Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 4 - Homework Post for [@awesononso] Blockchain Forks

Hello professor @awesononso, I'm happy to once again partake in your homework task. I really enjoyed learning something new and interesting from your lecture. Here's my homework post. I hope you like it.
1.What is a Fork? (In your own Words)
Blockchain Fork

Blockchain is an open-source technology. This simply means that its source code is available to anyone for modification, redistribution and usage as they see fit. This allows the creation of versions of a blockchain that could be an improvement of the original.
As time goes by Blockchain networks require upgrades due to newly identified problems and enhancement of the overall performance of the network. This is possible with the term known as Fork.
A Blockchain Fork is simply an upgrade or new version of a Blockchain. It is created by adding or changing rules to the code of a blockchain. Forks are possible because Blockchain technology is open source. This allows developers to make modifications to the blockchain protocol after an agreement has been made.
There are two types of Forks. These are Accidental Forks and Intentional Forks.
Accidental forks happen when two or more blocks are found at the same time, and it is resolved when subsequent blocks are added, and one of the chains end up being longer than the other. The blockchain network then abandons the blocks that are in the shorter chain, referred to as orphaned blocks.source
Intentional Forks are in two types, Hard Forks and Soft Forks.
Why Blockchain Forks?
Like a said earlier, problems are discovered as time goes on with the usage of something. At times new features are developed also to make usage enjoyable. Some of the reasons why we have Blockchain Forks include;
Bug fixes and security improvement
Reversals of transactions
Splitting the Blockchain for various reasons
Adding new features and improving performance
2.Explain in detail what a Hard Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
Hard Forks


A Hard Fork is a radical change in the blockchain protocol that creates a new version of the blockchain. It creates a new path for the blockchain with new rules. This results in two Blockchains.
Hard Forks are Backward-Incompatible. With Hard Forks, the nodes in the new version consider the blocks from the old version invalid, same with the nodes in the old version. Both blockchains share the same history but the rules make them different. The Blocks move parallel to each other.
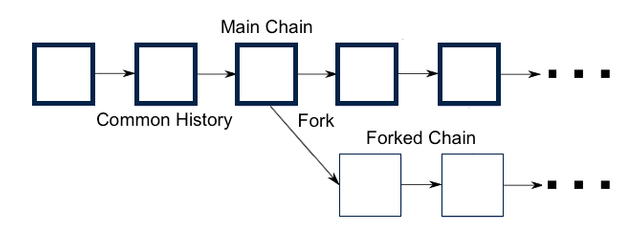
The miners on the old version can choose to remain or upgrade to the new version of the blockchain. Moving to the new version makes the Fork successful and shows that users like the improvements. A new cryptocurrency is created on the new version of the blockchain also, and since it has a history with the old blockchain it grants tokens to holders in the old blockchain.
Uses of Hard Forks
Hard forks are mainly implemented for security reasons. Other reasons include new features, reversal of transactions and enhancement of the performance of the blockchain. They help in correction and making the Blockchain safer and better.
Examples of Hard Forks
Bitcoin XT
This Hard Fork was launched in 2014 by Mike Hearn. Its purpose was to increase the number of transactions per second from 7 to 24. This initiative was successful initially, but people suddenly lost interest and abandoned the project. This Hard Fork is no longer available.
Aside from Bitcoin XT, Bitcoin has had several Hard Forks. Bitcoin Classic, Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin Unlimited are some examples.
On Ethereum, we have Ethereum Classic. A new Ethereum Hard Fork is said to take place on the 4th of August 2021. This is said to bring improvements to the Ethereum Blockchain network.
3.Explain in detail what a Soft Fork is with examples (Can be of any blockchain).
Soft Fork


A Soft Fork is quite the opposite of a Hard Fork. A Soft Fork upgrades the Blockchain without creating another Blockchain. Soft Fork allows backward compatibility, unlike Hard Fork. This is because the old nodes recognize the new blocks as valid. And so, the blocks continue in the same path.
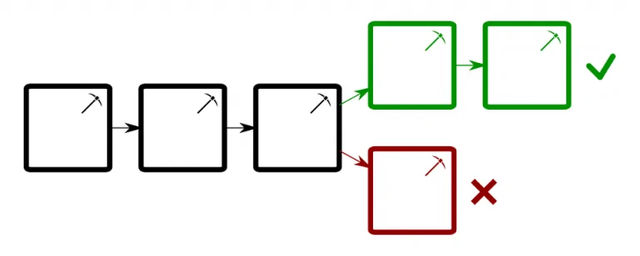
Soft Forks do not need all the nodes upgrading to be completely successful. They only require a higher percentage of the nodes upgrading. All nodes whether upgraded or not recognise newly created blocks. However, only upgraded miners can create new blocks that won't be rejected by the system. An increase in the upgrade of miners makes the network more secure. Soft Forks can't be reversed also without a Hard Fork.
Uses of Soft Forks
Soft forks can be used to add new transaction types to the Blockchain. They are used for gradual upgrades on a Blockchain network. Their main function is to improve the blockchain itself without creating another blockchain.
Examples of Soft Fork
Segregated Witness
This is a bitcoin soft fork implemented to increase the number of transactions contained in a block by reducing the size of a Bitcoin transaction.
Taproot
This is also a Bitcoin Soft Fork that was implemented to improve the privacy of the Bitcoin Blockchain.
4.What are the differences between Hard Forks and Soft Forks?
Differences Between Hard Forks and Soft Forks

While both Hard Forks and Soft Forks are to make improvements to a blockchain network, they have very significant differences. Below are the differences between the two forks.
A hard fork creates a new version of the blockchain which has the new features, while the soft fork upgrades the existing blockchain.
With the hard fork, the blocks move parallel to each other while in a soft fork the blocks continue in the same path. And so there is a repetition of block heights with Hard Forks while with Soft Fork there is no repetition.
A new currency is created with a hard fork. With a soft fork, no new currency is created.
Hard forks are backward-incompatible while a soft forks are backward-compatible.
Hard fork requires all the nodes to agree to the rules and upgrade to the new version to become successful. A soft fork requires just the majority of the nodes upgraded to function effectively.
5.Explain the following Bitcoin Forks and explore the blockchain where necessary. Indicate if they are hard forks or soft forks;
- Bitcoin Cash
- Segregated Witnesses
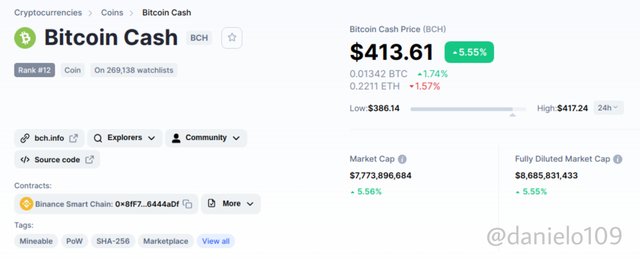
Bitcoin Cash

Bitcoin Cash is a hard fork initiated in August 2017 to increase the Block size and number of transactions that can be contained in a block. Unlike Hard Forks like Bitcoin XT, it has been a successful hard fork and is still in existence. This came about because users expressed their dissatisfaction with the performance of the network and didn't like the idea of the soft fork put in place to solve the problem. Since it was a hard fork a new currency(BCH) was created. One BCH is worth $413 currently and is ranked 12th on Coinmarketcap.
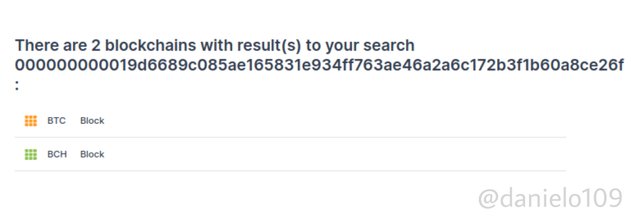
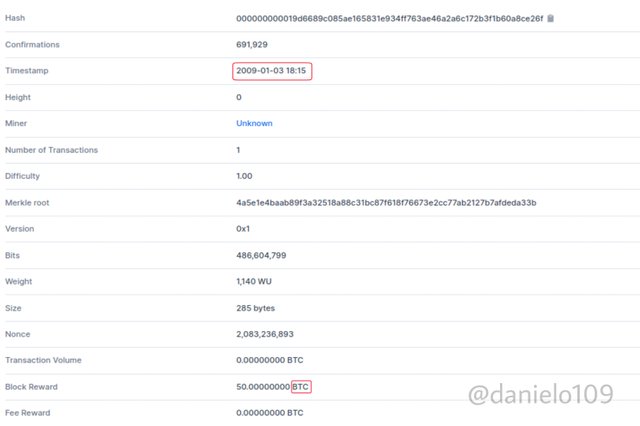
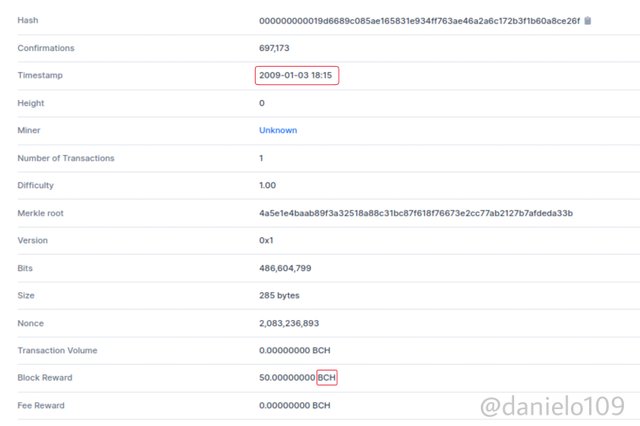
Bitcoin Cash nodes recognise blocks from the original Blockchain as invalid. The same with the original Blockchain. It also recognises the Bitcoin Cash blocks as invalid. Bitcoin Cash shares the same history with Bitcoin Blockchain. They both have the same hash for their genesis block. The hash is:
000000000019d6689c085ae165831e934ff763ae46a2a6c172b3f1b60a8ce26f
As you can see, they both record similar information with the genesis block.
Segregated Witnesses

Segregated Witness is a Bitcoin Soft Fork. It is also known as SegWit. SegWit was purposed to reduce the size of transactions, thereby increasing the number of transactions contained in a block. It was implemented in 2017 after it was proposed by Pieter Wuille in late 2015. This proposal was what triggered the Bitcoin Cash Hard Fork because some users didn't like the idea.
Unlike Bitcoin Cash, Segwit did not create a new currency and blockchain. It upgraded the Bitcoin blockchain by increasing the number of transactions per second by reducing the size of transactions and also increasing the block size to contain more transactions.
6.Write on the Steem and Hive Hard fork and show similarities in their Genesis Blocks(Provide screenshots).
Steem & Hive Fork

Steem Blockchain was forked to create Hive. This Hard Fork was due to the disagreement by some part of the blockchain community because of the integration of TRX and Steem blockchain. The developers decided to fork Steem blockchain to create Hive. Hive shares a lot of similarities with Steem Blockchain.
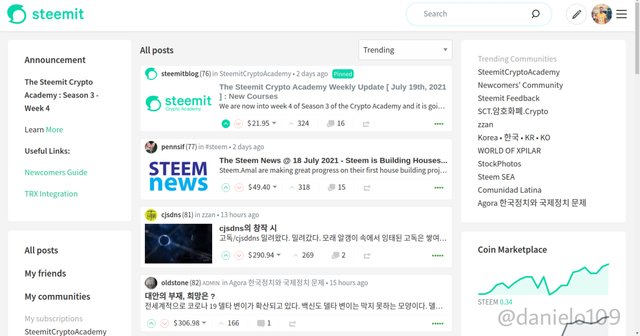
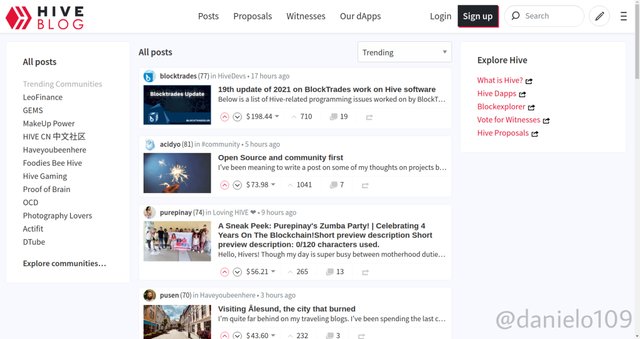
Below are screenshots of the two platforms;
As you can see they look almost the same. You can go to https://hive.blog and explore to see how similar it is to Steemit.
Like I said earlier, Hard Forks share the same history as the original Block. Hive and Steem Blockchain also have similar information with their Block data. Would use https://hiveblocks.com/ and https://steemworld.org/ which are block explorers for Hive and Steem Blockchain respectively to compare the similarities with their block data.
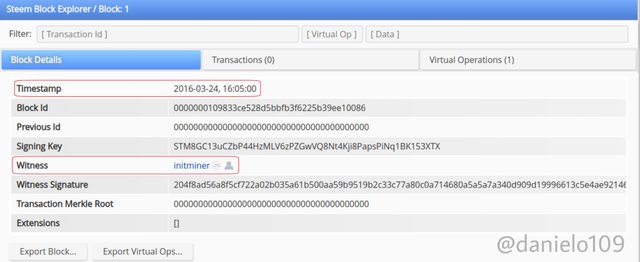
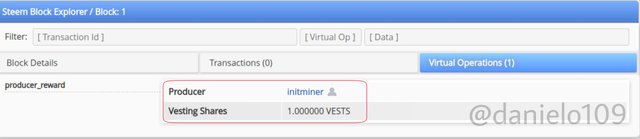
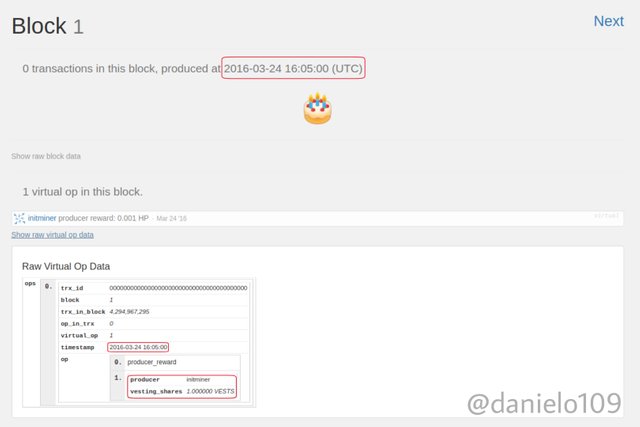
Checking the Genesis Block data;
As you can see the timestamp is the same for both Blocks. The vesting shares amount and producer is the same also. The only difference is the currency.
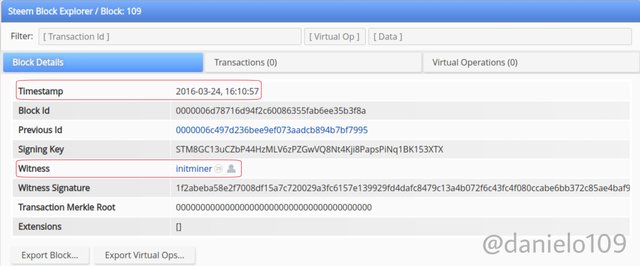
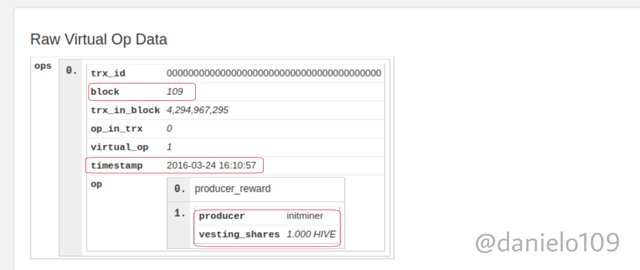
Let's compare another Block to confirm they share a common history and similarities in block heights. I'm using block height 109.
As you can see, both blocks have similarities. The timestamp and miner are the same also.
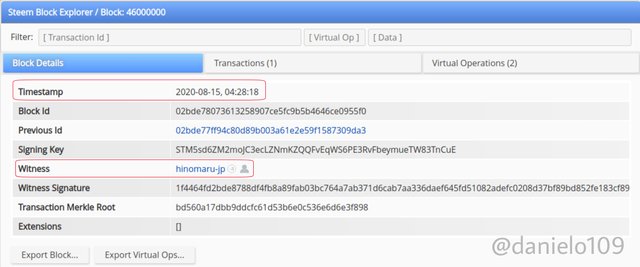
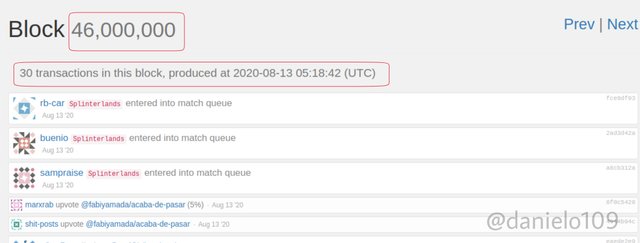
The change begins after the hard fork which leads to different operations on the two blockchains. Note that they share a common history but after forking, the Block details arent similar because we have two different Blockchains. An example can be seen below. I searched for Block 46,000,000 for each Blockchain.
As you can see, the time stamps for the two are different. The number of transactions is also different. You can click the source link below the images to view more details. This shows that the two Blockchains are operating differently although they share some similarities.
Conclusion

Forks are very important in improving a blockchain network and solving disagreement problems between members of the blockchain network. Hard Forks can reverse transactions and help to resolve cases like theft in a blockchain network. In general, they are important for making a blockchain better and safer.
Would like to thank @awesononso for this lecture. I really learnt a lot from you and the research I made.