Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 4- Homework Post for Professor @awesononso - Topic: Blockchain Forks.

In this the fourth week of the third season of Crypto Academy we discuss blockchain forks, i.e. hard forks and soft forks, the differences between them and several examples of each one of them.


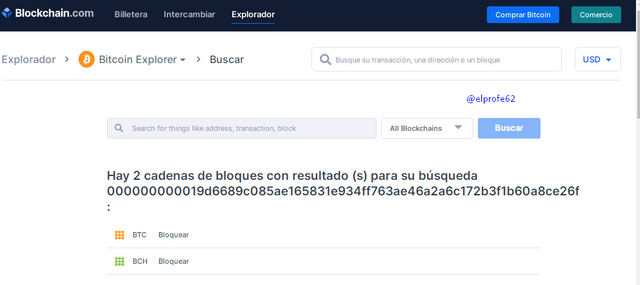
If we proceed to search for the following hash :(0000000000000019d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f), in the block explorer (https://www.blockchain.com/explorer/), we can see that there are two blockchains with the same hash, which are BTC and BCH, which means that this hash is the Genesis Block Hash of Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash.
Two different blockchains can have the same block (Genesis block) when one of them is the product of a fork.


A fork is an alternative version of the blockchain to the one that has been generated as the main one. It can originate maliciously, if a miner gains too much computing power, accidentally in case of a system error or intentionally if a protocol modification is introduced.
For a fork to be successful it needs to have the support of enough miners to obtain the longest chain within the blockchain.
There are two basic types of blockchain forks, which are hard forks and soft forks.


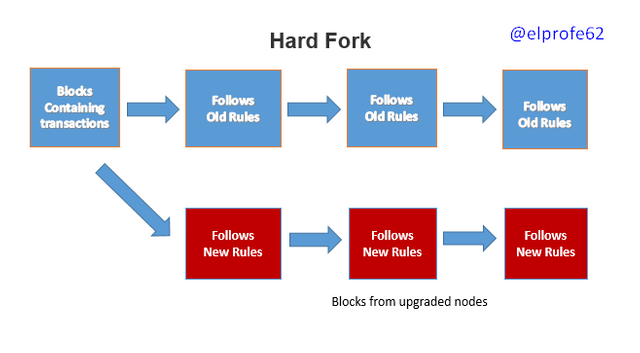
A Hard Fork is a fork in which there are two protocols, an original protocol and a new version of that protocol, i.e. one blockchain gives rise to a new blockchain, where one of those blockchains follows the original protocol and the other blockchain follows the new version of that protocol, also originating a new currency.
One example of a hard fork was Byzantium, on Ethereum and consisted of nine Ethereum Improvement Protocols (EIPs) designed to enhance Ethereum's privacy, scalability and security features.


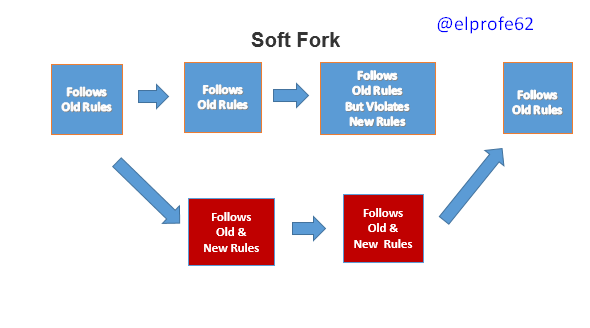
A Soft Fork is a small software update that is implemented to obtain new improvements in the network without altering the rules that break with the operation of the original version of the software, allowing users to continue operating even if they do not update.


There are two types of Soft Fork which are as follows:
1.- Soft fork activated by miner (MASF).
This is when most miners upgrade to enforce the new rules..
2.- User-activated soft fork (UASF).
This is when entire nodes coordinate to enforce the new rules, without the support of the miners.
An example of a soft fork is the modification made to the original protocol to increase the size of the blocks.


Hard forks are better than soft forks in terms of privacy, although they require a great effort in terms of time, resources and tool
A soft fork proves to be a more convenient and faster solution both in terms of decision making and total effort than a hard fork.
A Soft Fork is easier than a Hard Fork, as only small changes are made to the blockchain.




Bitcoin Cash was born as a result of the first hard fork that Bitcoin suffered and its main purpose was to overcome the efficiency of Bitcoin, in terms of its scalability and capacity to serve as a global scale payment system.Another of the reasons why it was made was to increase the maximum size of each block from 1 MB to 8 MB, thus achieving the scalability of transactions.
The new Bitcoin Cash blockchain started from Bitcoin block #478558 and from there the Bitcoin Cash begins its own history independent of the Bitcoint.


Due to the existence of two main weaknesses of Bitcoin, such as malleability and scalability, the SegWit proposal was presented and implemented to correct this situation.
SegWit is a backward-compatible software update to Bitcoin, which was implemented after a soft fork in the Bitcoin blockchain platform, which makes third-party malleability and scriptSig impossible by separating signature data from the rest of the data in a transaction, and increases the size of Bitcoin blocks (from 1 MB to 1.8 MB).
SegWit is not unique to Bitcoin; it has been implemented on other platforms such as Litecoin.
Bitcoin Forks - Segregated Witnesses (segwit) is a Soft Forks.


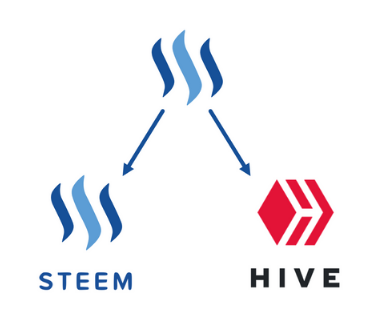
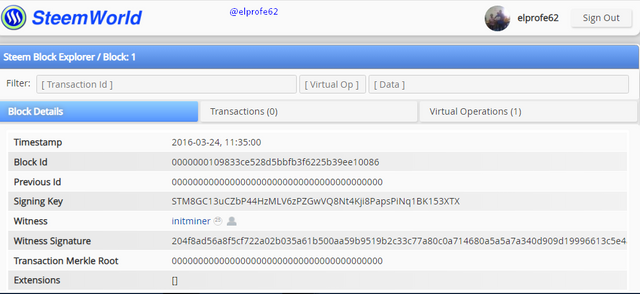
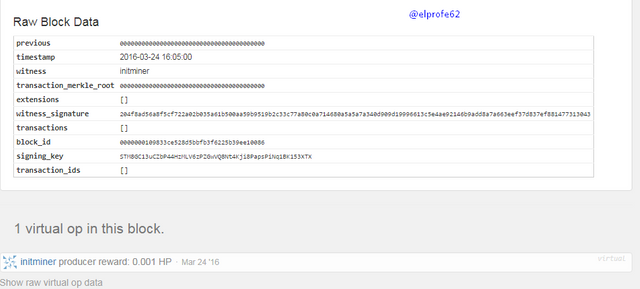
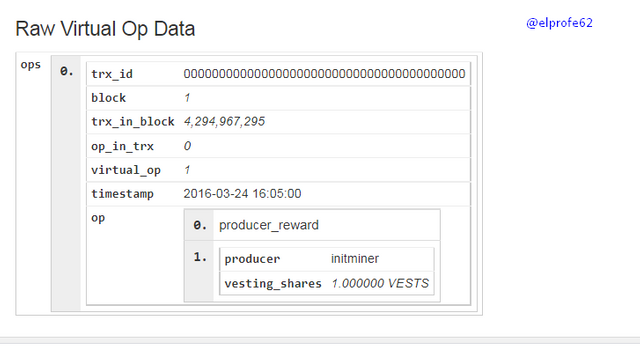
The Steemit community conducted a hard fork of the Steem Blockchain, giving rise to the HIVE Blockchain, which is completely independent of the Steemit platform.
In addition to the content and users at the time the blockchain snapshot was taken, their STEEM balances were transferred to HIVE as a 1: 1 ratio, e.g.: Steem accounts that had 10 STEEM, 10 SBD, and 100 SP, in the new Hive account got 10 HIVE, 10 HBD, and 100 HP.


Hello @elprofe62,
Thank you for taking interest in this class. Your grades are as follows:
Feedback and Suggestions
Always follow instructions.
You did not mention clear differences between hard forks and soft forks.
You did not state any clear example of soft forks.
You did not clearly indicate the similarities between Steem and Hive Genesis Blocks.
Thanks again as we anticipate your participation in the next class.