Crypto Academy Week 16 - Homework Post for @pelon53

Greetings everyone, I am excited to have meet all the requirements to participate in crypto assignments for the first time.I hope to do better and learn more. Before I start with my homework, I would like to go through the lecture of professor @pelon53 about the topic HASHGRAPH TECHNOLOGY a bit.
Hashgraph is a data structure with an associated distributed consensus algorithm. Simimlar to blockchain, hashgraph is a decentralized and public distributed ledger. It’s a compelling alternative to blockchain. The way it works differs from blockchain in different ways and even offers vast improvements. Hashgraph uses a gossip protocol to overcome the bandwidth issue with voting algorithms which makes the system much faster fairer and more secure than a blockchain .
Moving forward to answering the questions asked by the professor
1.Explain in detail the Gossip protocol, used in Hashgraph
As the name implies, Looking at one of the fastest and most resilient way primitive communication has travelled,is through gossip. There’s gossip in our everyday activities practically. For instance, if I should share a confidential matter about myself to my close friend A, and she also shares it to another closer friend of hers B,whom I might not even know. A then repeats this information with a different random member. B repeatedly does the same, and all other members do the same. This will spread exponentially fast through the community, until every member knows about it.
To know the fastest and most efficient way to achieve this, the gossip protocol can be thought of sort of a virus were each node infect a small amount of other node and then go on to infect another small amount of node and so on and this infections spread exponentially tray the cluster. It is mostly termed as epidemic protocol , just like how a disease spreads. Amazon, Cassandra, Database , bitcoin etc all uses Gossip protocol for a message or an update can be communicated from one node to another node.
Gossip protocol is not sequential. One node does not have to tell every node at the same time. It simply tells a small amount of nodes and then continue to passes the data alone. Practically, an interesting thing about gossiping is that there is some element of randomness, it doesn’t matter how the message gets there but the only thing that matters is that it eventually just gets there.
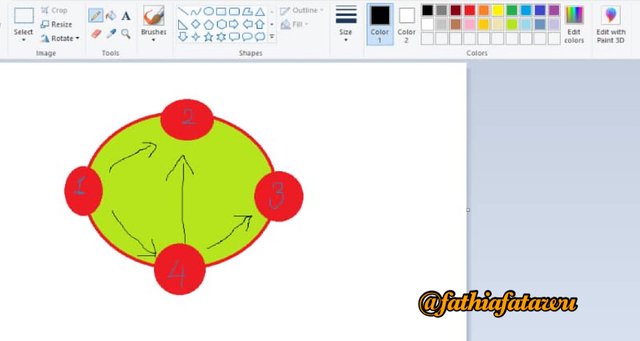
Technically, from the illustration above,let’s say we have node one , two, three and four. What happens is that node one will start a gossip protocol with node two and node four. Hence this means that node one will pass the data it knows to node two and the data it knows about itself to node four. Although node four is not directly connected to node one. Node four can still transfer the information to other nodes randomly.As the gossip spreads around the cluster, more nodes will become aware of more nodes. And so the gossip will contain more and more up to date data about the cluster until it reaches the point where every node almost knows everything about all nodes in the cluster.
You might say that in very very big clusters where they say 25,000 nodes, these gossiping sessions might contain quite a large amount of data.
There is a set number of steps that each node follow when it starts gossiping. They are divided into two data states which is Heartbeat state and Application state and from these data states , we have the basic steps as follows :
When started: it contains information on when the node begun.
Timestamp: it contains information on when this piece of gossip data was sent.
Status: it contains the current status of the node which can be normal, leaving or joining the cluster .
Load: it contains information on the load that the current node is under and the performance of the node with the disc pressure.
Severity: the combination of the load and the severity will give a good indication of the current performance of the node.
With gossip protocols, transactions of data are very fast and safe with larger amount of data transactions that can be delivered within the shortest possible time. The power and degree to which nodes reproduce information is magnificent and each node reproduces information to the same extent it was received.
2.Explain Tolerance to Byzantine Failures in Hashgraph.
Byzantine Fault Tolerance is the property of a system that is able to resist the cost of failures derived from the Byzantine Generals problem. In other words a Byzantine Fault Tolerance system is able to continue operating even if some of the nodes fail to communicate or act maliciously.
For Hashgraph technology, it is the Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance.
The Asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerance(ABFT) is a property which guarantees the timing and order of a set of transactions fairly and securely on the network.
Asynchronous can simply be understood as not making any assumptions about timing. What this means is that, it gives you strong guarantees as long as there is no bad nets in the world and sadly there are bad nets in the world and what you really want is Asynchronous Byzantine. It is the goal standard. Hashgraph has very detailed mathematical proofs with limits and theorems laid out with definitions, everything clearly defined mathematically vigorously.
In other to validate a transaction there has to be a minimum of 2/3 reaching a consensus. Mathematically,it was proved that BFT (Byzantine Fault Tolerance)systems could only reach deterministic consensus only if less than 1/3 of all the nodes were malicious. It also ensures that transactions are irreversible once
consensus is reached.
3.Make a comparison between Hashgraph vs Blockchain, for a voting process in your country Which technology would you choose? Why?
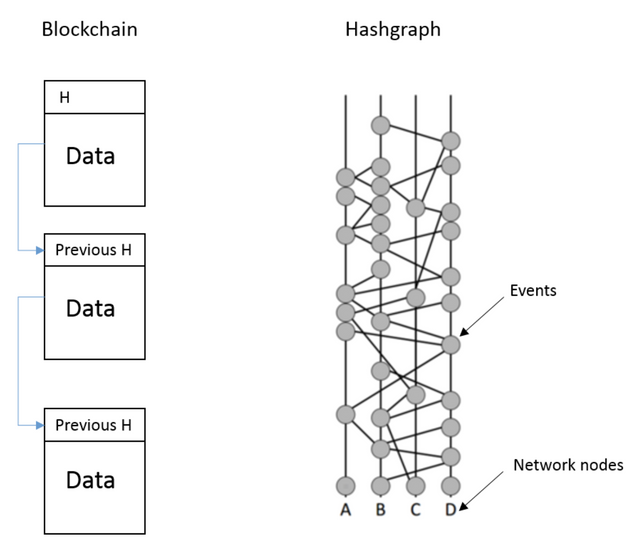
Comparing Hashgraph and Blockchain :
Throughput : The first point that I am going to consider comparing is the throughput. Hasgraphs improves on the performance statistics of the Bitcoin network. Bitcoin operates at a maximum of seven John’s actions per second while hashgraph is only limited in relation bandwidth and allows for over 250,000 transactions per second. Now the major component of hashgraph is its virtual voting and gossiped mechanism which makes the system much faster fairer and more secure than a blockchain .
Fairness: I will be considering fairness to compare as my next point. Hashgraph is fair because no single node can manipulate the transactions and the transactions are serialized with cryptographic time stamping unlike in a blockchain when miners determine the order at which transactions are placed within each block. The transaction order can be extremely important.
Proveable and verifiable: I will be comparing the prove ability and verify ability of both technologies. In hashgraphs, the transactions can be verified within a few seconds every node will be aware of the occurrences of new transactions and everyone in the community knows where the transaction is directed. Moreover all the community members know about the transaction and eventually the transaction gets deleted. In blockchain on the other hand, the transactions are available to everyone. Considering it’s a public blockchain and the transactions are recorded forever in an immutable ledger. Now unlike blockchain there is no need to carry the previous record in the ledger.
Byzantine agreement: This term simply means that no single member can hold up a community from reaching a consensus. It also prohibits consensus from being disturbed and once consensus has been reached, the smaller group or individual cannot change it and every member will know that the network reached consensus. On the contrary, blockchain is not Byzantine protected. The blockchain architecture is organized in such a way that miners are pigeon-holed into boxes and advancement of the block is dependent on the computing part of participating nodes. In such a scenario , a group of miners can discard the current consensus and then they can create their own consensus by foking from the original gene.
Cost and performance : no mind transactions ever become stale. This is because the list of transactions or what’s equivalent to the blockchain is never discarded by the community. All transactions are utilized to reach consensus whereas in the blockchain transactions are put into cointainers called blocks that from a single long chain. If two miners create two blocks at the same time, the community will eventually select one and discard the other. Resulting in wastage of efforts. In hashgraphs, every container is used and none are discarded. And as we have seen with the Bitcoin blockchain , public networks can be expensive to run and have a number of efficiency issues tied to the proof-of-work mechanism. Since hashgraph is proven to be fully asynchronous byzantine, this means that it makes no assumptions about how fast messages are passed over the internet and no proof of work is needed which makes hashgraph both cheap and efficient
Why I am choosing Hashgraph Technology as a virtual voting for my Country
Between Blockchain and Hashgraph, I will consider hashgraph as a voting technology in my country. My reasons for this decision are as follows:
To begin with,Hashgraph can handle 250,000 transactions per second.Even the fastest blockchains can perform a maximum of 10,000 transactions per seconds.
As at last year, my country casted 17,027,655 according to the electoral commission. Hence we will need a much faster technology to handle such huge population.
Implementation of a completely secure electronic voting system has many issues that are yet to be solved in my country.Fairness works well in Hashgraph if the majority of nodes know about the transaction. Hashgraph uses a gossip protocol to overcome the bandwidth issue with voting algorithms which makes the system much faster fairer and more secure than a blockchain .
This will help my country have a democratic and peaceful election since the nodes are randomly connected.
Finally, the validation of the transactions are well proven since hashgraph has very detailed mathematical proofs with limits and theorems laid out with definitions, everything clearly defined mathematically vigorously.
4.Explore Hedera Hashgraph. Show screenshots
Exploring Hedera Hashgraph, I visited hedera.com on my personal computer and this is what the homepage looks like.
On the menu bar of the homepage, I see six menu task and I explored on each. I will be sharing my summarized understanding of each menu one after the other.
NETWORK
The first option on the menu bar which is the network. It enables users to have access to the following:
Token Service. This service enables users to produce fungible and non-fungible tokens in the Hedera system network without a needing to deplay a smart contract
Consensus Service This gives users the opportunity for Hedera Consensus Service for verification , timestamping and the requesting for events of any application.
Dashboard: This provides the network activity of Hedera per second.
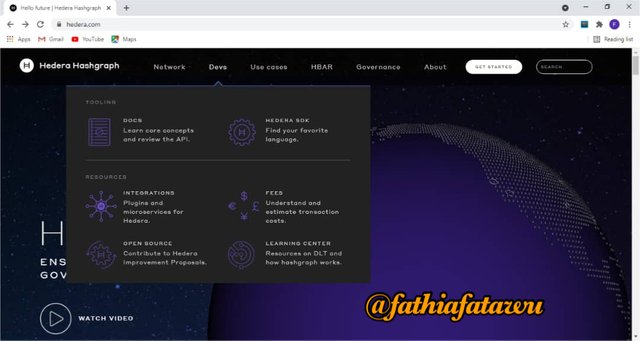
DEV
This is the second option and it enables users have access to the following below
Docs: this option contains information about hashgraph , contribution view and users reviews
Hedera SDK: with this option you can find several language options as well as some of the community supported development tools.
Fees: this option entails on fees documentation set by the Hedera Governing Council and always based in USD.
- Learning center: it gives detailed explanation to users on how Hedera works
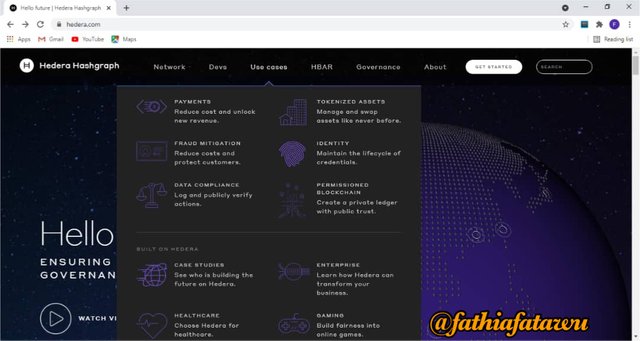
USER CASES
This particular option grants users to have information on the following:
Payments: it enable users have secured and cost effective payments in hbars or their preferred cryptocurrency.
Fraud Mitigation: It helps mitigate fraud, protects and build trust for all customers or stakeholders online applications and digital transactions.
Identity: it provides information on how to maintain the lifecycle of credentials.
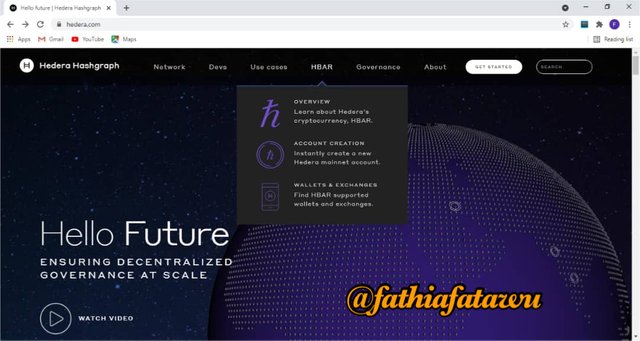
HBAR
This contains more detailed information on Hedera cryptocurrency under the overview option.
Account creation: as the name implies, it grants new users the chance to create an account.
Lastly, is the wallets and exchanges. It contains information about wallets supported by HBAR.

GOVERNANCE
It displays information on the council that governs the Hedera Hashgraph
The Governing Council is made up of up to 39 highly diversified leading organizations and enterprises, constituting 11 sectors and non- profits aroud the world. The constancy of the Hedera network is solely monitored and improved by the Governing council.
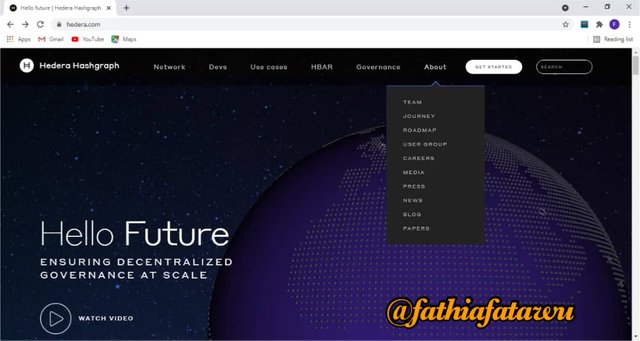
ABOUT
This is the last option on the menu and it offers information about their team, jourey, roadmap, usergroup, careers, media, press, news, blog and papers. All these contains much details depending on what the user is searching out for.
These screenshots below displays the Leadership Team and how far the Journey of the Hedera Hashgraph network has been.
In conclusion, I am much grateful to professor @pelon53 (/@pelon53) for the great lecture. Theoretically, Hashgraph is superior with really good advantages to Blockchain. I enjoyed exploring practically on the Hedera Hashgraph technology and learning about Its cryptocurrency HBAR. Hashgraph is much faster and secured as compared to Blockchain.
Gracias por participar en Steemit Crypto Academy:
Buen trabajo, Debes justificar el texto y profundizar un poco más en Tolerancia a Fallas Bizantinas asincrónicas.
Espero seguir leyendo tus publicaciones.
Calificación: 8.6
Thank you professor for the review. I will do well to improve in my next homework.