Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 4- Homework Post for Professor @awesononso - Topic: Blockchain Forks.
Hello steemains
Happy to be part of this week’s lecture by prof @awesononso on Blockchain Forks. It quite interesting and broad, I'm glad my knowledge for blockchain technology and forking is broaden. Thumbs up for this lecture.

INTRODUCTION
The cryptocurrency blockchains are decentralized systems, with a high level of security and transparency, although can also be imperfect in some areas, as it is being handled and managed by humans who have a limit to everything. Hence, the need for upgrades in the blockchain network are made with the intent of making the blockchain system close to perfection in terms of its efficiency, as such the need of forking comes into play in a blockchain protocol.
Since cryptocurrency blockchain is a decentralized system that gives it's user or shareholder power to decide what happens in a network, with time there is bound to be issues arising, due to the fact that we all have our different point of views to an issue, and some members may object or accept changes made on a blockchain.
Question 1: WHAT IS A FORK? (IN YOUR OWN WORDS)
Bitcoin was the first cryptocurrency created on a blockchain which served as a digital asset, and in no time many cryptocurrencies were created. The emergence of these new cryptocurrencies was as a result of fork.
Therefore, a Fork can be define as a change in software blockchain protocol which leads to a division in the network system. The division can be as a result of misunderstanding between two participants in a blockchain, or for the modification of the blockchain or for the creation of an advanced or upgraded version of a new blockchain from the old blockchain.
Forking is more experienced in cryptocurrency blockchain which is a decentralized system, that gives all the user's and shareholders equal power to vote or make a decision on what happens in the blockchain, as such it is quite difficult to enforce must of these changes on some persons who is not in agreement with the changes. But if a consensus agreement is reach amongst majority of the miner's these changes are accepted and is set on motion in the blockchain. Therefore, when changes are made in a software protocol of any blockchain, we can say that fork has occured and the network system becomes disarrayed, as there will be two-party play in the blockchain. This simply means that, if all the miners of that blockchain reaches to a consensus to completely abandon the pattern of the old blockchain and accept pattern of the newly created one, with time the new blockchain will realign, and the miners will embrace the new features of the blockchain.
However, if a consensus is not reached by all of the miners, and some of the miners decides to continue with the old blockchain pattern, while the other miners follows the pattern of the newly created blockchain, there will be a creation of two versions of the same blockchain.
There are two types of fork; Soft fork and Hard Fork.
Question 2: EXPLAIN IN DETAILS WHAT A HARD FORK IS WITH EXAMPLES (CAN BE OF ANY BLOCKCHAIN).
▪︎HARD FORK
A Hard fork is a type of fork which occurs when the software blockchain protocol is radically changed, resulting in the division of blockchain into two versions of the blockchain, forming a old blockchain and a new blockchain protocol which is incompatible backwards. In simple terms, a hard fork is change when the nodes of the latest version of a blockchain, doesn't accept the old blockchain protocol of a blockchain and leads to a permanent division of the blockchain into two versions.
Miner's who decides to continue mining with the new blockchain works on the modified protocol. The miners using the new blockchain will also be given the same number of tokens they had in the original blockchain(old one), before the change occured in the protocol. And miners in the blockchain who don't approve of the changes made in the blockchain protpcol, will still continue mining with the old blockchain protocol, this is because, the old and new blockchain both share a common origin.
The users/miners who decides to embrace the new protocol will be required to upgrade their software to the newly modified version, so as to be able to verify and validate transactions in the new blockchain, because hard fork is not backwards compatible.
A hard fork can occur in any blockchain, be it Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash or Bitcoin SV.
EXAMPLE OF HARD FORK
▪︎Ethereum Classic and Ethereum
Following the event that happened in 2016, when hackers penetrated Ethereum blockchain and stole $3.6 million worth of ether from the network. When this theft occurred, a meeting was held in the Ethereum blockchain on how to tackle the insecurity in the network that lead to the lose of $3.6 million ether stolen, the idea of forking came on board.
Majority of Ethereum user's approved of the idea of forking the blockchain, while others disapproved of the idea. At the end a consensus was reached to create a hard fork, giving it's users/ miners the liability to choose the software protocol they want to continue with. User's who decided to continue with the original version(old blockchain) did so and named their cryptocurrency "Ethereum Classic"(invalidating all transactions in the already existing blockchain), while Users, who decided to continue with the new blockchain continued with it, and named its cryptocurrency "Ethereum".
After the split, the Ethereum blockchain and Ethereum classic blockchain, both still share same origins. This can be seen, if you visit the ethereum and ethereum classic block explorer, you will see that both have same hash for their Genesis Block 0 and have same records from previous transactions in blockchain before the division.
•Ethereum Genesis Block 0
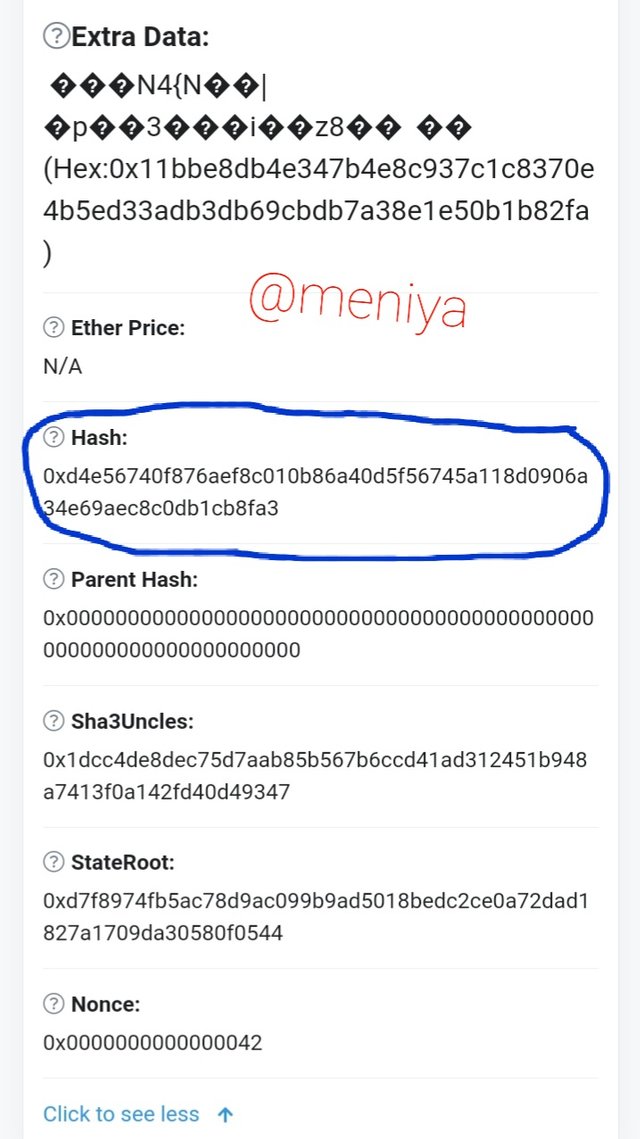
Hash: 0xd4e56740f876aef8c010b86a40d5f56745a118d0906a34e69aec8c0db1cb8fa3
•Ethereum classic Genesis Block 0
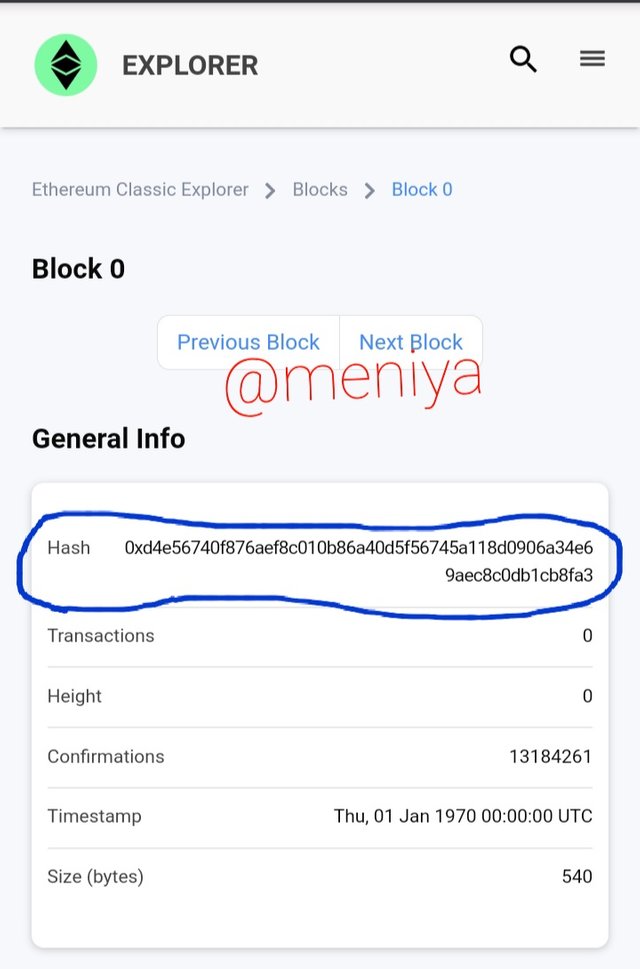
Hash Block 0:
0xd4e56740f876aef8c010b86a40d5f56745a118d0906a34e69aec8c0db1cb8fa3
Also hash of Block 99999 of both Ethereum and Ethereum classic blockchain are still same before the split.
•Ethereum Block 99999
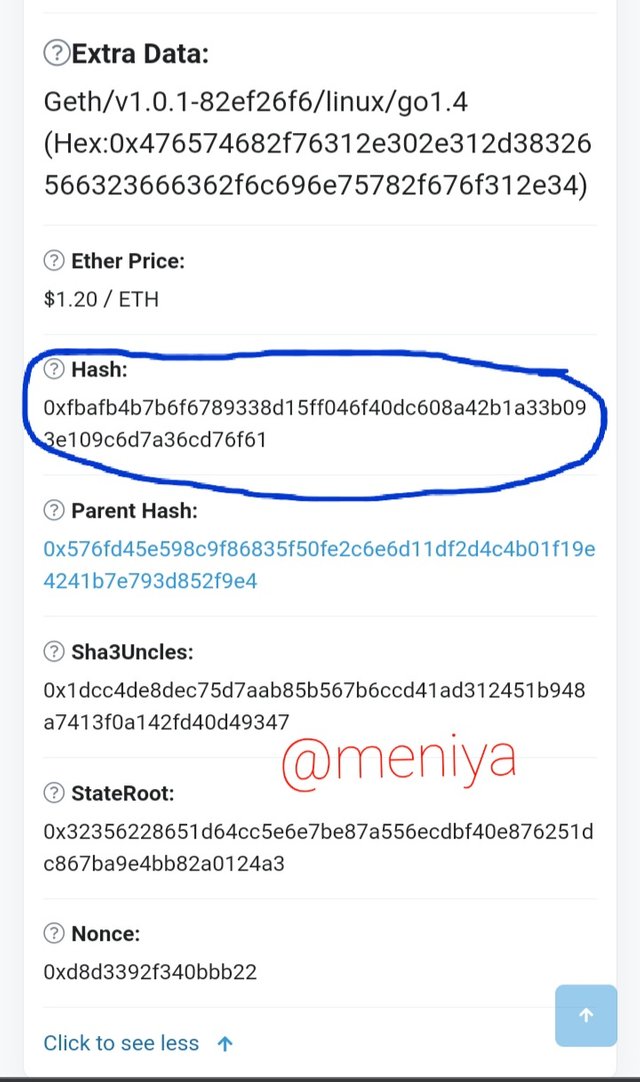
Hash block 99999:
0xfbafb4b7b6f6789338d15ff046f40dc608a42b1a33b093e109c6d7a36cd76f61
•Ethereum classic Block 99999
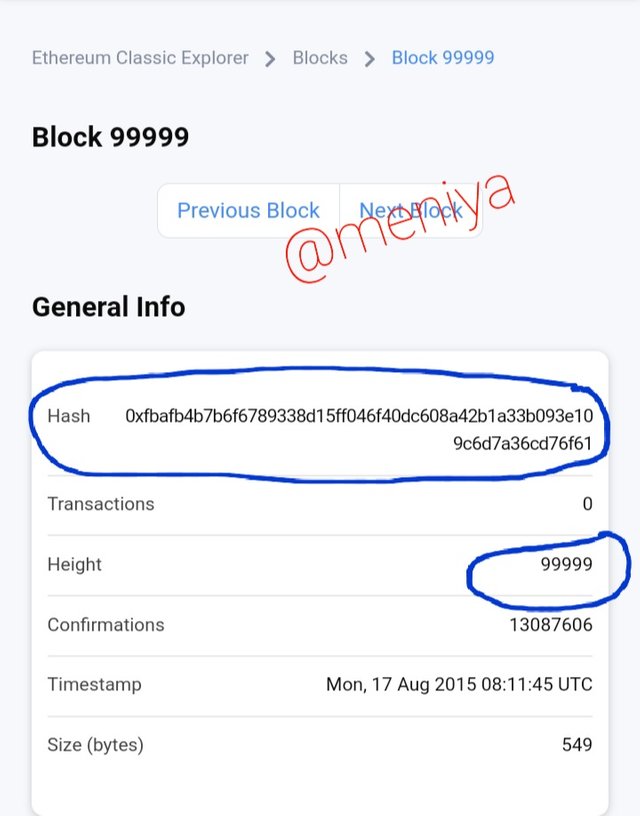
Hash block 99999:
0xfbafb4b7b6f6789338d15ff046f40dc608a42b1a33b093e109c6d7a36cd76f61
However, after the split the records of both version, Ethereum and Ethereum classic blockchains changed, this can be seen from the screenshots below.
For instance the hash of;
• Ethereum block 10,000,001 is: 0x7823fa4da327cf97a9b86da990b0755ebfaa3b490ecd0be80b0ed24106d1a8d7
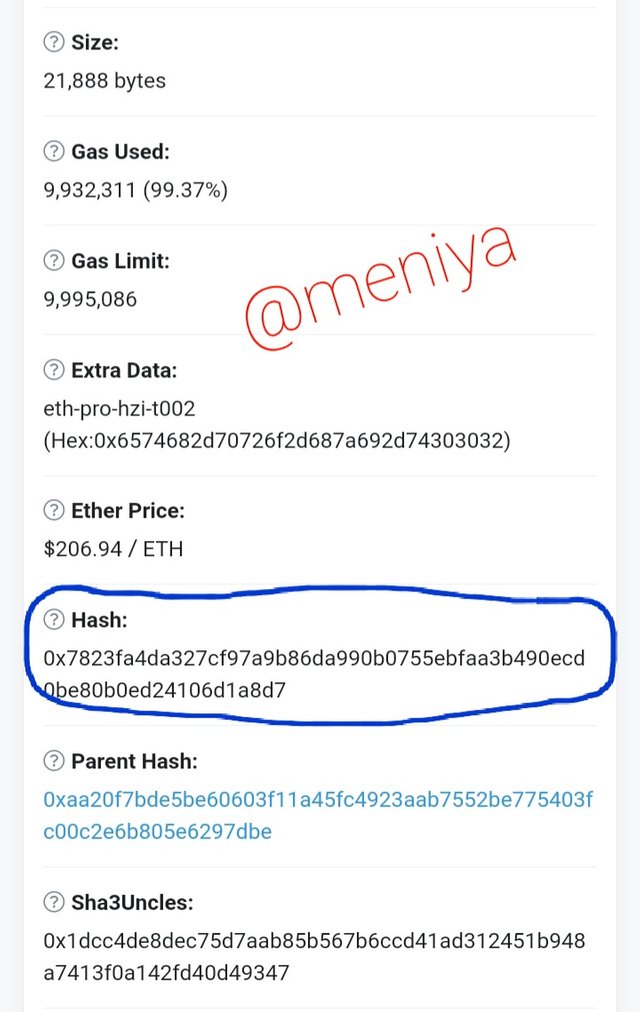
•Ethereum classic Block 10,000,001 hash is:
0xc8d7c80a173a694cc0b67261236920f4147eea02f4e791fd0b712459986ca288
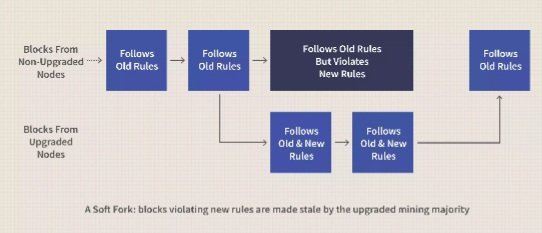
Question 3: EXPLAIN IN DETAILS WHAT A SOFT FORK IS WITH EXAMPLES (CAN BE OF ANY BLOCKCHAIN)
▪︎SOFT FORK
A soft Fork is a change that occurs in a software protocol, where transacations of the old protocol becomes invalid and the new nodes of the software protocol becomes valid, as the old nodes now recognize the new blocks. Even with the change in the blockchain's protocol, both nodes(Old and new) are still compatible with the original version.
which is to say a soft fork is backwards-compatible.
Sometimes soft fork occurs due to a temporary division in the blockchain when miners using the old nodes disregard the rules of new node consensus, which they are not aware of. It is also used in making small modifications like the addition of new features or functions in a blockchain. For a soft fork to be activate majority of the miners in the blockchain must reach a consensus to upgrade the old protocol to the new protocol and miners who do not agree to the upgrade of the new software will have access to verify and validate transactions in the blockchain, since soft fork is backwards compatible unlike hard fork.
•EXAMPLE OF SOFT FORK
▪︎Segregated Witness(SegWit).
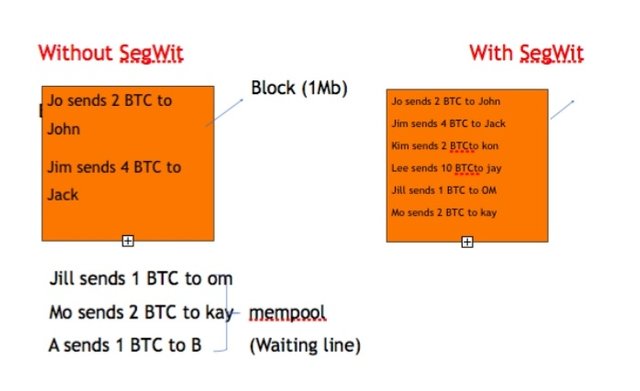
Segregated Witness also known as "SegWit" is a process that limits the size of blocks mined in a blockchain, it is a soft fork of Bitcoin blockchain. SegWit was suggested by some miners, who felt there was no wisdom in constant increase in the size of a Bitcoin's block, as each time the size is being increased, more hardwares will be needed to run a node. As such, Satoshi Nakamoto in 2010, suggested that it was best the size of Bitcoin's block be placed at one megabyte instead.
Segwit is simply a change in Bitcoin's blockchain protocol, which involves the separation of witness data from the input list. The witness data is only required to verify the validity of a transaction data in the blockchain, but is not effective in determining transaction effects. Thus, the removal of witness data doesn't necessarily affect the status of a transaction in a blockchain, but the witness data removal helps in reducing the size of Bitcoin’s block.
Summary of SegWit
Source
Question 4: WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HARD FORKS AND SOFT FORKS?
Following the explanations of hard forks and soft fork above, some of the difference between them includes;
| Hard Fork | Soft Fork | |
|---|---|---|
| With hard Fork there is a creation of a new software blockchain protocol | Soft Fork modifies an already existing blockchain | |
| There is Backwards incompatible with hard fork | Soft Fork is Backward Compatible | |
| The software protocol is immediately upgraded after forking before verifying transactions in the blockchain | Doesn't require upgrade immediately after forking in other to verify transaction in the blockchain | |
| There is repetition of blocks in both the old and new version of the protocol | There is no repetition of blocks, as no new block chain is created, rather the new block follows the protocol of the old block | |
| Requires the consensus of all miners to take place | Requires the consensus of only majority of miners to occur | |
| New cryptocurrencies are created due to hard fork | There is no creation of a new cryptocurrency with soft fork | . |
Question 5: EXPLAIN THE FOLLOWING BITCOIN FORKS AND EXPLORE THE BLOCKCHAIN WHERE NECESSARY. INDICATE IF THEY ARE HARD FORKS OR SOFT FORKS; BITCOIN CASH AND SEGREGATED WITNESSES
▪︎Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash cryptocurrency was created in 2017, as a hard fork of Bitcoin which was created to resolve many issues of the old Bitcoin. Bitcoin Cash came into existence when majority of miners in the Bitcoin blockchain, decided to modify the blockchain protocol by creating SegWit a soft fork and miners who opposed the SegWit idea, hard forked Bitcoin and created a new version of Bitcoin by making minor modifications to the Bitcoin. The hard fork resulted in the division of Bitcoin blockchain into two versions; Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash.
Bitcoin cash was created solely for resolving the time issues in transactions process with Bitcoin. With time the number of Bitcoin users increased which lead the to an increase in the transaction time in the network, making transactions process slow , as such the developers of the Bitcoin blockchain decided to resolve this time issue by generating a hard fork called "Bitcoin Cash" to help mitigate this issue. Bitcoin Cash is more scalable and has high speed for verifying transactions process.
Some key modifications that makes the new blockchain(Bitcoin Cash) different from the main Blockchain(Bitcoin) are:
•The transfer fee cost in the Bitcoin Cash is lower than Bitcoin's the transfer fee.
•Bitcoin Cash is able to carryout large number of transaction per second than Bitcoin.
•Transaction speed of Bitcoin Cash is faster than that of Bitcoin transaction. It takes less time to verify a transaction with Bitcoin cash.
Even after the splitting of Bitcoin, both Bitcoin Cash(BCH) and Bitcoin(BTC) blochains still have same origin. They both have same Genesis block 0 and the same record of history uptill the time of their splitting.
Below is a screenshot showing the hash for Block 0 for both BTC and BCH is:
•Bitcoin Block 0
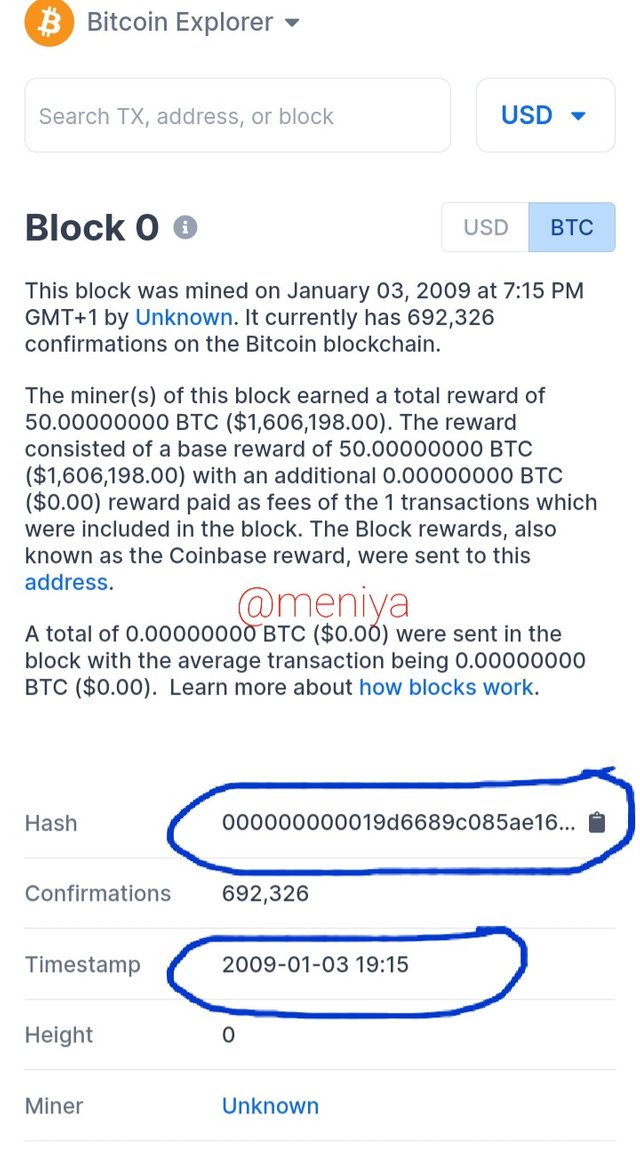
Hash:000000000019d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f Timestamp : 2009-01-03 19:15
•Bitcoin Cash Block 0
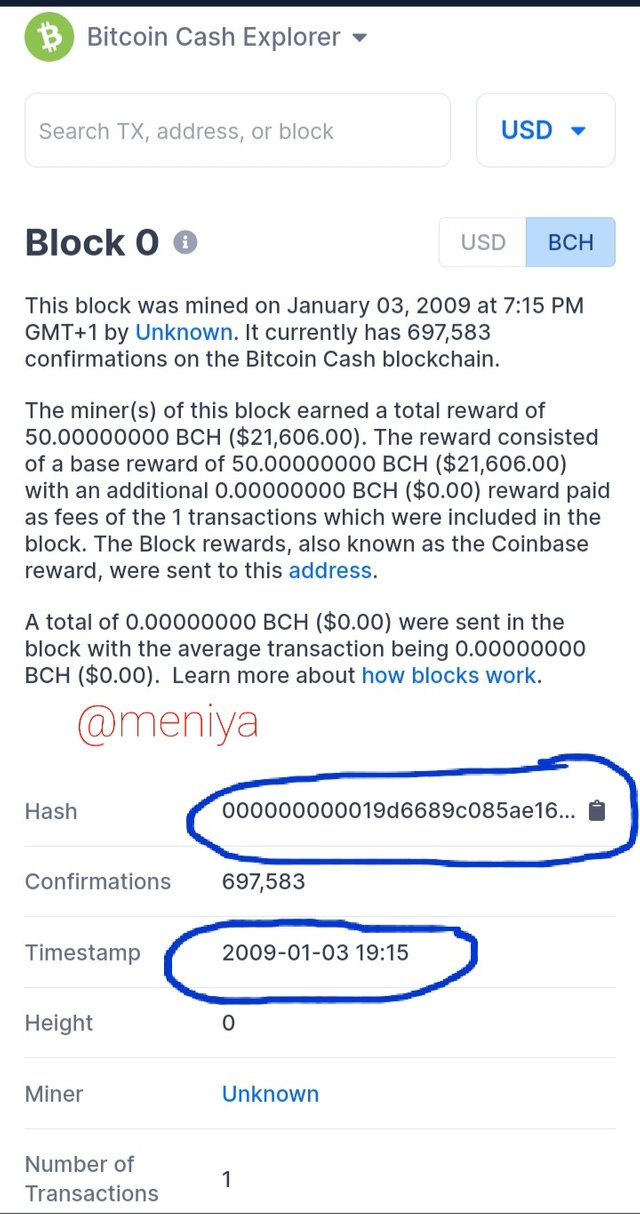
Hash:000000000019d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f
Timestamp : 2009-01-03 19:15
However, the hash of the two blockchains changed after they split in 2017. From the screenshots below we can see the difference in hash and Timestamp of both blockchains of Block 691867.
• Bitcoin Block 691867
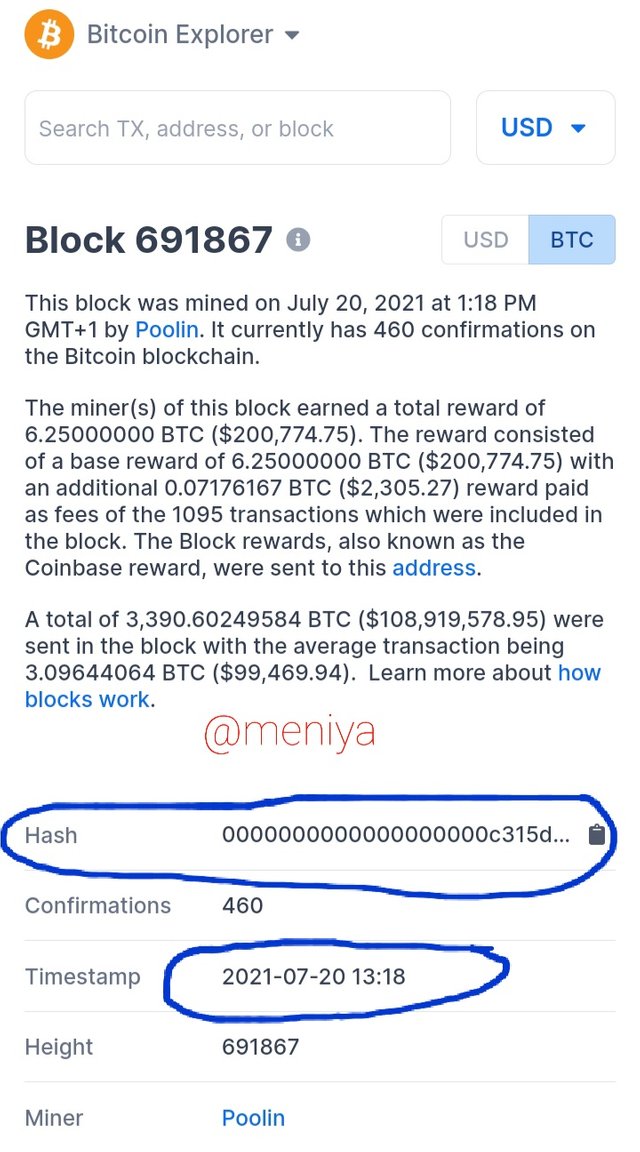
Hash:0000000000000000000c315d1b6143b982d26c5007d190437f54fc77b72c9f91Timestamp: 2021-07-20 13:18
• Bitcoin Cash Block 691867
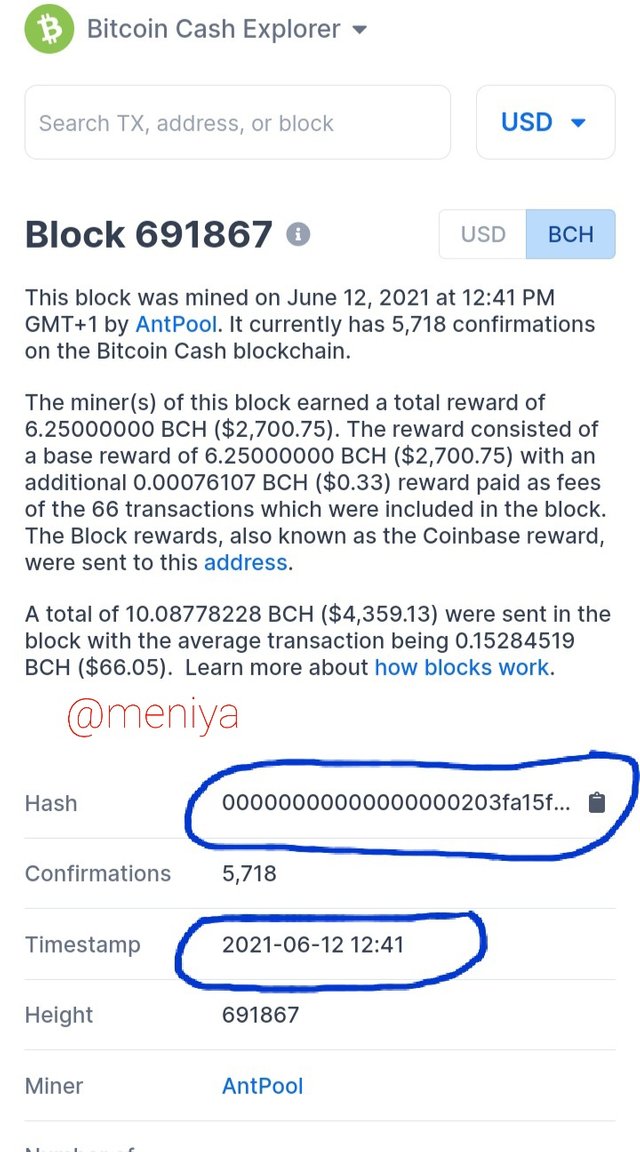
Hash:00000000000000000203fa15f9049b198c205a236f1927f57d879b661ddfc623 Timestamp: 2021-06-12 12:41
▪︎SEGREGATED WITNESSES
SegWit is a soft fork proposed by Bitcoin blockchain in other to limit the constant increase in the size of a Bitcoin block. This is because the shareholders or user proposed a suggestion that there was no wisdom in constantly increasing the size of a Bitcoin's block, as each increase results to the need for more hardwares to run a node in the network and they believed that it was best that the block size of a Bitcoin be placed at 1MB per block.
The idea of SegWit was proposed to make slight modification in Bitcoin's Blockchain Protocol and not for the creation of a new blockchain or a new cryptocurrency. Although this modification is a good one, but there are some participants in the Bitcoin blockchain who disapprove of the Segwit idea, with the fact that the reduction of the Bitcoin block size will also considerable reduce the number of transactions that are carried out in the blockchain per second, and for a cryptocurrency intending to be the number one dominating cryptocurrencies in the world, this doesn't look like a good idea.
SegWit was created the the support of majority shareholders in the blockchain to modify the software blockchain protocol, as a soft fork doesn't require the approval of every participant of a blockchain but just the approval of majority. Miners who were not in consesus with the SegWit idea and have refused to upgrade, are still able to verify transactions in the blockchain, as soft fork is backward compatible. The only limitation these miners who didn't approve of SegWit is that, their functionality is considerably reduced. Which us to say they will are not able to mine a block in the block chain, untill they upgrade their node to the new version.
Question 6: WRITE ON THE STEEM AND HIVE HARD FORK AND SHOW SIMILARITIES IN THEIR GENESIS BLOCKS(Provide screenshots).
STEEM, which is one of the fast rising cryptocurrency in crypto world is a hard fork. Steem hard fork, just like most blockchain happened as a result of a disagreement between the participants of the platform (the new steemit team, and the witnesses). The hard fork occured when Justin Sun, the founder of TRON came into Steemit team, he suggested the integration of TRX into the Steem blockchain. There was a disagreement between the participants,
some participants "the steem witness" especially the"whales" of the witness didn't concur with the idea suggested by the new steemit team. Since Steem is a decentralized system and gives participants equal say or power to what the like, some user's choose to move from steemit platform, and undertook a hard fork on the steem blockchain, which lead to the creation of a new cryptocurrency called Hive. The steem witnesses had copied the open source software of the Steem blockchain to create the HIVE platform.
After the division, the two platforms still looks identical, as only slight modifications were made to the software protocol, such as changing of the cryptocurrency from Steem dollar (SBD) to Hive dollar(HBD), Steem to Hive, Steem Power to Hive Power and also changes in the colours of both platforms from light green(steem) to red(Hive). Apart from these minor modifications, every other previous data or history in the blockchain remained the same. For instance, both STEEM and HIVE platforms have the same Genesis Block
•To check The Genesis block of Steem blockchain, visit https://steemworld.org
•Steemit Genesis Block
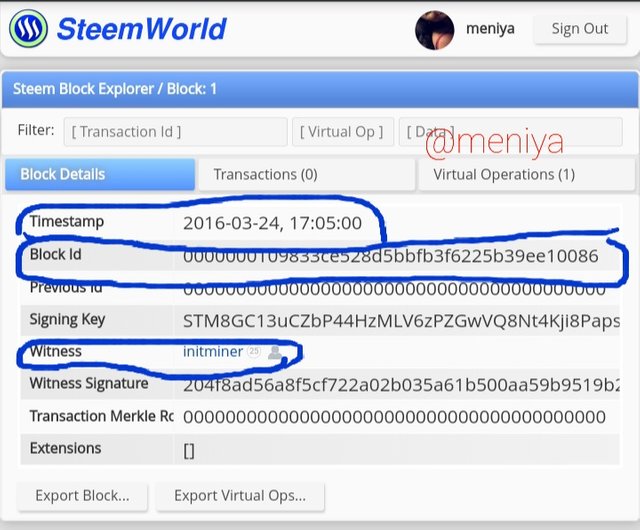
The Genesis Block for Steem blockchain is referred to as Block 1, and it's features is as follows:
The block ID:0000000109833ce528d5bbfb3f6225b39ee10086
Date of creation: 24th March,2016
Timestamp: 17:05 (UTC+1)
Witness: @initminer
•To check The Genesis block of the Hive blockchain, visit https://hiveblocks.com/
•HIVE Genesis Block
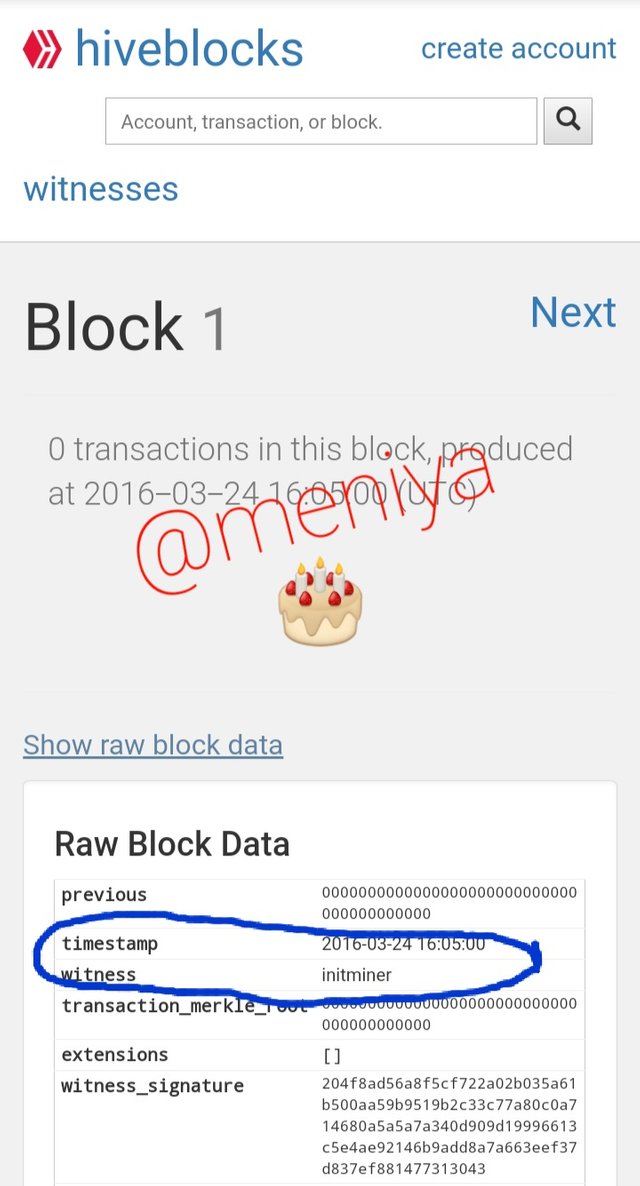
The Genesis Block for the HIVE blockchain is referred to as Block 1, below are it's features;
Date of creation: 24th March,2016 Timestamp: 16:05 (UTC)
Witness: @initminer
Same as Steem Genesis Block as shown in the screenshot Above
After the occurrence of hard fork on Steemit, users who had an account on steemit platform found out that they already have an existing account on Hive platform, with same username, reputation, password and other things. Also after the split, the user's of the new version of Steemit(that is Hive) still had the same exact number of currencies such as STEEM, SBD, and Steem power they had on steemit was duplicated on their Hive account as Hive, HBD and Give power respectively.
CONCLUSION
Blockchain Forks are changes introduced to a software protocol. Since blockchains are decentralized systems, where no single entity has total control over what happens in the platform, because of this privilege misunderstanding is banned to happen amongst participants of the platform as everyone has their own opinions/ views over an issue. Hence the need for forking becomes activated in the blockchain.
Alhough the Fork in the software protocol blockchain could be as a result of slightly modifying a blockchain protocol without the intention of creating a new blockchain or cryptocurrency (Soft fork), or it could be for the creation of a new blockchain and a new cryptocurrency (Hard fork). In all, it's still for the best, as blockchain forks leads to the general upgrading of blockchain technology.
Thank you professor @awesononso for such a broad and amazing lesson. Best regards.