Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 4- Homework Post for Prof @awesononso - Topic: Blockchain Forks
 source
source
Good morning and welcome to my homework task for this week, am glad to be here at the CryptoAcademy as a student once again. It have been a wonderful learning experience for the community and me especially, I thank the management team, the professor's and the students. This week is a very interesting topic in the cryptocurrency industry, Blockchain Fork and the lecture was delivered by prof @awesononso, thank you reading through.
What is a Fork
A fork is simply the process of upgrading a software system to improve performance or duplicating it for so many reasons. The blockchain designers or developers can take the code of a blockchain and start developing a separate blockchain or upgrading the existing one. Blockchain is a decentralized network which makes it easier to be forked from its original blockchain without permission, yet not violating copyright laws.
Forks are blockchains developed with same source code and shares a history, for instance, a road later splits into two, and diverse to their different directions. Splitting a blockchain network or upgrading the blockchain, can be done anytime since it's a decentralized open source code, anyone can decide to improve or experiment on the code and also facilitates updates to the blockchain.
A blockchain fork happens when the software of some miners aren't aligning or if argument arise among the team and the team couldn't decide unanimously, then this can lead to the creation of another versions of the blockchain or splitting it. These forking period can cause the blockchain to witness an increase in price volatility, but can even make the blockchain better in some occasion. There are two types of fork, which are hard fork and soft fork.

What is Hard Fork?
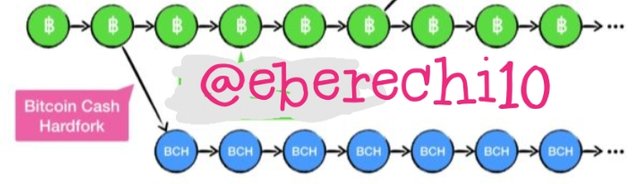
Hard forks are software updates that are backward incompatible, that take place when nodes update rules that conflicts with the rules of older nodes. These new nodes can communicate only with nodes that operate the new version, consequently cause the blockchain to splits into two separate networks. The old network will have the old rules while the new one have the new rules and the two network can no longer connect to each other, the two networks will be running in parallel and now have different native currencies.
Both blockchains will continue to create blocks and transactions, but not on the same blockchain. Before the fork, all nodes are on the same blockchain, so therefore shares histories that will remains, but going forward will have different blocks and transactions and with different history.
A good example of blockchain fork is Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash that fork at block 600,000. These blockchains now have shared history, this automatically make a user to have tokens on both blockchains if the user have them before the fork. These simply means that if you own 2 BTC when the fork occurred at Block 600,000, you will also have 2 BCH on the new blockchain.
The Bitcoin forking at block 600,000
In 2017 Bitcoin fork which saw Bitcoin to splits into two separate blockchains, Bitcoin (BTC), and a new token called Bitcoin Cash (BCH). These was after arguing over the best approach to scaling, proposed to increase the block size, these was a change opposed by some of the team members. These results in the Bitcoin fork of 2017.
Increasing the block size to accommodate more transactions requires to modifying the rules. The nodes with the new software can not communicate with the blocks with the previous version again because they are incompatible with the old protocol.
What is Soft Fork
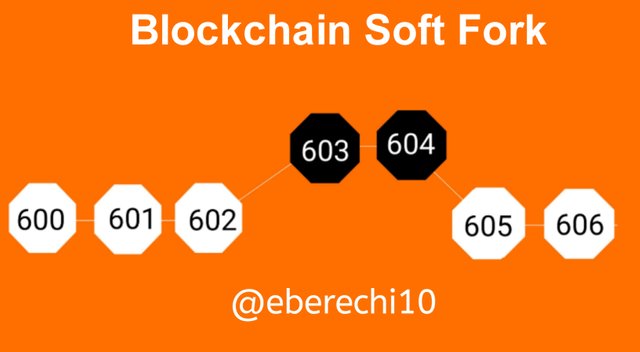
A soft fork is the process of implementing a backward compatible upgrade, in these process those nodes that has been upgraded can communicate with non upgraded nodes. In soft fork, only new rules are added, and won't clash with previous rules. If you decide to implement a block size decrease in soft fork, and set limit of how big a block is allowed, and no set limit to how small it can be. With this kind of soft forking, you accept the size of block you want and reject bigger ones above the limit you have set.
Consequently doing this won't automatically discommunicate or disconnect you from other nodes in the network. You still communicate with nodes that aren’t implementing your set rules, but you filter out some of the information they pass to you.
Bitcoin Soft Fork
The Bitcoin Soft Fork, these fork took place in 2017 and it is called the Segregated Witness (SegWit) fork. SegWit are update implemented to alter the blocks and transactions format in a very smart method.
SegWit fork divide the main block into two sections such as main block and an extended (witness) block. The code were removed from the transactions and inserts into extended block, these make more space available in the main block, therefore will contain transaction more efficiently and the witness segment is just a quarter of its previous size. The sender and receiver data will remain in the main block, and the new witness segment contain the code and signatures.
The older nodes still have the power to validate blocks and transactions because the rules weren't broken, but these older nodes won't understand the new rules. In these forking, you can only read some of the blocks when nodes switch to the new software and have analyze additional data. several years after the implementation of SegWit, yet not all nodes have upgraded and there is no urgency in doing so as there it's not a blockchain splitting change.
The difference between Hard and Soft Fork
| Hard Fork | Soft Fork |
|---|---|
| It is a backward incompatible updates | It is a backward compatible upgrade |
| New added rules are conflicting with the old rules | Newly added rules are not conflicting with the old rules |
| The new blocks can not communicate with the old block. | Old blocks communicate with the new blocks. |
| There is a blockchain splits, currency are created | There's no split of blockchain or new currency created. |
| There's a duplication of the old block | Older blocks aren't duplicated. |
Explain the Bitcoin Fork- Bitcoin Cash and Segregated witnesses.
Bitcoin Cash
The implementation of the SegWit cause many bitcoin developers and users to initiate a hard fork as to avoid the protocol updates. These hard fork lead to the creation of the Bitcoin Cash that was splits out from the main Bitcoin blockchain in August 2017, and the Bitcoin Cash start to see Bitcoin transactions and blocks as invalid.
Up till date Bitcoin Cash is the most successful hard fork of the Bitcoin family and is among the largest digital currency by market cap. The Bitcoin Cash uses blocks size of 8mb, and never accept the SegWit protocol. The proposal to hard fork Bitcoin in 2017 in order to increase its block size from 1 MB to 8 MB for faster and more transactions was opposed by many of the community.
Bitcoin Cash hard fork was implementated to solve the delayed transactions and lagging been experience by Bitcoin. The upgrade to 8mb blocks from the 1mb blocks been used by Bitcoin, these upgrade improve the scalability, and interacting with the blockchain. More data are hold on larger blocks, these help to improve the speed of transaction process. The Bitcoin Cash fork was implementated when the Bitcoin was at block 600000.
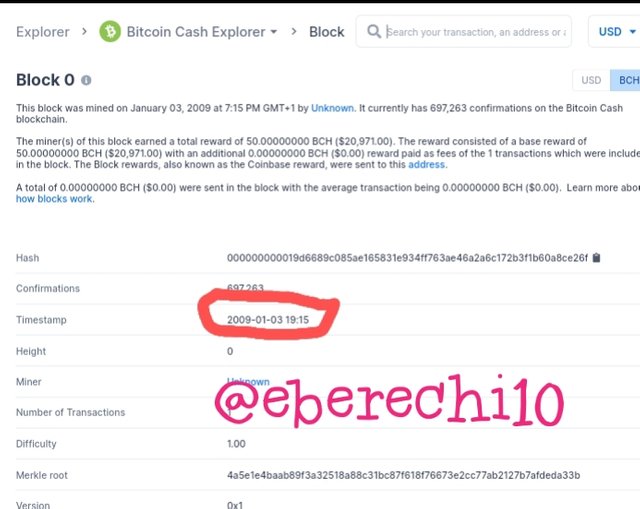
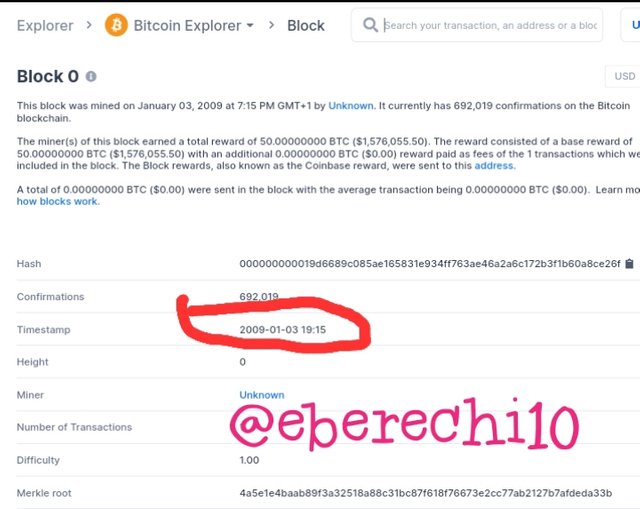
The Bitcoin genesis block have the following transaction data
Block hash:- 000000000019d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f
Timestamp:- 2009-01-03 19:15
The Bitcoin Cash genesis block have the following transaction data
Block hash:- 000000000019d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f
Timestamp:- 2009-01-03 19:15
From our investigation of the genesis blocks of both blockchains, it was confirmed that both blockchains are similar because of the duplication. Now let's investigate their block 605000 after the fork.
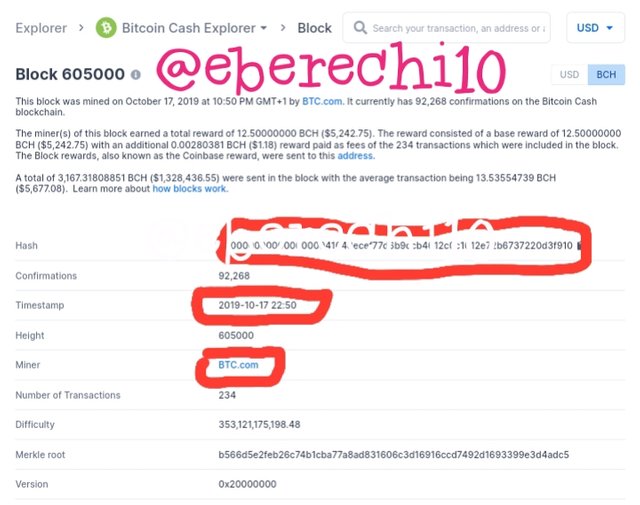
Bitcoin Cash Block 605000
Block hash:- 00000000000000000041048ecef77d6b9ccb4012c0c1012e72b6737220d3f910
Timestamp:- 2019-10-17 22:50
Miner:- BTC.com
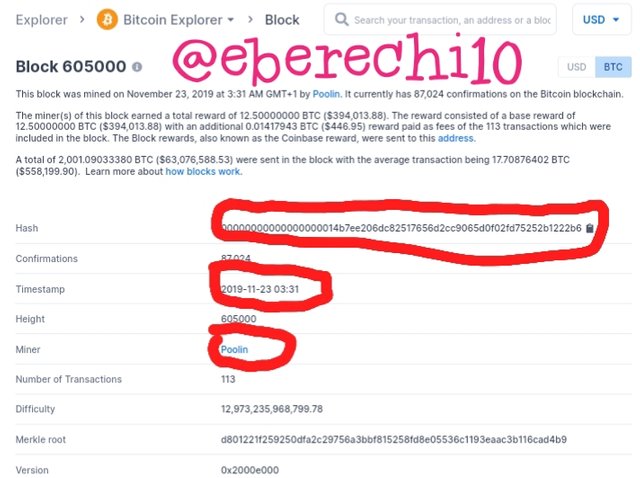
Bitcoin Block 605000
Block hash:- 00000000000000000014b7ee206dc82517656d2cc9065d0f02fd75252b1222b6
Timestamp:- 2019-11-23 03:31
Miner:- Poolin
From our investigation, it was confirmed that both blockchains after the forking of August 2017, each blockchain start to have there own blocks, with different block hash, timestamp, miner etc, so therefore can no longer communicate with each other.
Bitcoin Cash fork is not a backward incompatible, therefore it's a hard fork.
Segregated Witnesses
The protocol upgrade called Segregated Witnesses (SegWit) developed in 2015, with the intention of be the solution to the Bitcoin blockchain scalability problem. At that time validating a new block takes 10 minutes, and each of this block contains many transactions, this make the block size to limit the amount of transactions to be confirmed in each block. The idea in SegWit is to format the block data in a way that signatures and transaction data can't be in the same place again, which will create more storage space for transactions in a block, consequently improving the transaction speed of the network.
The SegWit protocol upgrade was developed by Bitcoin developer Pieter Wuille, and was implementated In August 2017. These protocol upgrade have turn out to been one of the greatest upgrade in cryptocurrency industry because SedWit are used today by many projects such as Bitcoin and Litecoin etc. Some of the many benefits of SegWit are improvement in transaction speed, improvement of block capacity and solved transaction malleability.
SegWit improve capacity of the block size by separating the signature data away from the transaction data, these make space for more transactions storage in a block. Before the implementation of the SegWit protocol upgrade, the signature data occupy also 65% of a block but separating the signature data from the transaction's data increase block size from 1 Mb to 4 Mb thereby increasing the transaction speed.
SegWit upgrade is a backward compatible, therefore is a soft fork.
Write on Steem and Hive Hard fork, what are the similarities in their Genesis Blocks
The Steem blockchain just like many other blockchains have had it own hard fork known as the Steem / Hive hard fork. When Mr Justin Sun of the Tron Function acquired Steem and proposed the integration ot TRX into Steemit the social media dApp on the blockchain, which many of Steem community opposed. This disagreement among the community members results to the Steem forking, splitting the blockchain into two blockchains, Steem and HIVE and a new currencies was created such as HIVE and HBD for the HIVE blockchain while the Steem blockchain retents Steem and SBD.
The Steem and HIVE blockchain shares many similarities which we are going to look at.
This is the interface of HIVE Blog on the HIVE blockchain and Steemit on the Steem blockchain, you will agree with that they are similarities on both interfaces
 HIVE Blog
HIVE Blog
 Steemit Blog
Steemit Blog
Now let's visit the block explorer of the two blocks to investigate about their genesis block.
Visit https://www.steemworld.com to investigate the genesis block of Steem blockchain.
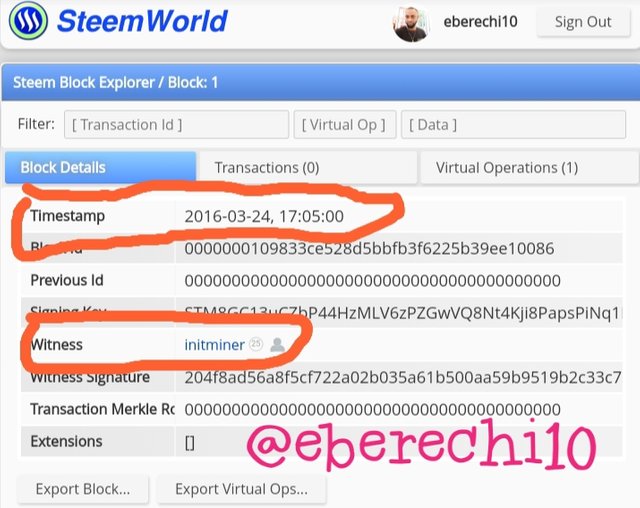
Steem blockchain genesis block is called the block 1 and have the below transaction data as follows:-
Block ID:- 0000000109833ce528d5bbfb3f6225b39ee10086.
Timestamp:- 24-03-20172016 17:05 UTC+1
witness:- initminer
For us to know about the genesis block of the HIVE blockchain we visit https://www.hiveblocks.com and investigate the HIVE genesis blockchain.
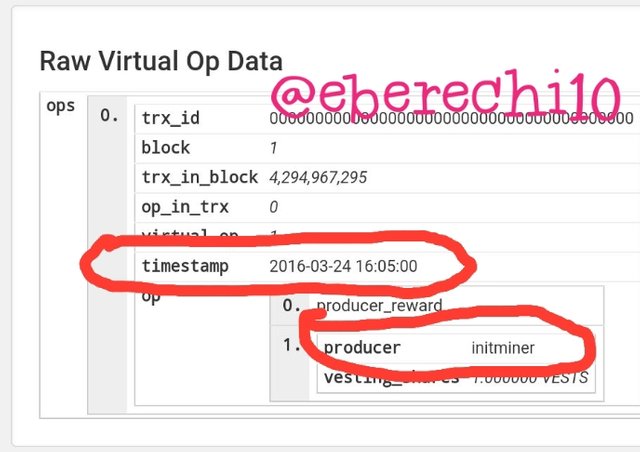
The HIVE blockchain genesis block is known as Block 1 and have the below transaction data as follows:-
Timestamp:- 24-03-2016 16:05
Witness:- @initminer
After the Steem/HIVE forking, because these two blockchains shares history, this automatically means that any user on the former Steem blockchain, will have their username on but blockchain. Likewise if you have currencies on the old Steem blockchain, you will now have currencies on both blockchains because of the blockchain duplication. For example if you have 10 Steem or 10 SBD on the former Steem blockchain, it will now duplicate as follows 10 Steem and 10 SBD on the Steem blockchain and 10 HIVE and 10 HBD on the new HIVE blockchain. The user reputation, username and password will still remain same in both blockchains because of the duplication.
Conclusion
The blockchain is build base on decentralized open source principle, which simply means that no central entity have control of it and that anybody can decided to fork if any protocol upgrade not suitable to him are implemented. Forking will always be in the cryptocurrency industry because it's decentralized and there might arise a need to upgrade protocol which could be soft forking if there is unanimous decision or could cause hard forking if there is opposing party.