SteemitCryptoAcademy [Beginners’ Level] | Season 3 Week 4-HOMEWORK for Professor @awesononso | Blockchain Forks by @dilchamo
Entire Question
1.What is a Fork? (In your own Words)
2.Explain in details what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
3.Explain in details what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
4.What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
5.Explain the following Bitcoin Forks and explore the blockchain where necessary. Indicate if they are hard forks or soft forks;
• Bitcoin Cash
• Segregated Witnesses
6.Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks(Provide screenshots).
Note: All Screenshots should have your username as a watermark on it.
1.What is a Fork? (In your own Words)
The first cryptocurrency was “Bitcoin” which was generated to function as a digital asset. With time many cryptocurrencies came into use. These newly emerged cryptocurrencies originated as a result of forks. Fork is a change is blockchain protocol which decides the transactions validity. Any Bifurcation in the blockchain can cause Forking.

How forks work
Forks occur when users think the fundamentals of the cryptocurrency that they use needs changes. A good example for this incident is Bitcoin and Bitcoin cash. New cryptocurrency Bitcoin cash was originated from Bitcoin. Users can decide which blockchain they would like to continue up. These changes of the fundamentals of a blockchain will create two versions of the same blockchain. These new cryptocurrencies can impact on price fluctuations.
These forks work by introducing new tokens. These new cryptocurrencies are created from scratch or by forking the existing cryptocurrency. Creation of tokens from scratch is simple as it has the method of copying and pasting techniques of the existing code. Forking the existing blockchain is different from the scratch method. Here the network splits to create another version of the original blockchain. Bitcoin cash was generated from Bitcoin using the forking method.
There are three main expectations of a blockchain. They are:
• One blockchain becomes dominant
• Both blockchains are adopted
• One blockchain is favored
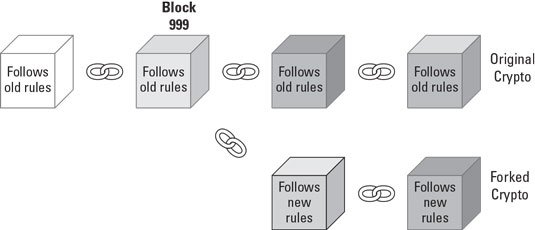
2.Explain in details what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
Hard fork makes invalid blocks with valid transactions. These forks are done by users who are unsatisfied with the current functionalities of the blockchain and needs developments. In hard Fork all users need to be upgraded to the new version. Hard Forks are referred to as radical changes of existing blockchain. Users with old blockchain tokens will be given new tokens. The users have to select which on to continue with.
There should be sufficient number of nodes need to be updated to the new version in order to continue. So a hard Fork needs majority support.
ETHEREUM HARD FORK
Ethereum which is known to be open source software, shares business, financial services and entertainment activities. Ethereum’s cryptocurrency is Ether or ETH. The market value of ETH is really high.
Ethereum had been attacked by a hacker whi has stolen more than 50 $ million ETH. So Ethereum created a hard fork named “Ethereum Classic” invalidating all transactions in the older existing blockchain. But there was a security issue that bugs enter and steal assets. So they have again updated Ethereum with st.Petersburg and contantinople which ensures the security of the block chain. Ethereum is uundergoing a vast update called Ethereum 2.0 which is will be all-in-one blockchain.
There were several hard forks of Ethereum from the origin based on different changes.
• Ethereum classic(ETC)
When a project of DAO was launched and was hacked by a bug this hard fork emerged. Ethereum changed its baseline to invalidate the past transactions. This has showed an active development and trading community with new advances.
• Expanse(EXP)
Expanse is designed and operated through a decentralized organization to be community managed.
• Quorum
Quarom is designed for high speed transactions.
Some other Ethereum Hard forks are:
• Ether Zero(ETZ)
• Serenity
• Metropolis
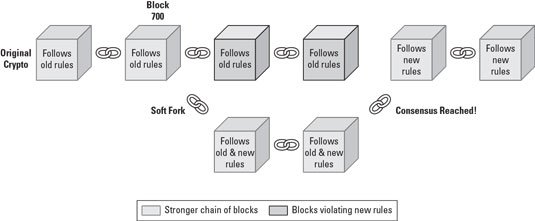
3.Explain in details what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
A soft Fork is a change done to the old protocol which makes previously allowed transactions invalid. A soft fork is backward compatible. In a soft fork only majority of miners need to be there to function the new version.
How Soft Fork Works
In many new transaction types there can be soft forks which needs only participants and miners need to understand the new type of transaction. When a soft fork occurs older nodes will still recognize new transactions as valid. A soft fork can occur due to temporary changes in the blockchain. In soft forks new rules also follow older rules. A soft fork cannot be reversed. A soft fork allows communication and transactions between new upgraded users and not upgraded users. The soft forked users may have new facilities and benefits but it is not a disturbance for the transaction among new and old users.
Ethereum Soft Fork
Mainly In Ethereum I found two soft forks. They are:
• Gas
• Size
Gas is the unit that measures the amount of computational effort need to execute the program. Gas is the fee required to conduct the transaction on Ethereum. Gas fees help to secure the Ethereum Network. The amount of gas depends on the number of steps conducted in the transactions.
Blocks are bounded by the size. Each block has a gas limit so that the consuming fo gas limit should be less than the limit. The block gas limit of block 0 was upto 5000 at the initial stages. But now it is around 15000000.
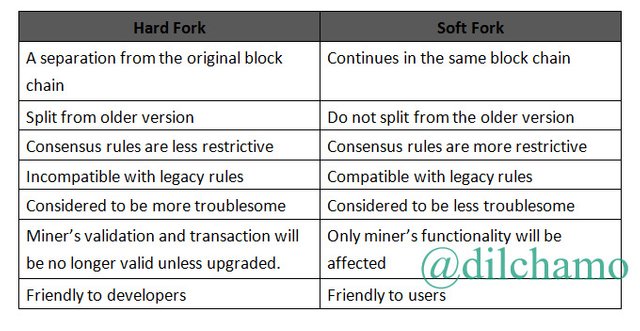
4.What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
As I have explained what are soft forks and hard forks and how it functions in question 3 and 4 I will directly point out the key differences between them.
5.Explain the following Bitcoin Forks and explore the blockchain where necessary. Indicate if they are hard forks or soft forks;
Bitcoin Cash
What is Bitcoin cash
Bitcoin Cash was generated as a hard fork of Bitcoin which emerged separately giving solutions to many issues of old Bitcoin.
By the time the number of Bitcoin users increased. So the waiting time became longer. Bitcoin network processed seven transactions per second. As the number of users increased the transaction time took minutes to proceed. The developers as a solution for this time issue generated the Hard fork Bitcoin Cash.
Bitcoin cash brought solutions for the prevailed shortcomings of Old Bitcoin. Bitcoin cash has the ability of scaling and increasing the speed of the transaction verification process. Bitcoin cash was generated in2017 as an effective cryptocurrency, BCH.
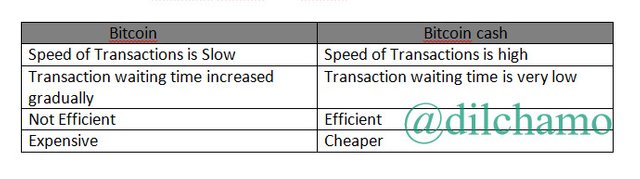
Key Differences Between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash
-Bitcoin Cash performs transaction quicker than old Bitcoin.
-Bitcoin cash performs more transactions than Bitcoin per second.
-The real worls usability of Bitcoin cash is lesser than Bitcoin as Bitcoin has the world’s largest Market cap.
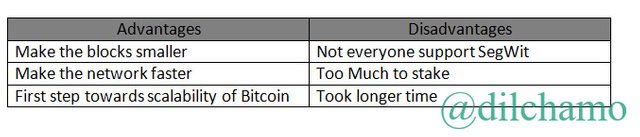
Segregated Witness which is known as SegWit is a process which limits the size of blocks in a blockchain. The limits can be increased by removing the signature data from the blockchain transactions. This process gives the capacity to add more transactions to the blokchain. SegWit is a soft fork in Bitcoin.
How does SegWit works?
SegWit processes by reducing the weight of transactions and segregates the transaction into two sections. Wallet addresses of the sender and receiver are contained in the first part and in the second part contain transaction signatures which are “transaction witness”. This transaction requires less space which enables more transactions per block. Ultimately it will result for the capacity of Bitcoin Network.
6.Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks(Provide screenshots).
Steem Hard Fork
Steem is also a very popular crypto blockchain. Steem is activated in the Steemit platform. The steem tokens are known as SBD. Steem is a decentralized blockchain. As many cryptocurrency blockchains, steem also had short comings which requests some changes. A hard fork of Steem emerged as a solution for all shortcomings of Steem.
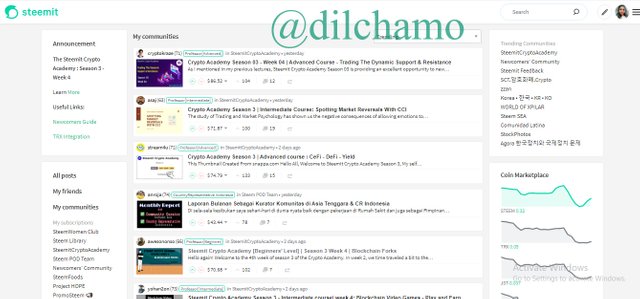
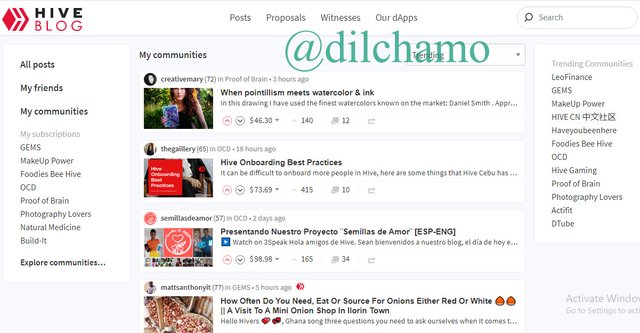
Hive is a separate blockchain which is practiced in “Hive.blog”. I will show you the similarities in both blockchains by using screenshots.
Interface
Here is the Steemit Platform main page.
Here is the Hive.blog platform main page.
You can see similar interfaces in both platforms.
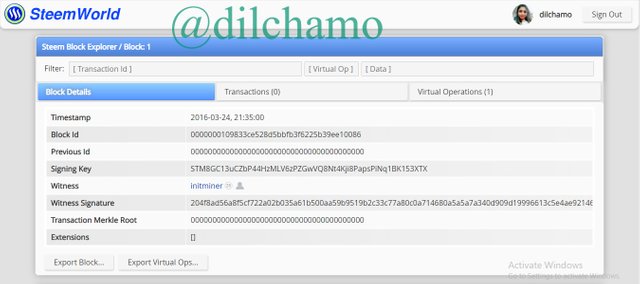
Genesis Block
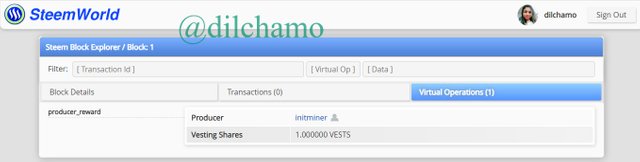
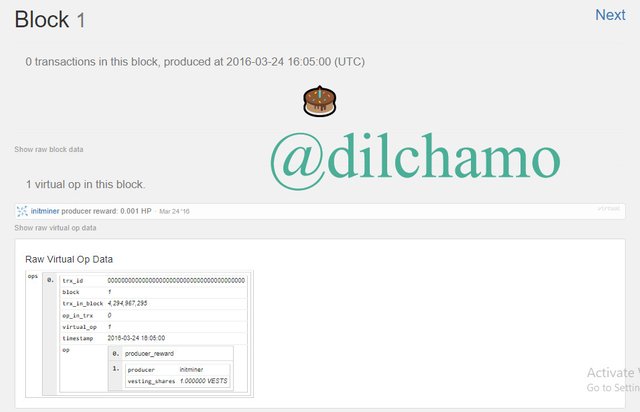
Here is the Genesis block of Steem.
Here is the genesis block of Hive.
As you can see clearly, the producer and vesting shares are equal in both blockchains.
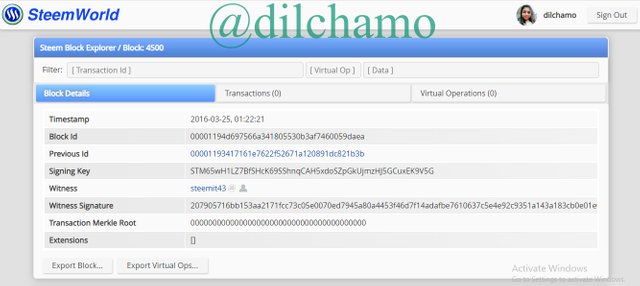
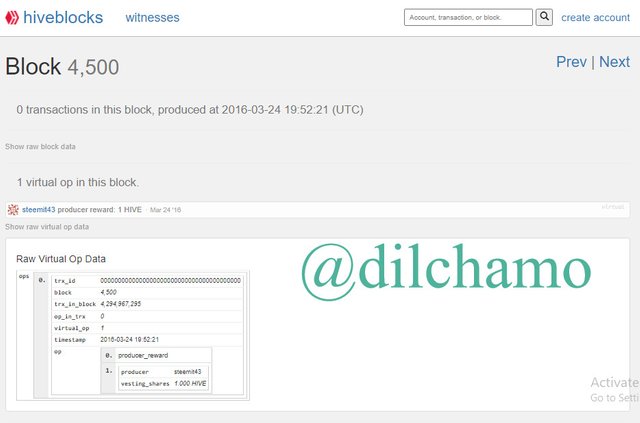
I took another block to prove the similarities. Here are the screenshots of the Block 4500 of both blockchains.
The producer of Steem block 4500 is @steemit43 and vesting shares is 1.000 VESTS.
The producer of Hive block 4500 is @steemit43 and the number of vesting shares is 1.000 HIVE.
Human being always expects something more than the existing thing. Same as in decentralized blockchains there is no any single authority to make decisions so due to that there can be changes which occur with existing shortcomings. This is done by developers or miners. To generate new blockchians or to have updates is their intension. For this change of blockchain into a diferent branch with same hash is known as a hard fork and generating any update being in the same blockchain is known as soft fork. There are pros and cons of each of those. It is necessary to understand the value of learning about forks as blockchain users.
Thank you Professor @awesononso for giving this important know-how.
![Steemit Crypto Academy [Beginners’ Level] Season 3 Week 4 Blockchain Forks.png](https://steemitimages.com/640x0/https://cdn.steemitimages.com/DQmPj816vZAuUgRptEiEHWjKsyzpcwsBHafMhhaz7kvApGM/Steemit%20Crypto%20Academy%20[Beginners%E2%80%99%20Level]%20Season%203%20Week%204%20Blockchain%20Forks.png)