and Hash G and session H to produce Hash GH, which are also known as branches.
Those four branches, Hash AB, Hash CD, Hash EF, and Hash GH, now are joined to form Hash ABCD and Hash EFGH, as illustrated in the diagram above.
When we combine the Hash ABCD and Hash EFGH, they have the *Hash ABCDEFGH, which is also called as root hash. As noted previously, the analytical errors store all the hashes of each activity.
Importance of Merkle Tree
A Merkle tree summarises all of the actions in a block by generating an unique signature of the complete collection of transactions, allowing a user to check not whether an event will be included in the block.
Merkle trees are made by hash pairs of node continuously only until one hash remains (this hash is called the Root Hash, or the Merkle Root). They're built from the ground up, using hash of actual accounts (known as Transaction IDs).
Every non-leaf nodes is a hash of its preceding hashes, while each leaf is a hash of data information. Merkle trees are binary, hence an even number of leaf nodes is required.
Practical + Theory, do some practical research, study on Blockchain Demo: Public / Private Keys & Signing and then explain the functionality of Key, Signature, Transaction, Blockchain with proper screenshots of your practical. (Do study well for this topic)
Key.
In cryptography, a key is a set of data, usually a sequence of digits or words kept in a file, that may encode or decode crypto info when handled using an encryption technique. The key can be various sizes and variations regardless of the method used, but in all situations, the encryption's strength is dependent on the key's safety.
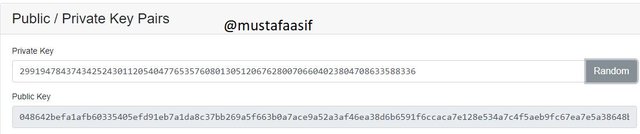
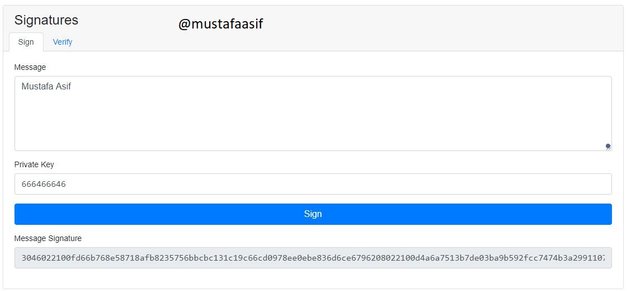
in above screenshot
Private key is 29919478437434252430112054047765357608013051206762800706604023804708633588336
and its public key is
048642befa1afb60335405efd91eb7a1da8c37bb269a5f663b0a7ace9a52a3af46ea38d6b6591f6ccaca7e128e534a7c4f5aeb9fc67ea7e5a38648b12c5c5d645e
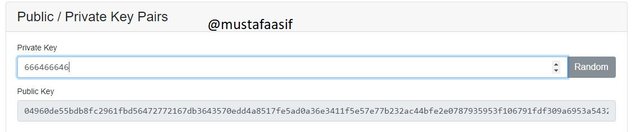
In the above screenshot I changed the private key to 666466646 and its public key is 04960de55bdb8fc2961fbd56472772167db3643570edd4a8517fe5ad0a36e3411f5e57e77b232ac44bfe2e0787935953f106791fdf309a6953a5432ccee5b6f1e9
Digital Signature
A mathematical method is frequently used to confirm the validity and integrity of a message (e.g., an email, a credit card transaction, or a digital document) using a digital signature, which is a sort of electronic signature.
As you can notice in the screenshot image, I've included my username in the text box and also the same private key that I used during the keys. After pressing the sign button, a digital signature will be generated which is,
3046022100fd66b768e58718afb8235756bbcbc131c19c66cd0978ee0ebe836d6ce6796208022100d4a6a7513b7de03ba9b592fcc7474b3a29911076109a6f7735f1718c8567a0bf
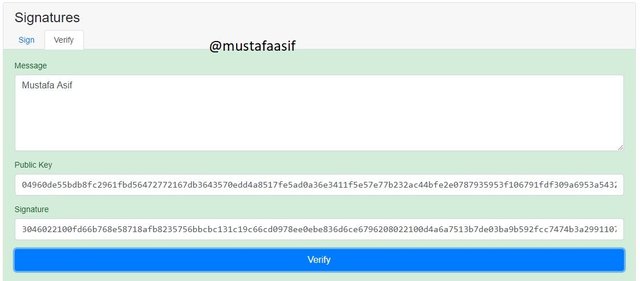
Verify Function:
We must click the verify option, as indicated in the image above, to see if the transaction is verified.
The backdrop colour changes to green as quickly as I click the verify option, indicating that the transaction is genuine or accurate.
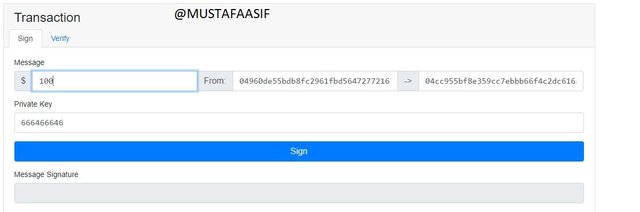
Transaction.
Because I'll be giving $100 to anyone, my public key will be immediately supplied in the from field, and the receiver public key will be placed in the next field. My private key is also included since every transaction requires a persistent secret key. Now, by pressing the sign option, a text signature is generated, which is used in conjunction with the public key to verify the text from the other side. The following is a screenshot:
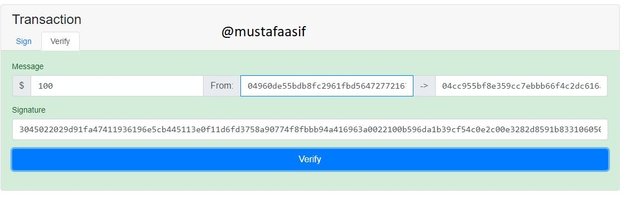
Verify.
To confirm this transaction, simply go to the confirm page and a page will display with the signatures, note, and destination all filled in immediately. All you have to do is to click the verify button to see if it is legitimate or not.
Conclusion. - Overall understanding of CryptoGraphy
Despite several obstacles and challenges, blockchain cryptography continues to evolve across the world. It is becoming increasingly important in keeping personal data secure. It adds another layer of protection to the system. Blockchain cryptography is a foundational technology enabling the networked movement of goods. It's a method of making data private and secure communications so that only the individual who has the key may access it without the intervention of a third person.
Finally, I should say that blockchain cryptography and cryptos are truly a new a kind specialised thing which has decided to make the world today more effective and has bring a sense of advancement to this world today of innovations, and we can anticipate more advancement in blockchain technology in the years ahead.
Cc: @stream4u
#cryptoacademy #stream4u-s3week8 #blockchain #steem #steemit #steemexclusive