CryptoAcademy Season 3 Beginner's Course - Homework Post for Task 2 : Definition of Blockchain, How data is protected on blockchain, meaning of data, hash, and previous hash tag.
The question is:-
WRITE THE DEFINITION OF BLOCKCHAIN. AND HOW IS BLOCKCHAIN PROTECTED FROM HACKERS? AND WRITE DETAILS ABOUT DATA, HASH AND PREVIOUS HASH TAG AND EXPLAIN THROUGH SCREENSHOT.
Long before the advent of the Blockchain technology, traditional financial institutions, businesses and business organisations uses the system of ledgers to take records of all deals or completed transactions.
The ledger is a book (s) in which all transaction information are recorded or stored. Information about the sender, recipient, amount, time and dates are all recorded in the ledger.
Such records are stored and controlled by the central authority of the organisation and sometimes the government and other regulatory agencies can have access to it.
The Blockchain uses the same principles of ledgers but in a way far better.
The term Blockchain and cryptocurrency have become buzzwords of the last decades and even more recently due to the rise in the popularity of the Blockchain and it’s associated cryptocurrencies.
The term Blockchain is a compound word that is derived from two words “block" and “chain".
Simply put, Blockchain is a chain of blocks that contains information. That is a shallow definition though.
For a more detailed meaning of the term Blockchain, let me delve deeper.
As we established earlier that a chain of blocks makes up the Blockchain. We need to understand the two key words separately for a better understanding of the word Blockchain.
A block with respect to the subject of our discussion, is like a book that contains records or information about certain transactions that took place on the blockchain.
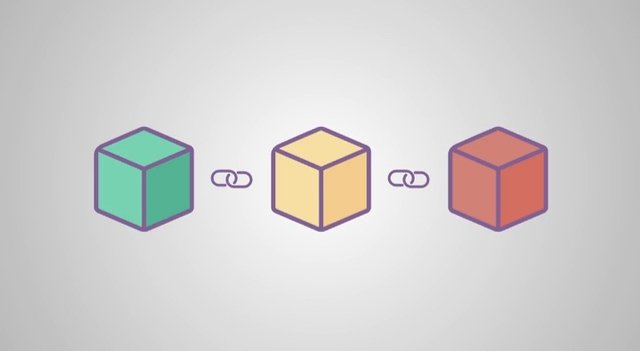
A chain on the other hand, is a series of things that are interconnected or linked together in this case, chain is a series of linked blocks.
Therefore, we can say blockchain is a series of blocks that contains transaction information.
Each time transaction is initiated on the blockchain, the system creates a separate block for the transaction. All the information about the transaction are stored in the block. The new block is connected to the previous block on the blockchain by what is called Hash (I will discuss it in detail later).
The new block also has its own unique Hash assigned to it as a digital footprint which will serve as the link to subsequent block. This way, a chain of several blocks is made. Hence, the term Blockchain. It is created by linking existing or previous blocks with the current/new block using Hash as the linkages.
More comprehensively, the term Blockchain refers to a decentralized of distributed ledger technology (DLT) that is capable of taking records of user’s transactions while eliminating the need for any intermediaries through a process called peer-to-peer (P2P).
It is a “decentralized” system of ledgers because it has no central authority, regulatory bodies or agencies, third parties or intermediaries that may influence decision making in processing transactions. Thus, users have 100% autonomy to decide when, how, what amount and with whom the transaction is made.
It is a “distributed ledger" because everyone on the blockchain receives a copy of each transactions record. Everyone has access to the information. The other computers (nodes) on the network confirms the authenticity and validity of the transaction before the deal is completed and send a copy of the information to all the users on the blockchain.
Blockchains operates on protocols called consensus mechanisms. The Bitcoin blockchain for instance, uses the proof-of-work (PoW) as the main consensus mechanism. This mechanism requires the computers on the network (nodes) to solve mathematical problems or puzzles in order to validate the integrity and the legitimacy of the transactions. The nodes that solves the puzzle first, is rewarded with some coins. This process is called mining.
The consensus mechanism is a method utilised by the blockchain to bring about agreement, trust, and security. Though the PoW consensus mechanism is energy demanding compared to the proof-of-stake (PoS) which is the main consensus mechanism of Etherium blockchain.
The proof-of-capacity (PoC) consensus mechanism allows the sharing of storage capacity among the different nodes on the blockchain network. Hence, the more storage space a node has, the more information it can store.
Whereas power lies in the hands of stakeholders and company owners in the traditional financial institutions, the blockchain technology takes power from the few elites and give it back to the masses.
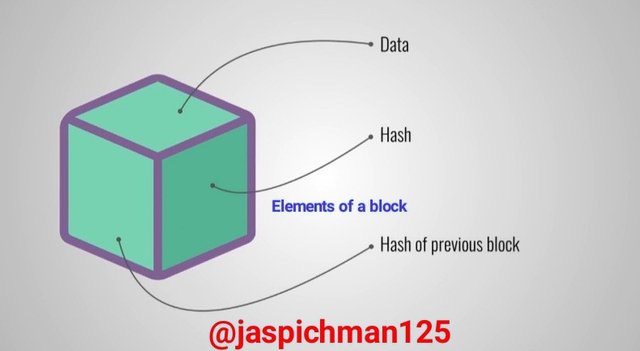
Block elements are variables that are used in verifying the information necessary in each block. The elements are Data, Hash and the Hash of previous block.
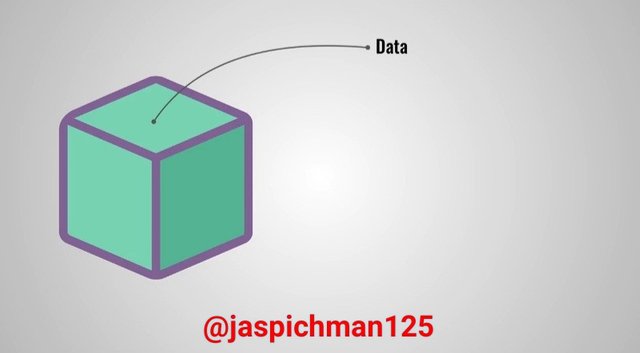
Data:
The kind of data stored on a blockchain depends largely on the type of blockchain. For instance, a blockchain that is designed for the health sector takes records of patient’s data such as gender, age, kind of disease, etc.
While a blockchain that is designed for financial purposes such as Bitcoin, takes data such as the sender, time, amount of money, and receiver into account. Such data are recorded in blocks each time the transaction is completed. A copy of the record is then distributed to all parties on the blockchain. The data stored in a particular block is unalterable because it’ll require you to change all the records on other people’s copy of the transaction data on the entire blockchain which is highly impossible.
Hash:
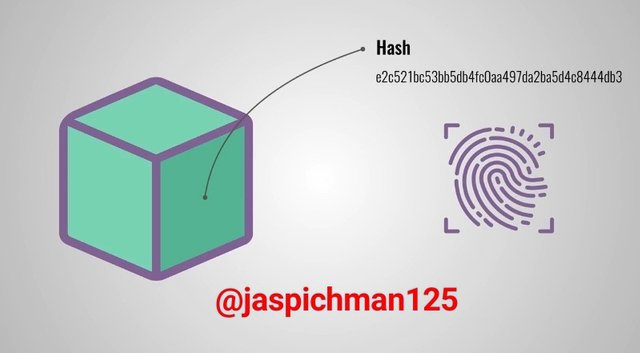
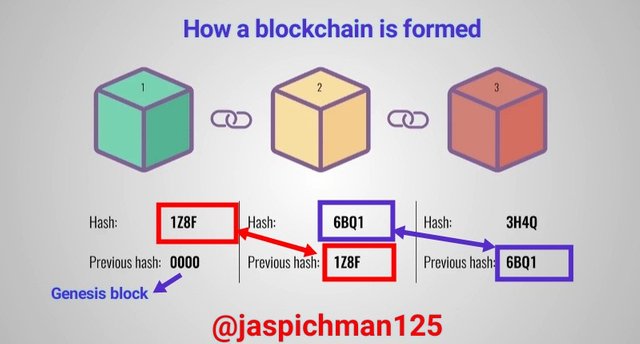
For simplicity, we can say Hash is the digital footprint of a block in a blockchain. As we established earlier, the block contains all the details of a particular transaction. The Hash is a unique cryptographic alphanumeric number assigned to every block on the blockchain. It serves as the “identifier” or a reference number to a specific block. It also serve as a link to subsequent block.
The presence of Hash helps in authenticating the integrity of transactions on the blockchain. The nodes on the network confirms the Hash of a transaction block before completing the transaction, if the Hash tends to be incorrect or faulty, the nodes will detect and stop the transaction.
In addition, the Hash helps in encrypting not only transaction data, but also text messages sent on the blockchain network so that only the sender and the recipient should have access to the information. This is good for security purposes because it prevents the risk of tampering the information.
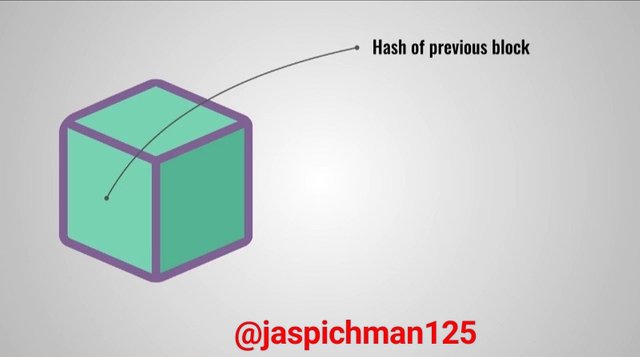
Previous Hash Tag
The previous hash tag is like a "gene" that transfers information from the previous transaction block to the subsequent block.
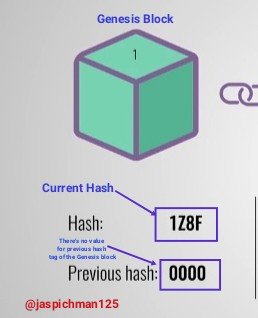
The first block on a blockchain called Genesis block does not have a previous hash tag because there's no existing block before the Genesis block. Therefore the previous hash tag of the Genesis block is 0000.
The Genesis block is the foundation upon which subsequent blocks are created and interconnected in a manner to form whatbis known as blockchain.
Hashing: simply put, is the process of generating a unique cryptographic code that serves as identification number for each block on the blockchain.
Hash rate (Hash power):
Is the rate or number of times hashing operations are processed per time during mining activities on the blockchain.
In other words, it is the summation of all the computational power that is being used to mine and process transactions on blockchains that runs on the PoW protocol (e.g. Bitcoin and Etherium).
Machines or nodes with higher computation power have higher Hash rate. The higher the Hash rate, the better the productivity, the efficiency and the security of the blockchain.
Questions that keeps coming up in the minds of sceptics as well as investors of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies is “how secure is my assets on the network”?
Well, every serious investor is most likely to ask such question. It is amazing to know that there are inherent protocols on the blockchain for security checks.
There are three (3) ways in which the blockchain network achieves and maintains security. These are: -
Hashing:
As discussed earlier, hashing operations provide additional security to blockchain because every single block is being assigned a unique code, a kind of fingerprint. Blocks are interconnected with each other via the Hash in order to from a chain.
The information contained in the previous block is transferred or copied to the new block via the “previous hash tag". When this happens, it makes the information on the previous block unalterable since the new block contains a copy of the information, violation cannot take place because you’ll have to erase all the data on the entire network which is practically impossible. But hashes are not enough to provide the high level security that is expected to be found on the blockchain network.
Proof-of-work: with respect to security on the blockchain, PoW is an inbuilt protocol that slows down the rate at which new cryptocurrencies are mined. On the Bitcoin blockchain for instance, it takes an average of 10 minutes to calculate the accurate proof-of-work and add new block to the blockchain. This protocol makes it difficult to change any information because you’ll have to recalculate the Proof-of-work of all the blocks on the blockchain.
Distributed ledger:
When a transaction is complete, a copy of the block information including the Hash of the block is distributed to all the nodes or parties on the entire blockchain network. For instance, if a hacker wants to tamper with the information on block A, he/she will have to change the records on other people’s copy of the block data. When the system detects any attempt to make changes to a certain block, it triggers the other users on the blockchain to verify whether the change is legitimate. This way, security becomes tighter on the blockchain.
He blockchain technology revolution has changed how businesses are working, and how transactions are done by challenging the traditional financial institutions and their systems.
Not only that, but the blockchain is making its way to influence sectors such as government (in terms of voting), health care, etc.
To truly replace the existing institutions, the blockchain must undergo some metamorphosis to deliver the things it promises us.
Users of blockchain can secure their account by storing their account details on a hardware wallet, a printed paper or written in a book that is kept in a safe place.
Account security can also be achieved by not sharing one's keys, seedphrases, and other confidential information about your account. This will reduce the risk of being attacked by hackers.

Thanks for reading through my homework.
Special thanks to CryptoAcademy Beginner's Course Professor
@yousafharoonkhan



.png)
Nice work bro, keep it up
Thanks bro