Steemit Crypto Academy [Beginners’ Level] | Season 3 Week 4 | Blockchain Forks, for the Cryptoprofesor @awesononso by @g0h4mroot.
forks in cryptocurrencies are usually given for various reasons, since it is a fully decentralized network and its code is accessible to the general public, a programmer can make a code update whenever he wishes, resulting in an update to the source code of the blockchain to improve it, or simply to create another project, although in order to carry out this update, this patch, so to speak, must be accepted by miners and then by network users in order to be successful.
These forks are made in order to protect the ecosystem from possible malicious attacks, or in order to update the chain and improve it, or to create a new currency.
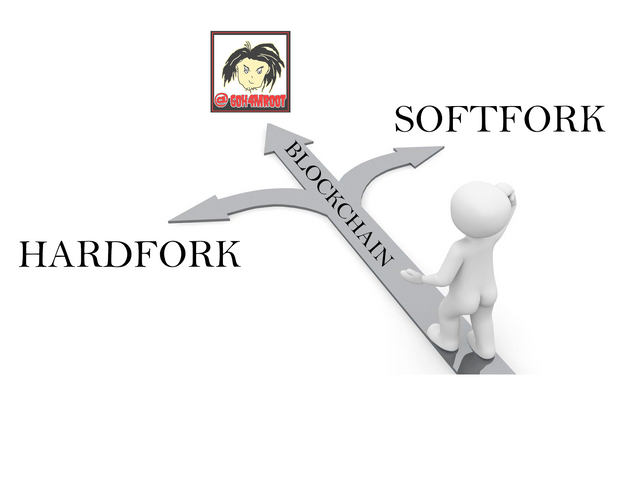
There are several types of forks, among the main ones are HARDFORK and SOFTFORK.
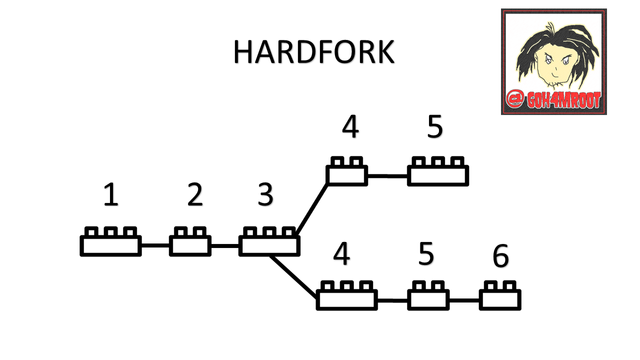
a hardfork, this term is used in cryptocurrencies to indicate the update, separation, division or the creation of a new block, an update cancels any previous transaction and disables it for the new block, resulting in a new project, is to say a hard fork is a separation of a project through which another is created, these separations can occur in various ways, whether they are problems between the parts of the project for various reasons, the main reasons for a hard fork can be economic or political, or as The case of steemit that Mr. JUSTIN SUN bought steemit and wanted to centralize it, the community upon learning of this, a large part of it decided to create HIVE.
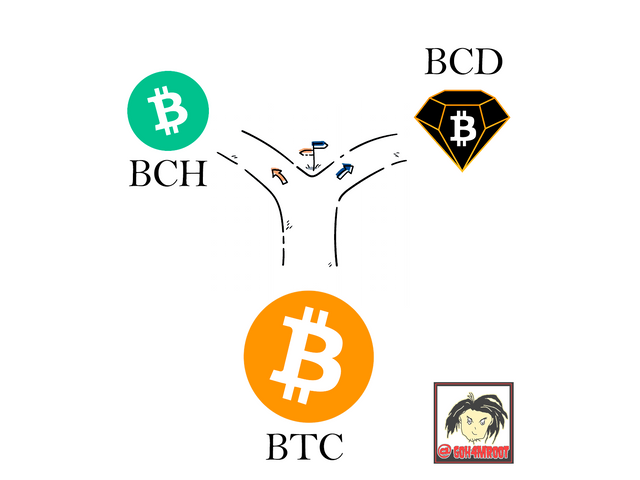
BITCOIN DIAMOND or BCD, is a btc hardfork, created in 2017, by a team of programmers who wanted to make improvements to the btc code, to improve the speed and cost of the btc transaction, and make the interaction more fair and economical on the blockchain.
All the blocks are numbered and when a hard fork occurs, in the block where said separation was generated, the following blocks continue in parallel following the same numbering that they brought previously, that is, suppose that the separation was created in block 50, from From there there will be 2 separate blockchains but with the exact same numbering and advancing identically, this means that now there are two parallel blocks # 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, etc.
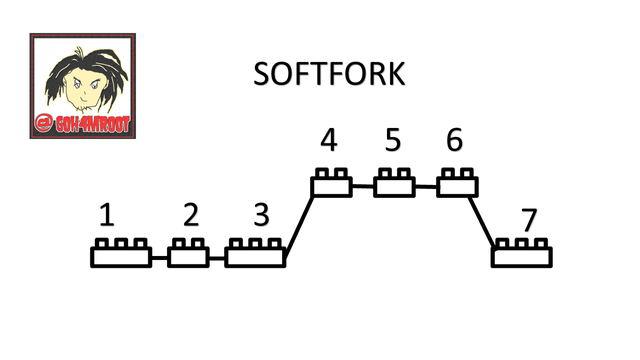
the softfork is created to update the network, unlike hardfork, it is not made to create a new project, but to improve it, this means that the old transactions will be able to continue working in the new network without any problem rather, all the Transactions will work in a similar way in the same updated network without any problem, it is softfork updates the code, fixes bugs and improves transactions in the blockchain.
An example of a softfork is the update that is made to a miner in his software to improve the system of the same, to validate the transactions that have been left out for some reason, to correct some bugs that may be beneficial to pirates.
When a softfork is generated, a different block is generated but this block will retain the same numbering that it had without separating, and without generating any separation it only creates an update to improve the chain of blocks.
the hardfork is mostly done to create a new network trying to disable the previous one, a new chain of blocks is generated and all the transactions that have remained to be validated are canceled.
the softfork is made to improve the ecosystem making it stronger and more robust, the two networks are compatible and new and old transactions continue to be validated simultaneously.
differences
| Hardfork | Softfork |
|---|---|
| used to create a new project | improves existing project |
| creates a new block | updates the existing block |
| disable previous transactions | all transactions are supported |
| projects are separated for disagreements or monetary purposes | there is no problem between the creators of the project |
• Bitcoin cash
BCH or BITCOIN CASH, is a hardfork created in order to improve transactions and time in the bitcoin network, resulting in a New Project that aims to minimize the time in the creation of blocks and reducing the cost of each transaction, this Separation happened because the programmers did not agree with the policies promoted by the counterpart.
BCH is a HARDFORK of BTC.
• Separate witnesses.
Separate Witnesses or SegWit, was created to expand the size of the Bitcoin block by improving its transactions and eliminating the data that is saved by each transaction signature on the blockchain.
SegWit is a BTC SOFTFORK.
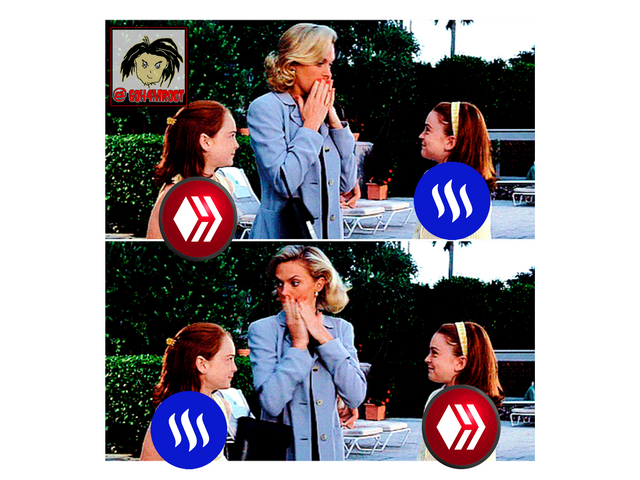
The purchase of steemit by Mr. Justin Sun Ceo of TRX, started a confrontation between the creative parties of steemit and between the community in general, resulting in a separation of the programmers creating HIVE, Hive is a decentralized social network almost identical to STEEMIT, I say almost identical because hive does not have an owner like steemit, the interface in view is very similar, you can even enter the 2 platforms using the same credential, be it hive or steemit no matter which one .
One of the big differences lies in the currencies we receive, since in steemit SBD, STEEM and TRX are received, while in HIVE only HBD and HIVE ARE RECEIVED, in the two blockchains the LEVEL POWER is used in HIVE ES HP (HIVEPOWER ) and STEEMIT ES SP (STEEM POWER).
rewards are received in the two blockchains.
In conclusion, forks exist to improve an existing ecosystem or blockchain, correct bugs and repair errors, or to create a new project. If there is a problem between the developers, they will have the option of making a hardfork, while if what we want is only to improve the blockchain we can do a softfork, as long as we have the knowledge to do such work.
In this class we learned about the fork in cryptocurrencies, having sufficient knowledge in programming we could create our own blockchain starting from a source code of another blockchain since these source codes are open source and are accessible to the general public.
We inquired about the steemit ecosystem and its fork that HIVE generated, we bought its blocks and talked about them, giving examples with our own screenshots.
NOTE: All images are created by me in photoshop, using images without copyright.
Cc:
@awesononso
.png)

.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)

.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
.PNG)
