Crypto Academy / Season 3 / Week 4- Homework Post for Professor @awesononso - Topic: Blockchain Forks

Hello everyone,
I want to thank God for this opportunity given me to be part of this week lecture. The lecture was very interesting and the home work a bit harder than the previous ones. I spent days learning and doing my best to present a quality home work. I hereby present my home work.
Question 1:

Fork in blockchain network is an upgrade or a change in the blockchain protocol that is meant to improve the blockchain to meet ever growing modern trend.
Blockchain Fork can result in the creation of two versions of the blockchain. This occurs when different miners do not unanimously agree on which blockchain that should continuosly be in use.
Because of the decentralized nature of blockchains, before any update can be successful, it must be unanimously accepted and decided by different miners and adopted by the node users of the network.
Since blockchain network is an open source software, and its code accessible to the general public, anyone can propose improvements and change the code.

Question 2:

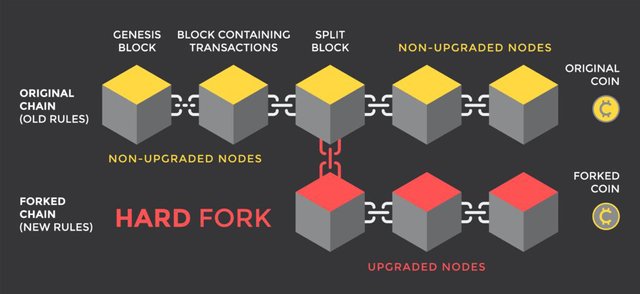
Hard Fork in blockchain technology refers to a radical change to a blockchain network's protocol that is running on the previous version of the software that would no longer be accepted on the new version. This requires that all users of the blockchain network should upgrade to the latest version of the software.
Hard Fork results in splitting blockchain into two different branches. The first one follows the original protocol (old rules), while the second one follows the new version (new rules). Both branches share a common history but move on two different directions.
One good example of Hard Fork is Ethereum Classic and Ethereum.
In July 2016, hackers invaded Ethereum platform and stole $50 million worth of ETH. To find solution in other to restore all the funds of those who had suffered losses in the hack, there was a controversial debate that some community members supported maintaining of the original unforked blockchain as Ethereum Classic (ETC) while Majority of the community supported the idea of ignoring the old blockchain and continue with new a blockchain.
At the end of the controversial debate, there were some people who disagreed and wanted to continue using the original unforked blockchain as Ethereum Classic (ETC) while those who wished to continue with the new blockchain continued with it as "Ethereum".
The blockchain splitted into two separate active blockchains, each with its own cryptocurrency.
There are so many other examples of Hard Fork, some of them are:
- Bitcoin Gold (BTG)
- Bitcoin Diamond (BCD)
- Ethereum Classic
- Wanchain (WAN)
- DigitalNote (XDN)

Question 3:

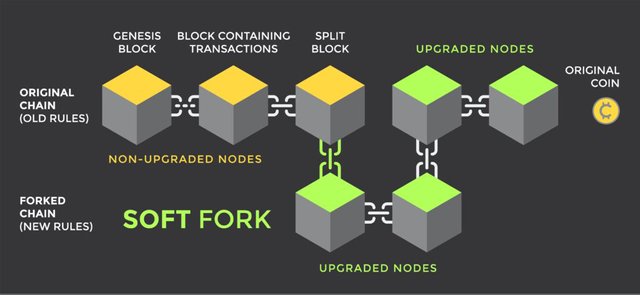
A soft fork in blockchain is the second type of fork that upgrades the blockchain protocol in such a way that only the previously valid transaction blocks are made invalid. Soft fork is meant only to improve the original blockchain protocol and not to create a new project or split the direction of the blockchain as in Hard Fork.
Soft fork is regarded as Backward-compatible because both old transactions can still continue to work together in the new upgraded network without any problem. This type of fork does not require all nodes to upgrade to the new rules to work effectively on the network. Blocks created with the new rules are still regarded as valid by old blocks.
Soft fork in a simple sentence is the addition of a new protocol that does not clash with the previous rules.
A very good example of soft fork is Segregated Witness (SegWit) fork,
When there was a split between Bitcoin and Bitcoin Cash, SegWit soft fork was introduced to update the format of blocks and transactions. This update did not break the blockchain rules, in the sense that old nodes could still validate blocks and transactions.
After two years of SegWit activation, so many nodes were not upgraded but they still continued to work together in the new upgraded network without any problem.
Not withstanding, soft fork upgrading is very necessary and has a lot of advantages. My point here is that soft fork does not clash with the previous rules and can not prevent old nodes from working in the new rules and user are not under pressure to upgrade there software. They can upgrade anytime they wish.

Question 4:

From the above explanation of Hard Fork and Soft Fork, you will notice that there are clear differences between the two types of forks. Here I will highlight the key differences between them.
Hard Fork results in splitting blockchain into two different branches, while Soft Fork does not split blockchain into two. It only improves the original blockchain protocol and does not split the direction of the blockchain.
Hard Fork creates entirely new project. It changes a blockchain network's protocol that would no longer be accepted on the new version. While Soft Fork does not create a new project.
Hard Fork is a software update that is not backwards compatible, any block coming after the activation of the software update can not work together in the new upgraded software. It will have to follow the new rules in order to be considered valid. While Soft fork is regarded as Backward-compatible because old software can still continue to work together in the new upgraded software without any problem
Hard Fork requires all nodes to upgrade to the new rules to work effectively on the network. While Soft Fork does not require all nodes to upgrade to the new rules to work.
Hard Fork results in the repetition of blocks both in the new and old version of blockchain network. While Soft Fork does not create repetition of blocks, because it does not create new block chain.

Question 5:

Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash (BCH) Bitcoin is a decentralized cryptocurrency that is designed to have the very nature of money. It is a peer-to-peer electronic cash system that does not depend on any central authority like a government or financial institution.
Bitcoin Cash was created on 1st of August 2017 and is considered Bitcoin Fork.
These are some features that make Bitcoin Cash an interesting decentralized cryptocurrency :
- Bitcoin Cash is not own and control by anybody. it is free to be used by anyone, without censorship.
- All transactions of Bitcoin Cash are recorded on the Bitcoin blockchain network for everybody to easily access.
- Bitcoin Cash technology ensures that all transaction once recorded in the blockchain cannot be altered.
- Bitcoin Cash is a very good alternative means of payment just like Visa and Mastercard. It is very reliable, fast, and affordable.
- Bitcoin Cash is a long-term store of value and a highly effective medium of exchange.
It is worthy to note that in November 2018, Bitcoin Cash later splited into two cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin Cash and Bitcoin SV.
Segregated Witnesses
One of the major challenges faced by bitcoin platform was the weight of transactions represented by the blocks. Then, as more and more transactions are being conducted and more blocks are being added to the blockchain, The platform generates a lot of weight that weighs down the network and causing processing and verification transactions to over delay.
To bring solution to this challenge, Dr. Pieter Wuille, Bitcoin developer suggested that the digital signature needs to be separated from the transaction data. Then digital signature occupies about 65% of the space in a given transaction.
So SegWit was designed to remove the signature from within the input and moving it to a structure towards the end of a transaction to increase the capacity blocks size.
Segregated Witnesses comprises of the two key words "Segregated" means to separate and "Witnesses" means the transaction signatures.
Segregated Witness (SegWit) refers to the process of removing signature data from bitcoin transactions to increase the block size on a blockchain thereby helping Bitcoin network to run faster and more smoothly.
SegWit frees up space or capacity to add more transactions to the chain when certain parts of a transaction are removed.
Segregated Witness (SegWit) is a soft fork.

Question 6:

In March 2020, Steem blockchain network was acquired by TRON.
Steem and Hive hard fork occured as a result of struggle for control of the Steem blockchain.
This struggle started after Justin Sun, the founder of TRON Foundation acquired Steemit. There was a disagreement between the new steemit team and the witnesses over the suggestion made by Justin Sun to integrate TRX into the Steem blockchain. Some key steem witnesses were not happy with the integration of TRX into the Steem blockchain and they opposed TRON’s recent acquisition of Steemit.
After TRON officially announced taking takeover Steem, the key Steem community members responded to the hostile takeover by launching an alternative blockchain network called Hive.
Hive is a content creation blockchain network just like Steemit blockchain.
Hive platforms are somehow identical to Steemit.
Hive made some changes to their tokens for example, SBD was changed to HBD, Steem changed to Hive and Steem Power modified to Hive Power.
Similarities in their Genesis Blocks with screenshots
Steemit and Hive blockchain have similar Genesis Block.
To view Genesis block of Steem blockchain, go to https://steemworld.org
Click on Block Explorer
Enter "1" and click OK
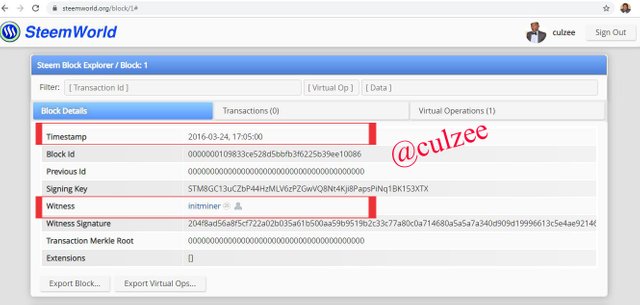
Let’s us examine some similarities on the Genesis Block.
In the highlighted parts of the block on the above screenshot, The Timestamp is 2016-03-24, 17:05:00 and the witness is Initminer. Also the producer name is Intiminer.
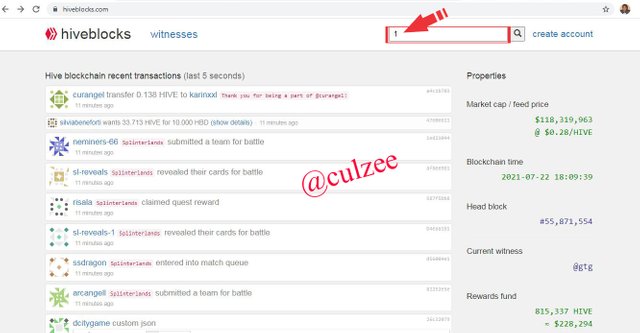
Now let us check Hive. Log on to https://hiveblocks.com/
Type "1" and search for the Genesis Block.

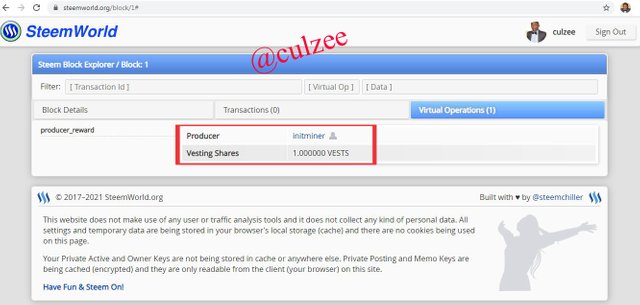
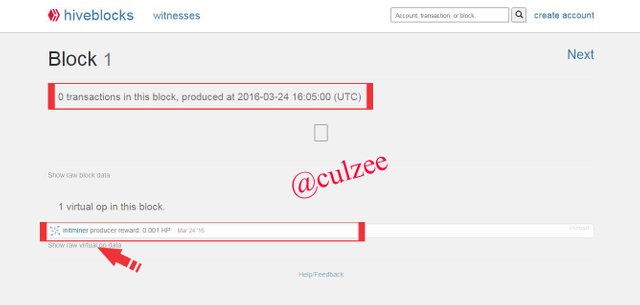
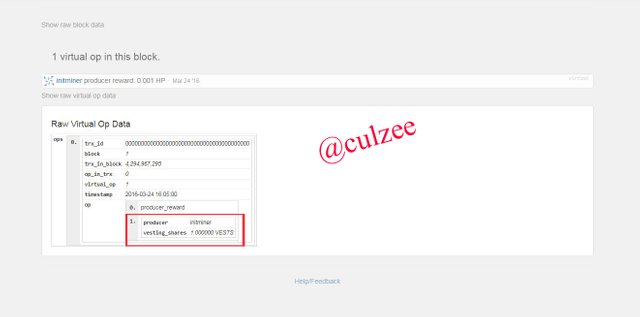
Click on "show raw virtual on data"
Now observe that the Minner/producer and the Mining date are the same with that of Steem.

CONCLUSION
Blockchain Fork as an upgrade or a change in the blockchain protocol is meant generally to bring an improvement to the blockchain technology to meet our ever growing modern trend. While Hard Fork results in splitting blockchain into two different branches and Soft fork upgrades the old blockchain in such a way that both the old and new rules can still continue to work together in the new upgraded network without any problem, all these are means of making blockchain technology much better.
I am very happy to have learnt a lot in this intensive lecture by professor @awesononso. I remain grateful to all Steemit Crypto Academy leadership team.
Thank you all.




Hello @culzee,
Thank you for taking interest in this class. Your grades are as follows:
Feedback and Suggestions
You have clearly done some research but you expression needs some work.
You have missed some Very inportant points on the topic.
Thanks again as we anticipate your participation in the next class.