Sidechains - Crypto Academy || S4W8 || Homework post for pelon53
.png)
INTRODUCTION

Good day Professor, fellow Steemit Crypto Academy students, crypto enthusiasts, and steemians alike. This is my entry for professor @pelon53's assignment on Sidechains. Hope you enjoy reading!

Explain in detail the Sidechains with the use of ZK-Rollups.
Sidechains are a layer 2 innovation created by developers in order to tackle some pertinent issues concerning major blockchains, including but not limited to speed, scalability, and affordability. A side chain is a separate block chain which runs in parallel to a main blockchain and can be integrated with the main blockchain via a two-way peg.
To quickly, but fully, understand this concept, let us consider what happens when one uses a centralised exchange.
An individual transfers his cryptocurrency assets from his crypto wallet to an address given to him by the exchange. This takes his assets out of his possession and puts them in the possession of the exchange, so he has to trust that the exchange will not mismanage his assets. He then conducts his transactions within the exchange, and, whenever he is done transacting, can move back what remains of his assets to his wallet again, giving him full control of his assets once again. This is somewhat similar to what a sidechain does.
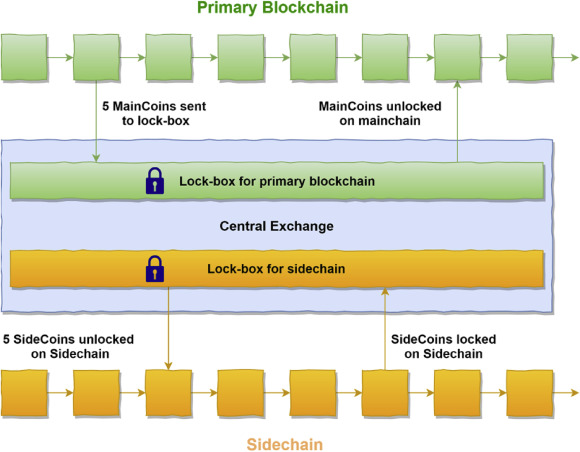
With a sidechain, one can transfer their assets to an address given to them by the sidechain, after which those assets are recreated on the sidechain, and can be used to carry out transactions within the sidechain. When one is done transacting, they can then move what is left of their assets back to the main blockchain.
When the user's crypto assets are moved to the specific address given by the sidechain, he/she will wait for a time for the blockchain network to completely immobilize the assets and determine that those assets are not being used elsewhere or belonging to someone else.
When this is confirmed, those assets are recreated on the second blockchain, where the user can then gain control of them, and carry out transactions as they wish. When the transactions are over, the assets can be returned to the main blockchain, under the control of the last owners on the sidechain.
Why is this important?
With a sidechain, you remain in complete control of your assets, unlike a centralised exchange. In essence, you are moving the assets to another blockchain. This can be for various reasons, including but not limited to: faster transaction speed, lower transaction fees, etc. The user also maintains security of his assets and can benefit from any other advantages of the sidechain.
ZK-Rollups
ZK-Rollups (Zero Knowledge Rollups) are a sidechain/layer 2 solution which aims to improve the scalability of the Ethereum blockchain. With the use of ZK roll-ups developers hope to reduce transaction fees and increase transaction capacity and speed through grouped transfer processing.
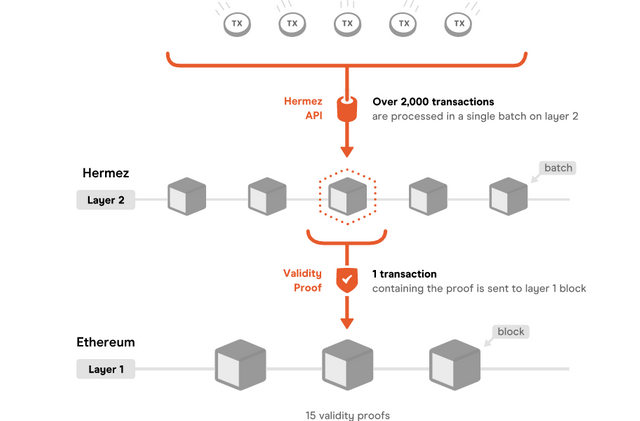
ZK roll-ups function by collecting a large bundle of transfers data into one "roll-up" on layer 2, and then generating a cryptographic proof called a validity proof for all the data. The validity proof of the bundle is then submitted to the layer 1 in place of all the transfer data, significantly reducing data size and lowering gas cost, and time required for validation of a block.
This method requires the input of two types of users:
- Transactors: These are the users who create the transactions and broadcast them to the network. Transaction data is essentially made up of 5 components
- Sender's address
- Recipient's address
- Transaction value
- Network fee
- Nonce
The addresses are shortened into indexes which reduces processing time and storage, and the value of the transaction (either greater or less than zero) determines whether it is a deposit or withdrawal. This transaction data is then recorded by the smart contact into two Merkle Trees; one for addresses, and the other for transaction values.
- Relayers/Certifiers: These are the users who group the transactions into roll-ups. Their major job as certifiers is to generate the cryptographic proof of the grouped roll-ups called the SNARK (Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge) proof or the validity proof.
The SNARK proof is a hash function that shows/represents the change in the state of the blockchain from before the transactions occured to after the transactions have occurred.
This SNARK proof then gives the main block chain the ability to verify the computation of transactions from the layer 2.
Certifiers are incentivized not to tamper with or withhold a roll-up by having them steak a required amount in the smart contract.
ZK roll-ups have the benefit of reducing transaction fees and block data size, as well as increasing speed, throughput and scalability. However, they also have a few disadvantages including difficulty in computing of the zero-knowledge proofs as well as the majority being incompatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
Here are some projects which use the ZK roll-ups system:
zkSync
Aztec
LoopRing
Matter Labs

zkTube


Explain the Liquid Network side chain
The Liquid Network is a federated Bitcoin sidechain protocol that was developed by Blockstream, and had it's trial version released in 2017, and was eventually officially launched in October, 2018. It is majorly used by, and mostly useful to, traders and exchanges, due to its quick transaction speed, and the possibility of creating one's own unique digital assets.

As a Bitcoin sidechain, its major function is to decongest the Bitcoin blockchain network, by taking some transactions off it, as well as to provide solutions to the slow transaction speed, high transaction fee, and scalability issues found with the main bitcoin blockchain network. The liquid network is now used by a great number of cryptocurrency exchanges, brokers, market makers, wallets and other market participants, as a much quicker and faster payment option.
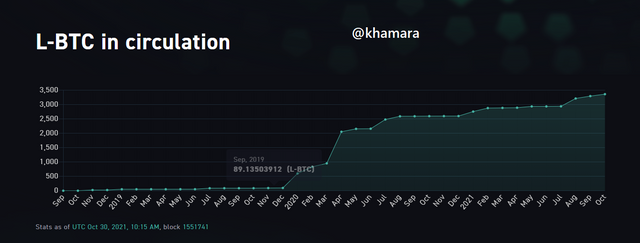
The liquid network functions, much like most other sidechains, through a two-way peg to the main blockchain. When a user's bitcoin is sent to the sidechain's specific bitcoin address and these coins are confirmed to no longer be in use on the Bitcoin network, the coins are locked and the liquid network issues tokens equivalent to the number of Bitcoin that has been sent by the user, to that user on the Liquid network sidechain. It uses the token, L-BTC, which is pegged to Bitcoin at a 1:1 ratio.
One of the major advantageous features of the liquid network is the two-minute transaction time. This is much faster when compared to Bitcoin's probabilistic 10 minute transaction time. It also gives its users the opportunity to create and issue their own set of tokens within the sidechain.
Although the liquid network is open-source it is still governed and managed by a group of authorised member institutions collectively called the federation. These operators act as an intermediate point/node between the main chain and the sidechain, and guarantee system interoperability. They also ensure the safety and security of the pegged in bitcoins which can only be pegged out after being authenticated by a sufficient number of operators. This significantly reduces the cost requirement of the proof-of-work consensus system.
Here are some of the major features of the liquid network:
- It increases the speed of transactions for bitcoin transactions.
- It reduces transaction confirmation time. All transactions are carried out within 2 minutes.
- It increases efficiency of exchanges and other platforms which make use of it
- It also increases the privacy of transactions. Transactions are set up to not disclose transaction amounts to third parties.
- It allows users to issue new cryptocurrency assets which can range from stablecoins to altcoins, security tokens and others.


Describe the steps to connect the Metamask wallet and the Polygon network wallet. Show screenshots.
In order to connect our Metamask wallet and the Polygon network wallet, we need to have an already existing Metamask wallet account, which we can then connect to the polygon network wallet. I will not go through the numerous steps required to create the Metamask wallet, however, when one has created their Metamask wallet, they can go through the steps below to connect it to the polygon network wallet.
- Visit the Polygon network website.
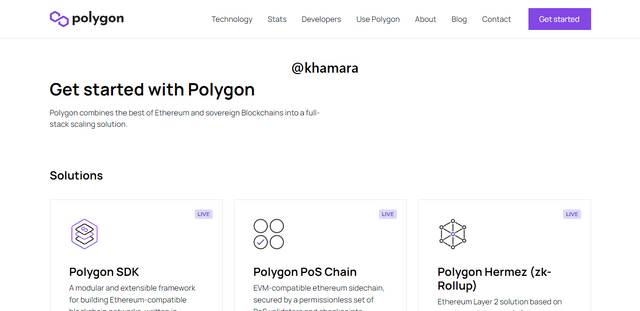
- Click on Use Polygon at the top of the page, and then click on Polygon Wallet on the drop-down menu that follows.
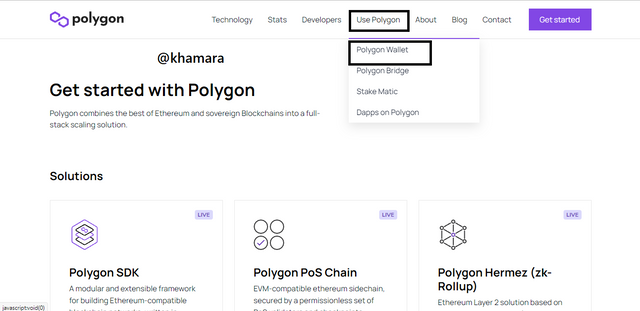
- This takes you to the page below. Click on the Polygon Wallet icon box.
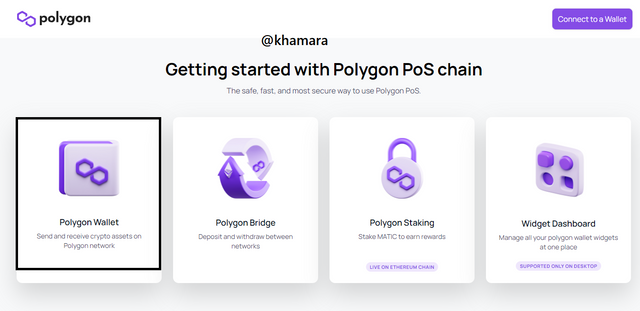
- Click on Metamask to connect your Metamask wallet to the polygon network.

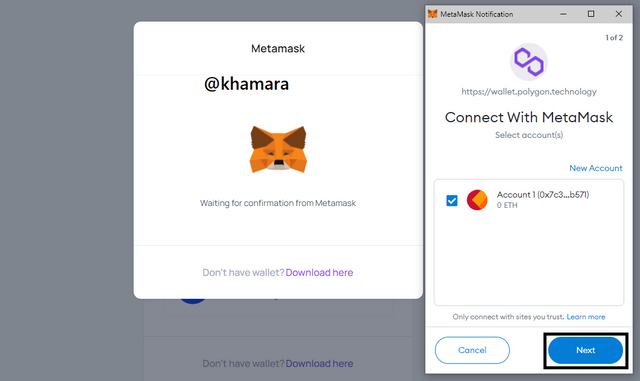
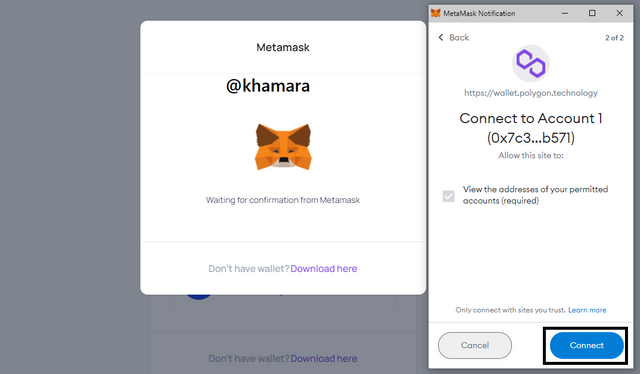
- Your Metamask wallet extension then pops up, requesting you to connect the polygon wallet. Click Next.
- The next page shows you the permissions being given to the polygon wallet, click Confirm.
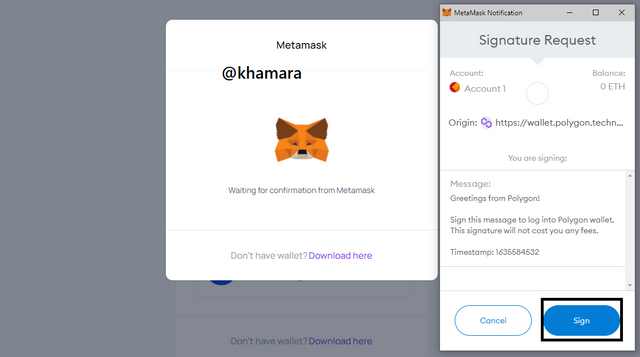
- The next page requests your signature to log in to the polygon wallet. It is worth noting that this does not cost you anything. Click Sign.
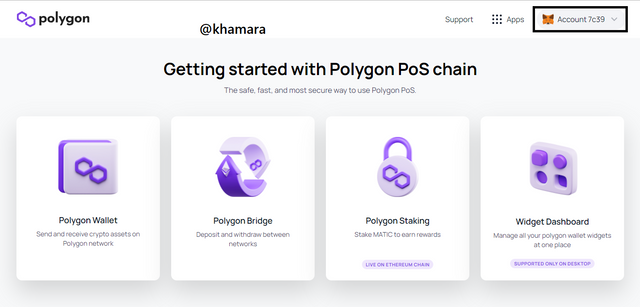
- After doing this, your wallet is now connected to the Polygon PoS chain.

According to the polygonscan block explorer, when will the block 25,000,000 be generated? Show screenshot. Explore the 12,000,000 block, at that time, what was the price of the Matic? Show screenshots.
In order to complete this task:
- I visited PolygonScan. In the search bar i typed the number 25000000 and clicked on search.
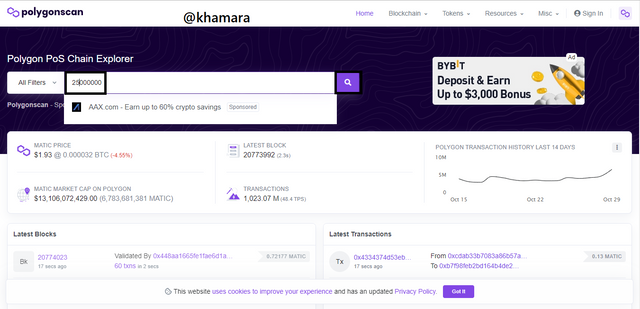
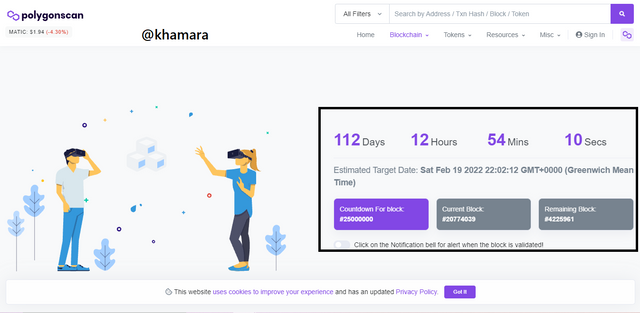
- I was taken to the page below which shows that at the time of writing this, there are 112 Days, 12 Hours, 54 Minutes, and 10 Seconds to the creation of block 25,000,000. That is to say, it will be created at exactly Sat, Feb 19, 2022, 22:02:12 GMT
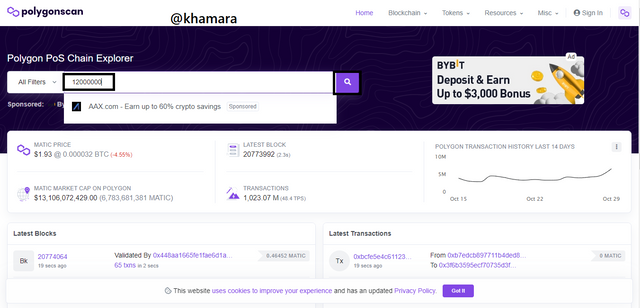
- In order to find the information on block 12,000,000, i returned to the homepage, and repeated the action of searching for the block.
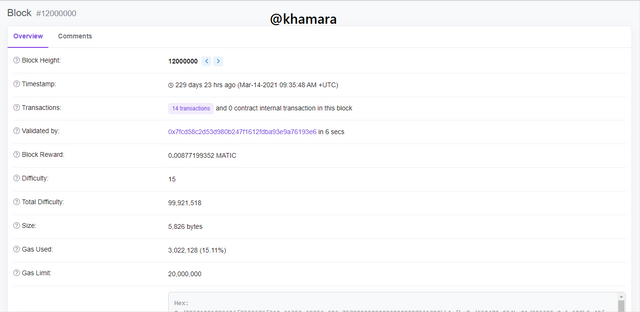
- Upon searching for block 12,000,000, the following result came out, showing all the information concerning the block.
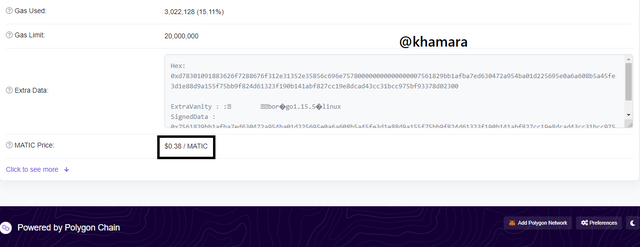
We can see above that the price of Matic at the time was $0.38.

CONCLUSION
This was a very interesting topic to research and learn on. I have, above, discussed lengthily on sidechains, how they work, their uses and benefits. I have also written extensively on ZK Rollups, and their method of operation, as well as the Liquid Network. Thank you for reading through!
NB; All pictures used in this post were either taken from the respective websites or designed by me on Canva. Thanks.