Different types of Consensus Mechanisms - Steemit Crypto Academy Season 4 - Homework Post for Task 6
.png)
~INTRODUCTION~
Good day Steemians!
This is my entry for Task 6 of the Steemit Crypto Academy Season 4 Beginner's Course on Different types of Consensus Mechanisms. I will be answering Question 1 of the homework task.
(1) What is the difference between PoW & PoS? Advantages & Disadvantages? Which one is better in scaling Capacity? Examples?
What is the difference between PoW & PoS?
Blockchain technologies have become very prominent in the past few years, and are seemingly beginning to dominate the future of finance, and even the internet as a whole. A blockchain is, essentially, a peer-to-peer decentralized distributed ledger which is created and securely linked through the use of advanced cryptographic techniques. It eliminates the need for a middleman through a peer to peer system that allows participants on the network validate records through consensus.
How is consensus reached? Through Consensus mechanisms.
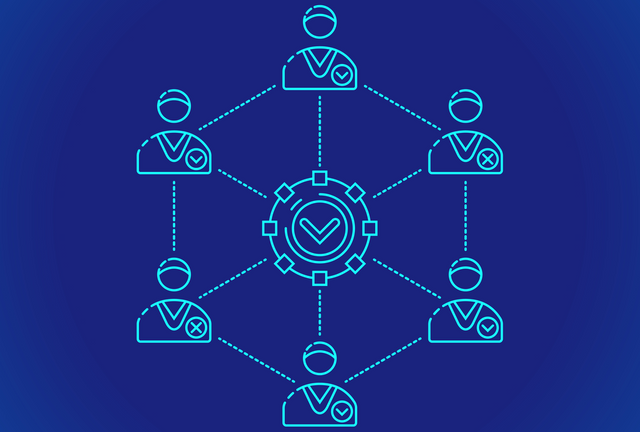
Consensus mechanisms are systems put in place to maintain trust between participants/nodes on the network. These are the mechanisms by which nodes on the decentralized network can verify and secure records created on the blockchain. There are different types of consensus mechanisms that have been created and are used in blockchain networks. We will be looking at the Proof-of-Work (PoW) system, and the Proof-of-Stake (PoS) system.
Proof-of-Work (PoW)
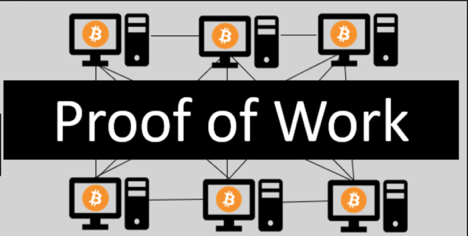
The Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism is a method by which blocks on a blockchain are verified, and new coins, produced.
The PoW system was introduced with the first ever cryptocurrency: Bitcoin. Essentially, it requires block validators, called miners, to solve complex mathematical puzzles, in order to find the correct hash (which is an alphanumeric code unique to each block) for the current block.
Solving these complex puzzles and finding the correct hash, usually consumes a certain amount of time and requires for a lot of computing power to be spent. In exchange for their time and computing power, miners are rewarded with a stipulated amount of the cryptocurrency, as well as transaction fees.
Because it uses a ton of computing power and energy, miners can be trusted to validate blocks correctly and not manipulate any of the information within the blocks.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS)

The Proof-of-Stake consensus mechanism is another system of reaching consensus which was popularized by Ethereum.
With this system, the block validator is not required to solve any equations, rather, block validators are deemed reliable due to the stake they have in the system.
In this system participants pledge some of their owned cryptocurrency, in order to be allowed to validate blocks on the blockchain. The greater the amount staked, and the longer it is staked for, the higher the probability of validating blocks.
Differences between PoW and PoS
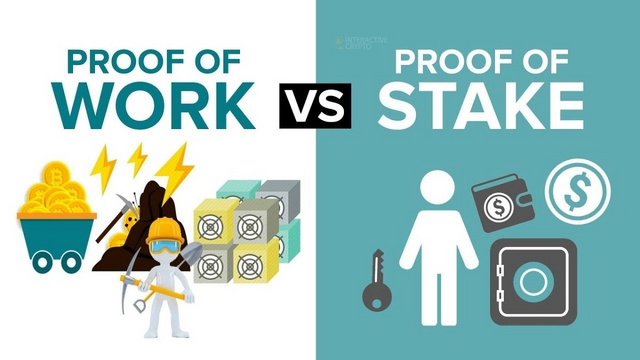
| PoW | PoS |
|---|---|
| Block validation probability is based on the speed and quality of hardware of the validators | Block validation probability is based on the amount of cryptocurrency staked and the amount of time it has been staked for |
| Uses a very huge amount of computational power and electrical energy | Uses much less computational power and electrical energy (about 10% or less) |
| Block validators/miners are rewarded in cryptocurrency for the solving of the mathematical puzzles | Block validators get network fee as a reward based on how much they have staked. |
| Finding the proof of work takes time, hence this method is slow | Much faster than the proof of work method |
| To conduct a 51% attack one would need to own at least 51% of the total computational power used in mining | To conduct a 51% attack one would need to own at least 51% of the staked cryptocurrency |
Advantages & Disadvantages of PoW & PoS?
Proof-of-Work (PoW)
Advantages
- The proof of work model of consensus is very difficult and costly to attack hence warding off hackers and potentially malicious agents
- Miners are rewarded with a certain amount of cryptocurrency and this is how new units of cryptocurrency are added into the system.
- It is highly decentralized and creates a trustless system for recording transactions.
- Miners are also rewarded with transaction fees from processed blocks.
Disadvantages
- The proof of work method uses a high amount of computational power and electrical energy.
- It costs a lot to maintain and manage.
- It is not environment-friendly.
- This system has poor scalability and hence low transaction speed.
- The proof of work method is a very slow method due to the need to solve the complex mathematical puzzles
- It requires the purchase of heavy expensive hardware for the mining of blocks
Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
Advantages
- It is more scalable than the proof of work method resulting in higher transaction speeds.
- One does not need to purchase heavy expensive equipment to begin validating blocks.
- The proof of stake method consumes much less energy and electricity than the proof of work method
Disadvantages
- Coins are staked for a set amount of time and cannot be used within that period of time
- It has a higher tendency to words centralization than the proof of work method due to the fact that it only requires validators to stake coins and so whales can easily hijack the system.
- This system may be a little less secure than the proof of work system.
Which one is better in scaling Capacity? Examples?
Scalability is a very important concept in any network. A network's scalability is the ability of that network to handle a growing amount of work. For a cryptocurrency blockchain network, it is the network's ability to handle a higher amount of transactions within a given period of time.
Between the proof-of-work consensus mechanism and the proof-of-stake, the proof-of-stake is more scalable than the proof-of-work. The proof-of-work mechanism requires heavy, expensive, large-scale hardware, and has a set time for mining of blocks. However, the proof-of-stake mechanism does not require mining hardware or software. This allows it to be a more scalable system than the proof-of-work and enables it to carry out more transactions within a shorter period of time.
Some examples of highly scalable cryptocurrency blockchain networks that use the proof-of-stake system include:
Cardano: This blockchain network can process up to 250 transactions per second
Solana: The Solana blockchain network can go a whooping 50,000 transactions per second.
Algorand: 1,000 transactions per second.
~CONCLUSION~
Blockchain consensus mechanism is a very important factor to consider when analysing a block chain, and is a very important part of the blockchain network. Decentralization, scalability, and trust are the major factors that are considered when building a consensus mechanism. These consensus mechanisms enable blockchains to function in a decentralized manner. Thanks for reading!
-IamEl the ModestPoet
N/B: All pictures not cited, were designed by me using Canva, powerpoint, or gotten from the respective websites.
