Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 4 - Homework Post for Professor @awesononso
WHAT IS A FORK?
A fork can be said to be an update or upgrade on a blockchain network and whenever this happens, the protocol of the blockchain is altered. Because we are living in a dynamic world, people's expectations of a particular system are also dynamic, and so it is with the blockchain network. So to cater for these expectations means that the blockchain network system must be improved. These improvements on the blockchain come in form of fork.
Since this network is a decentralized system, it is important to note that the consent of all of the miners must be gotten before any change can be added to the blockchain protocol, and even for this update introduced to stand, all the connected network users must accept it. Anyone could make the code upgrade at anytime.
EXPLAIN IN DETAILS WHAT A HARD FORK IS WITH EXAMPLES
A hard fork is a type of upgrade on a blockchain that leads to the division of the blockchain into two branches. This means that in the process, a new blockchain is created. One blockchain will continue to work with the original version. The other new blockchain has its own new protocol, new rules and also a new currency too following the new version. After the division, the nodes that are working with the original version will not recognize the new blocks as valid again. And the nodes that are upgraded to the new protocol will no longer recognize the previous chain working with the original version as valid again. This is despite the fact that the two blockchain have the same history, they now work side by side. Its good to note that after the division, the users in the old blockchain will get some coin in the new blockchain.
Example of hard fork
Ethereum hard fork. The first fork that Ethereum went through was the Ethereum Classic (ETC). In 2016, after a vulnerability was discovered within the system which led to approximately 3.6 million ETH being stolen, the hard fork took place so that the developers could take very fast action against the hack and get the money back. The proposal splitted the ethereum ecosystem into two groups. While one group was happy that the developers took action, the other group disagreed saying that the networks' updates compromised its decentralization. At the end of the day, the developers went through with the hard fork, while the old blockchain became known as the Ethereum Classic.
We also have Ether Zero (ETZ) which is another hard fork designed to make transactions completely free.
EXPLAIN IN DETAILS WHAT A SOFT FORK IS WITH EXAMPLES
Soft fork is a type of upgrade on a blockchain that does not lead to division of the blockchain into two. The upgrade simply improves the original version, which means that it is compatible with the original version. The implication is that after the upgrade process, both the former nodes and the upgraded nodes will continue to work hand in glove to establish new blocks on the network. This also means that the new blocks will be recognized as valid by the old ones. We can therefore say that soft fork is backwards compatible with the older version.
Example of Soft fork
SegWit is a soft fork for Bitcoin. SegWit was developed in an effort to speed up transaction times. SegWit was developed as a way to free up space within blocks so that it could be used to hold more transactions. Despite this change, the old blocks of course which do not have the extra free space can still work together with the new blocks. So, no new currency was created.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HARD FORKS AND SOFT FORKS
Hard fork
- Hard fork is backwards incompatible
- There is division of the original blockchain into two branches.
- A new currency is formed because the new blockchain has new protocols.
- All previous transactions are disabled.
- You also notice that new projects are seperated because of disagreements.
Soft fork
- Soft fork is backwards compatible.
- There is no division of blockchain into two.
- No new currency is formed.
- All transactions are supported.
- There are no disagreement as all the miners are ok with the upgrade.
EXPLAIN THE FOLLOWING BITCOIN FORKS AND EXPLORE THE BLOCKCHAIN WHERE NECESSARY. INDICATE IF THEY ARE HARD FORKS OR SOFT FORKS: (A) BITCOIN CASH(B)SEGREGATED WITNESSES
SEGREGATED WITNESS (SegWit)
This is a soft fork. The goal of the SegWit was to minimize the size of each bitcoin transaction so that more transactions could be allowed to take place at once.
BITCOIN CASH
This is a hard fork. The reason for this hard fork was because some miners and developers felt that Bitcoin was too slow because of it's reliance on SegWit. They felt that SegWit was not fast enough, they decided to initiate a hard fork to change that and that resulted to Bitcoin Cash. This new blockchain separated from the original blockchain in 2017.
WRITE ON THE STEEM AND HIVE HARD FORK AND SHOW SIMILARITIES IN THEIR GENESIS BLOCKS
Just like in any other blockchain, the steem blockchain at one time also had a hard fork which led to creation of a new blockchain called Hive blockchain. This happened when TRX was about to be introduced on the steem blockchain. That was not welcomed by everyone. One group accepted while the other group said no. So at the end of the day, the forking led to the creation if the new blockchain Hive. The creation of Hive took place in March 2020. The new currencies on this platform are Hive, Hive Backed Dollars (HBD), and the influence token is Hive Power.
Similarities in their Genesis blockchain.
For the steem, you go to the steemworld.org, I logged in with my username and posting key, then I go to Block explorer, a dialogue box will come up and I clicked OK, the information below will come up.
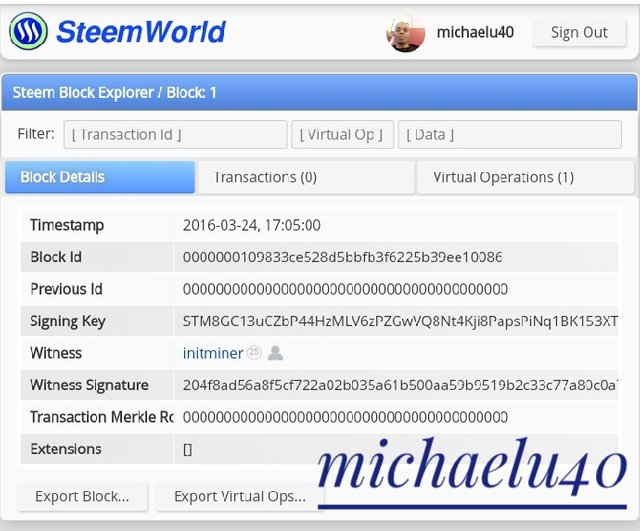
Please note the time and miner identity.
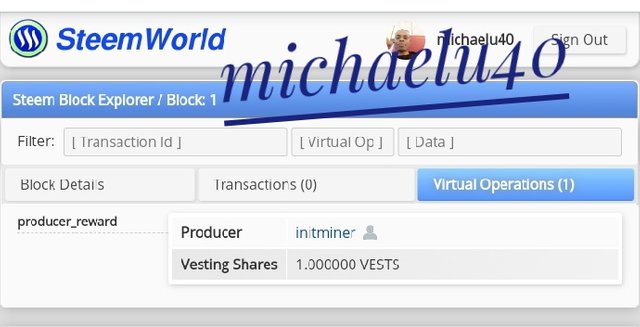
For the Hive, you go to https://hive blocks.com/
Then you search number 1 and you see the following
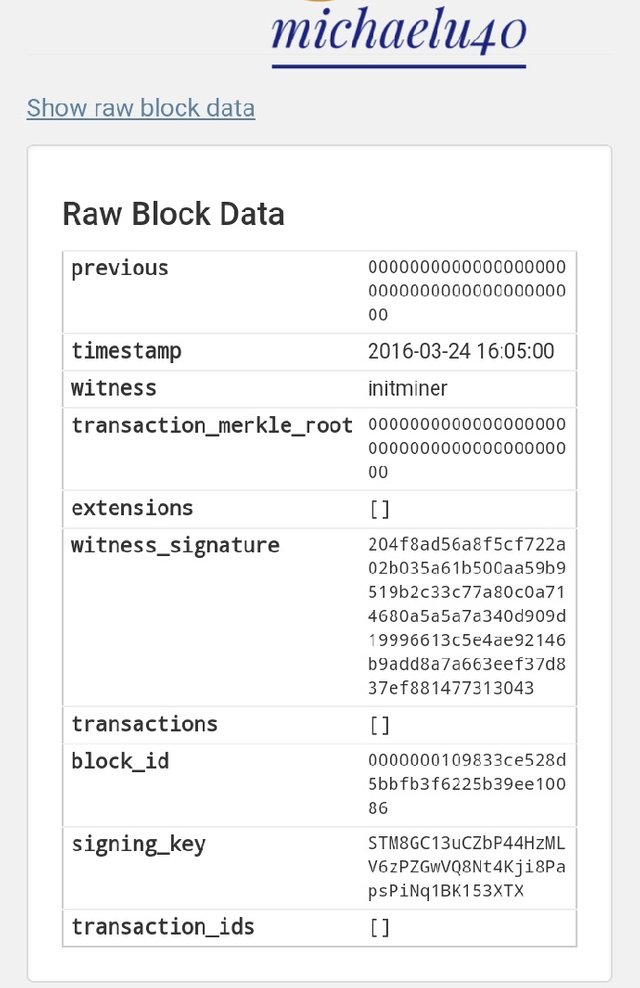
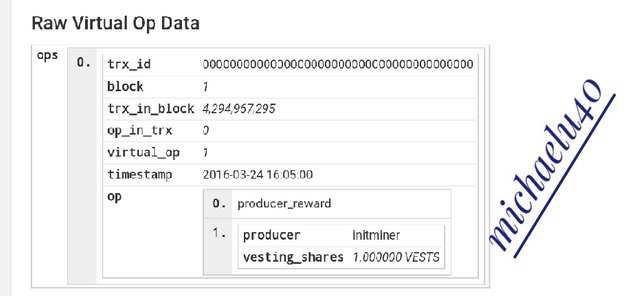
You will notice from the Genesis block of the two blockchain that
- They have the same mining date and time.
- The same miner identity
This is an indication that they share the same history.
I am grateful to Professor @awesononso